Abstract
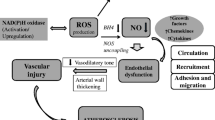
Lipoproteins have an important influence on arterial tissues. High levels of low density lipoproteins (LDL) may inhibit arterial function in terms of the release of nitric oxide from the endothelium. This inhibition is enhanced by the oxidation of these lipoproteins which may occur during the development of atherosclerosis. Many of these effects are due to lipid oxidation products. The impairment of the release of nitric oxide and vasodilatation may be partially attenuated by antioxidants. LDL may also enhance the activity of blood platelets, especially when they are mildly oxidized. Oral administration of antioxidants may decrease the activation of platelets to a limited extent. Lipid peroxides may play a role in these processes.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HDL:
-
high density lipoproteins
- LDL:
-
low density lipoproteins
- mmLDL:
-
minimally oxidized LDL
- nLDL:
-
native LDL
- NO:
-
nitric oxide
- oxLDL:
-
oxidized LDL
References
Rice-Evans C.A., and Bruckdorfer, K.R. (1992) Free Radicals, Lipoproteins and Cardiovascular Dysfunction,Mole. Aspects Med. 13, 1–112.
Andrews, H.E., Bruckdorfer, K.R., Dunn, R.C., and Jacobs, M. (1987) Low-Density Lipoproteins Inhibit Endothelium-Dependent Relaxation in Rabbit Aorta,Nature. 327, 237–239.
Chowiencyk, P.J., Watts, G.F., Cockroft, J.R., and Ritter, J.M. (1992) Impaired Endothelium-Dependent Vasodilation of Forearm Resistance Vessels in Hypercholesterolaemia,Lancet 340, 1430–1432.
Sorensen, K.E., Celermajer, D.S., Deanfield, J.E., and Macrae, D.J. (1994) Impairment of Endothelium-Dependent Dilation Is an Early Event in Children with Familial Hypercholesterolaemia and Is Related to the Lipoprotein (a) Level,J. Clin Invest. 93, 50–55.
Jacobs, M., Plane, F., and Bruckdorfer, K.R. (1990) Native and Oxidised LDL Have Differential Inhibitory Effects on Endothelium Derived Relaxing Factor in Rabbit Aorta,Brit. J. Pharmacol. 100, 21–26.
Buckley, C., Bund, S., McTaggart, F., Bruckdorfer, K.R., Jacobs, M., and Oldham, A. (1993) Oxidised Low-Density Lipoproteins Inhibit Endothelium-Dependent Relaxations of Rabbit Coronary Arteries,Br. J. Pharmacol. 100, 222.
Minor, R.L., Myers, P.R., Guerra, R.J., Bates, J.N., and Harrison, D.G. (1990) Diet-Induced Atherosclerosis Increases the Release of Nitrogen Oxides from Rabbit Aorta,J. Clin. Invest. 86, 2109–2116.
Plane, F., Bruckdorfer, K.R., Kerr, P., Steuer, A., and Jacobs, M. (1992) Oxidative Modification of Low-Density Lipoproteins and the Inhibition of Relaxations mediated by Endothelium-Derived Nitric Oxide in Rabbit Aorta,Br. J. Pharmacol. 105, 216–222.
Buckley, C., McManus, D., Bruckdorfer, K.R., and Jacobs, M. (1994) 9-Hydroxy- and 9-Hydroperoxy-Linoleic Acids Inhibit Endothelium-Dependent Relaxations of Rabbit Aorta,Br. J. Pharmacol. 112, 222.
Buckley, C., McManus, D., Bruckdorfer, K.R., and Jacobs, M. (1994) Hydroperoxy- and Hydroxy-Derivatives of Arachidonic Acid Inhibit Endothelium-Dependent Relaxation,Br. J. Pharmacol. 112, 222.
Gleeson, A.M., Bruckdorfer, K.R., and Jacobs, M. (1995) Oxysterols and Endothelium-Dependent Relaxations,Endothelium 2, S8.
Jacobs, M., Plane, F., and Bruckdorfer, K.R. (1993) Probucol and Other Antioxidants Prevent the Inhibition of Endothelium-Dependent Relaxation by Low-Density Lipoproteins,Atherosclerosis, 103, 73–79.
Bruckdorfer, K.R., Gleeson, A.M., Allot, C., and Jacobs, M. (1995) Regression of Atherosclerotic Lesions and the Associated Impairment of Vasodilation by Probucol,Endothelium 2, S10.
Bruckdorfer, K.R. (1989) The Effects of Plasma Lipoproteins on Platelet Responsiveness and on Platelet and Vascular Prostanoid Synthesis,Prostagland., Leukot. Essent. Fatty 38, 247–254.
Naseem, K.M., Goodall, A.H., and Bruckdorfer, K.R. (1993) The Effects of Native Lipoproteins of Platelet Activation,Biochem. Soc. Trans. 21, 140S.
Naseem, K.M., and Bruckdorfer, K.R. (1995) Hydrogen Peroxide at Low Concentrations Strongly Enhances the Inhibitory Effect of Nitric Oxide on Platelets,Biochem J. 310, 149–153.
Salonen, J.T., Salonen, R., Seppanen, K., Rinta-Kiikka, S., Kuukka, M., Korpela, H., Alfthan, G., Kantola, M., and Schalch, W. (1991) Effects of Antioxidant Supplementation on Platelet Function: A Randomized Pair-Matched, Placebo-Controlled, Double-Blind Trial in Men with Low Antioxidant Status,Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 53, 1222–1229.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Richard Bruckdorfer, K. Antioxidants, lipoprotein oxidation, and arterial function. Lipids 31, S83–S85 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02637056
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02637056