Abstract
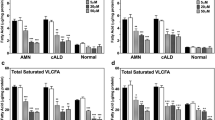
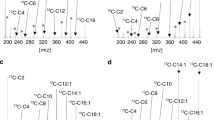
Abnormally high levels of very long-chain fatty acids (VLCFA) are a feature in nine of the fifteen peroxisomal disorders that have been identified so far. Saturated VLCFA accumulate in X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy, appear to disrupt membrane structure, and may play a role in the pathogenesis of a brain inflammatory response. Dietary therapy initiated when patients are still asymptomatic may be of clinical benefit.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AMN:
-
adrenomyeloneuropathy
- AOX:
-
acyl-CoA oxidase
- BIF:
-
bifunctional enzyme
- DHA:
-
docosahexaenoic acid
- IRD:
-
infantile Refsum disease
- NALD:
-
neonatal adrenoleukodystrophy
- RDCP:
-
rhizomelic chondrodysplasia punctata
- VLCFA:
-
very long-chain fatty acids
- X-ALD:
-
X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy
References
Subramani, S. (1993) Protein Import into Peroxisomes and Biogenesis of the Organelle,Ann. Rev. Cell. Biol. 9, 445–478.
Moser, A.B., Rasmussen, M., Naidu, S., Watkins, P.A., McGuinness, M., Hajra, A.K., Chen, G., Raymond, G., Liu, A., Gordon, D., Garnaas, K., Walton, D.S., Skjeldal, O.H., Guggenheim, M.A., Jackson, L.G., Elias, E.R., and Moser, H.W. (1995) Phenotype of Patients with Peroxisomal Disorders Subdivided into 16 Complementation Groups,J. Pediatr. 127, 13–22.
Mosser, J., Lutz, Y., Stoeckel, M.E., Sarde, C.O., Kretz, C., Douar, A.M., Lopez, J., Aubourg, P., and Mandel, J.L. (1994) The Gene Responsible for Adrenoleukodystrophy Encodes a Peroxismal Membrane Protein,Hum. Mol. Genet. 3, 265–271.
Powers, J.M., Liu, Y., Moser, A., and Moser, H. (1992) The Inflammatory Myelinopathy of Adreno-Leukodystrophy: Cells, Effector Molecules, and Pathogenetic Implications,J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 51, 630–643.
Moser, H.W., Moser, A.B., Smith, K.D., Bergin, A., Borel, J., Shankroff, J., Stine, O.C., Merette, C., Ott, J., Krivit, W., and Shapiro, E. (1992) Adrenoleukodystrophy: Phenotypic Variability: Implications for Therapy,J. Inher. Metab. Dis. 15, 645–664.
McGuinness, M.C., Griffin, D.E., Raymond, G.V., Washington, C.A., Moser, H.W., and Smith, K.D. (1995) Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha and X-Linked Adrenoleukodystrophy,J. Neuro-immunol. 61, 161–169.
Knazek, R.A., Rizzo, W.B., Schulman, J.D., and Dave, J.R. (1983) Membrane Microviscosity is Increased in the Erythrocytes of Patients with Adrenoleukodystrophy and Adrenomyeloneuropathy,J. Clin. Invest. 72, 245–248.
Whitcomb, R.W., Linehan, W.R., and Knazek, R.A. (1988) Effects of Long-Chain, Saturated fatty Acids on Membrane Microviscosity and Adrenocorticotropin Responsiveness of Human Adrenocortical Cellsin vitro, J. Clin. Invest. 81, 185–188.
Ho, J.K., Moser, H., Kishimoto, Y., and Hamilton, J.A. (1995) Interactions of a Very Long Chain Fatty Acid with Model Membranes and Serum Albumin: Implications for the Pathogenesis of Adrenoleukodystrophy,J. Clin. Invest., 96, 1455–1463.
Evrard, P., Caviness, V.S., Prats-Vinas, J., and Lyon, G. (1978) The Mechanism of Arrest of Neuronal Migration in the Zellweger Malformation: An Hypothesis Based upon Cytoarchitectonic Analysis,Acta Neuropathol. (Berl) 41, 109–117.
Kaufmann, W.E., Theda, C., Naidu, S., Watkins, P.A., Moser, A.B., and Moser, H.W. (1996) Neuronal Migration Abnormality in Peroxisomal Bifunctional Enzyme Defect,Ann. Neurol. 39, 268–276.
Martinez, M., Pineda, M., Vidal, R., and Martin, B. (1993) Docosahexaenoic Acid: A New Therapeutic Approach to Peroxisomal Patients. Experience with Two Cases,Neurology 43, 1389–1397.
Rizzo, W.B., Leshner, R.T., Odone, A., Dammann, A.L., Craft, D.A., Jensone, M.E., Jennings, S.S., Davis, S., jaitly, R., and Sgro, J.A. (1989) Dietary Erucic Acid Therapy for X-Linked Adrenoleukodystrophy,Neurology 39, 1415–1422.
Aubourg, P., Adamsbaum, C., Lavallard-Rousseau, M.C., Rocchiccioli, F., Cartier, N., Jambaque, I., Jakobezak, C., Lemaitre, A., Boureau, F., Wolf, C., and Bougneres, P.F. (1993) A Two-Year Trial of Oleic and Erucic Acids (“Lorenzo's Oil”) as Treatment for Adrenomyeloneuropathy,N. Engl. J. Med. 329, 745–752.
Poulos, A., Gibson, R., Sharp, P., Beckman, K., and Grattan-Smith, P. (1994) Very Long Chain Fatty Acids in X-Linked Adrenoleukodystrophy Brain After Treatment with Lorenzo's Oil,Ann. Neurol. 36, 741–746.
Moser, H.W., and Borel, J. (1995) Dietary Management of X-Linked Adrenoleukodystrophy,Ann. Rev. Nutr. 15, 379–397.
Zierz, S., Schroder, R., and Unkrig, C.J. (1993) Thrombocytopenia Induced by Erucic Acid Therapy in Patients with X-Linked Adrenoleukodystrophy,Clin. Invest. 71, 802–805.
Kickler, T.S., Zinkham, W.H., Moser, A., Shankroff, J., Borel, J., and Moser, H. (1996) Effect of Erucic Acid on Platelets in Patients with Adrenokeukodystrophy,Biochem. Mol. Med., in press.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Moser, H.W., Moser, A.B. Very long-chain fatty acids in diagnosis, pathogenesis, and therapy of peroxisomal disorders. Lipids 31, S141–S144 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02637066
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02637066