Abstract
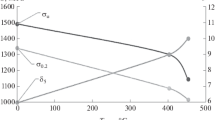
The aging of hooks, anchors, and other bent reinforcing steel bars in concrete structures are considered in modern international standards. Rebend test procedures have been designed in order to predict the aging embrittlement susceptibility by submerging bent reinforcing bar specimens in boiling water. Subsequently the bars are rebent or straightened in order to determine the loss of ductility or embrittlement of the aged material. The present work considers the influence of carbon, sulfur, and niobium on the performance of reinforcing bars in rebend tests of 300 heats of microalloyed steel bars with a variety of compositions. The microstructural evidence and the statistical results clearly indicate the strong influence of carbon and sulfur on rebend failure, while niobium-rich precipitates contribute to the hardening of the ferrite grains during aging.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
BS 4449: 1988—“British Standard Specification for Carbon Steel Bars for the Reinforcement of Concrete,” Committee Reference ISM/9, BSI Publications, Milton Keynes, U.K., May 1988, p 1–13
Y. Maehara and T. Nagamichi,Mater. Sci. Technol., Vol 7, 1991,p 915
R. Abushosha, R. Vipond, and B. Mintz,Mater. Sci. Technol., Vol 7,1991, p 1101
E. Valdez and C.M. Sellars,Mater. Sci. Technol., Vol 7,1991, p 622
H.J. Kestenbach, J.A. Rodrigues, and J.R. Dermonde,Mater. Sci. Technol., Vol 5, 1989, p 29
Y. Maehara, K. Yasumoto, H. Tomono, T. Nagamichi, and Y. Ohmori,Mater. Sci. Technol., Vol 6,1990, p 793
T. Gladman et al., Effects of Second Phase Particles on the Mechanical Properties of Steel, The Iron and Steel Institute, London, 1971, p 68
I. Kozasu and J. Tanaka,Sulphide Inclusions in Steels, American Society for Metals, 1975, p 286
D.C. Hilty and W. Crafts,Trans. AIME, Vol 188, 1950, p 414
I. Kozasu and J. Tanaka,Sulphide Inclusions in Steels, American Society for Metals, 1975
I. Kozasu and H. Kubota,Trans. Iron Steel Inst. Japan, Vol 11, 1971,p 321
M. Korchynsky and H. Stuart, Low Alloy High Strength Steels,Proc. London-Scandinavian Conf., Nuremburg, 1970, p 17
V. Castaño and L. Martínez,J. Mater. Res., Vol 15 (No. 3), 1990, p 658
J.D. Baird,Metall. Reviews, No. 4, London, Iliffe, 1963
F.B. Pickering and T. Gladman, Special Report 81, Iron and Steel Institute, 1963, p 10
K. Hulka and F. Heisterkamp,Steel India, April 1985, p 1
B. Campillo et al.J. Mater. Sci., Vol 27, 1992, p 1365–1368
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Campillo, B., Perez, R. & Martinez, L. Study of aging and embrittlement of microalloyed steel bars. JMEP 5, 615–620 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02646091
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02646091