Abstract
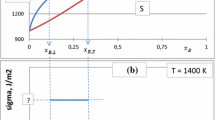
A reversible electrochemical cell was used to determine the thermodynamic activity of aluminum in a series of α-phase Al-Zn and Al-Zn-Ag alloys, and a dew-point technique was used to determine the thermodynamic activity of zinc in a series of ε-phase Ag-Zn-Al alloys. The compositions investigated for both systems included those at which previous authors had related the stability of the phase to electronic factors. The data are presented in the form of graphs showing the excess relative partial molal Gibbs free energy of aluminum, (Δ•GA1 xs), and zinc, (Δ•GZn xs), as a function of both mole fraction(X i ) and electron-to-atom ratio (e/a). The latter curves are interpreted to be indications that the effect of electron concentration upon alloy phase stability has been experimentally isolated. Equations are developed which predict the effects of ternary additions in these alloy systems. The rigid-band model is shown to be incapable of predicting the direction of the effect and an argument based upon electron screening of ion-ion interactions is offered.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
W. Hume-Rothery and G. V. Raynor:The Structure of Metals and Alloys, Inst. of Metals Monograph and Report Series #1,3rd ed.,Inst.of Metals, London,1954.
W. Hume-Rothery, G. W. Mabbott, and K. M. Channel-Evans:Phil. Trans. Roy. Soc., Ser. A, 1934, vol. 231, p. 1.
H. J. Axon and W. Hume-Rothery:Proc. Roy. Soc, London, Ser. A, 1948, vol. 193, p. 1.
H. Jones:Proc. Roy. Soc, Ser. A, 1934, vol. 147, p. 225.
H. Jones:Proc. Roy. Soc, Ser. A, 1934, vol. 49, p. 396.
H. Jones:Proc Phys. Soc, Ser. A, 1937, vol. 49, p. 250.
A. B. Pippard:Phil Trans. Roy. Soc, Ser. A, 1957, vol. 250, p. 323.
P. S. Rudman, J. Stringer, and R. I. Jaffee, eds.:Phase Stability in Metals and Alloys, McGraw-Hill Book Co., Inc., New York, 1967.
J. Friedel and A. Guinier, eds.:Metallic Solid Solutions, W. A. Benjamin, Inc., New York, 1963.
W. Himmler:Z. Physik Chem, 1950, vol. 195, pp. 244, 253.
C. Wagner:J. Chem. Phys., 1951,vol. 19, p. 626.
B. B. Argent and D. W. Wakeman:Trans. Faraday Soc, 1958, vol. 54, p. 799.
G. A. Chadwick and B. B. Argent:Trans. Faraday Soc, 1961, vol. 57, p. 619.
B. B. Argent and D. W. Wakeman:Trans. Faraday Soc, 1958, vol. 54, p. 804.
G. A. Chadwick and B. B. Argent:Trans. Faraday Soc, 1961, vol. 57, p. 2138.
B. B. Argent and K. T. Lee:Trans. Faraday Soc, 1965, vol. 61, p. 826.
T. B. Massalski and H. W. King:Acta Met., 1962, vol. 10, p. 1171.
G. V. Raynor and D. W. Wakeman:Phil Mag., 1949, vol. 40, p. 404.
K. I. Hirano and Y. Takagi:J. Phys. Soc. of Japan, 1954, vol. 9, p. 730.
W. Gordy:Phys. Rev., 1946, vol. 69, pp. 604–07.
P. S. Rudman:Trans. TMS-AIME, 1965, vol. 233, pp. 864–72.
H. J. Axon and W. Hume-Rothery:Proc. Roy. Soc, London, Ser. A, 1948, vol. 193, p. 1.
J. L. Straalsund and D. B. Masson,Trans. TMS-AIME, 1968, vol. 242, p. 190.
A. H. Geisler, C. S. Barrett, and R. F. Mehl,AIME Trans., 1943, vol. 152, pp. 201–25.
J. E. Hilliard, B. L. Averbach, and M. Cohen,Acta Met., 1954, vol. 2, pp.621–31.
T. C. Wilder and J. F. Elliott,J. Electrochem. Soc, 1967, vol. 107, pp. 628–35.
M. Hillert, B. L. Averbach, and M. Cohen,Acta Met., 1956, vol. 4, p. 31.
C. Wagner:Thermodynamics of Alloys, pp. 91–94, Addison and Wesley Press, Inc., Cambridge, 1952.
R. H. Fowler and E. A. Guggenheim:Statistical Thermodynamics, pp. 461–72, Cambridge Press, Cambridge, 1939.
R. Hultgren, R. L. Orr, P. D. Anderson, and K. K. Kelley:Selected Values of Thermodynamic Properties of Metals and Alloys, Minerals Research Laboratory, University of California, Berkeley, 1963.
P. S. Rudman and B. L. Averbach:Acta Met., 1954, vol. 2, p. 576.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Formerly Graduate Students, Metallurgy Department, Washington State University, Pullman, Wash.
This paper constituted a portion of the theses submitted by RONALD E. MILLER and JERRY L. STRAALSUND in partial fulfillment of the requirements of the degree of Doctor of Philosophy in Engineering Science at Washington State University.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miller, R.E., Straalsund, J.L. & Masson, D.B. The effect of electron concentration on the thermodynamic properties of two alloy phases in the Al-Zn-Ag system. Metall Trans 3, 549–554 (1972). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02642060
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02642060