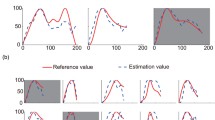
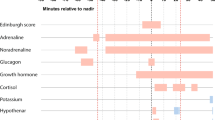
Abstract
Recurrent severe hypoglycaemia is often an unsolved problem in diabetic patients under intensified insulin treatment. As no reliable long-term stable blood glucose sensor has yet been developed, registration of other body function changes could help to detect severe hypoglycaemia. A measuring system is described, capable on the one hand of recording EEG, heart rate, peripheral pulse, skin temperature, respiratory movements, skin impedance and arterial blood pressure, and capable of registering plasma glucose, counter-regulatory hormones, symptoms and cognitive performance under experimental conditions during hypoglycaemia, on the other. In a clinical study involving both insulin-induced hypoglycaemia in healthy subjects and insulin-dependent diabetic patients, the practical value and the character of changes of the recorded parameters are investigated. Currently insensitivity to hypoglycaemia, impracticability, complexity or susceptibility to artefacts make use of most parameters unsuitable for hypoglycaemia prevention. It is believed, however, that future efforts could result in indirect registration of hypoglycaemia, including a qualified combination of different parameters, individual adaptation in accordance with particular responses of individual patients, together with new measuring and sensor techniques.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Auer, R. N. (1986): ‘Progress review: hypoglycaemic brain damage’,Stroke,17, pp. 699–708
Bendtson, I., Gade, J., Theilgaard, A., andBinder, C. (1992): ‘Cognitive function in Type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetic patients after nocturanal hypoglycaemia’,Diabetol.,35, pp. 898–903
Berne, C., andFagius, J. (1986): ‘Skin nerve sympathetic activity during insulin-induced hypoglycemia’,Diabetol.,29, pp. 855–860
Clarke, W. L., Carter, W. R., Moll, M., Cox, D. J., Gonder-Frederick, L. A., andCryer, P. E. (1988): ‘Metabolic and cutaneous event associated with hypoglycemia detected by sleep sentry’,Diabetes Care,11, pp. 630–635
DCCT Research Group (1991). ‘Epidemiology of severe hypoglycaemia in the diabetes control and complications trail’,Am. J. Med.,90, p. 450–459
DCCT Research Group (1991): ‘The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long-term complications in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus’,N. Eng. J. Med.,329, pp. 977–986
Frier, B. M., Fisher, B. M., Gray, C. E., andBeastall, G. H. (1988): ‘Counter-regulatory hormonal responses to hypoglycaemia in Type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes: evidence for diminished hypothalamic-pituitary hormonal secretion’,Diabetol.,31, pp. 421–9
Gale, E. A. M., Bennett, T., Macdonald, I. A., Holst, J. J., andMathews, J. A. (1983): ‘The physiological effects of insulin-induced hypoglycemia in man: Responses at differing levels of blood glucose’,Clin. Sci.,65, pp. 263–271
Gerich, J. E. (1988): ‘Glucose counterregulation and its impact on diabetes mellitus,’Diabetes,37, pp. 1608–1617
Hansen, K. A. andDuck, S. C. (1983): ‘Teledyne Sleep Sentry: Evaluation in pediatric patients for detection of nocturnal hypoglycemia’,Diabetes Care,6, pp. 597–600
Hanssen, K. F., Dahl-Jörgensen, K., Lauritzen, T., Feldt-Rasmussen, B., Brinchmann-Hansen, O., andDeckert, T. (1986): ‘Diabetic control and microvascular complications: the near-normoglycaemic experience’,Diabetol.,29, pp. 677–684
Hanson, P. J., Loughridge, L. W., Mulhall, B. P., andPackham, D. K. (1984): ‘Hypothermia in hypoglycemia’,Br. Med. J.,288, pp. 1212–1213
Harrad, R. A., Cockram, C. S., Plumb, A. P., Stone, S., Fenwick, P., andSönksen, P. H. (1985): ‘The effect of hypoglycemia on visual functions: A clinical and elektrophysiological study’,Clin. Sci.,69, pp. 673–679
Hilsted, J., Bonde-Petersen, F., Madsbad, S., Parving, H.-H., Christensen, N. J., Adelhoj, B., Bigler, D., andSjontoft, E. (1985): ‘Changes in plasma volume, in transcapillary escape rate of albumin and in subcutaneous blood flow during hypoglycemia in man’,Clin. Sci.,69, pp. 273–277
Howorka, K., Grillmayr, H., andWaldhäusl, W. (1986): ‘Incidence of severe hypoglycaemia during near-normoglycaemic insulin substitution: The “hypoglycaemia-cluster” phenomenon’,Diabetol.,29, p. 551A (abstract)
Howorka, K., Heger, G., Pumprla, I., Anderer, P., Zeitlhofer, J., Tribl, G., andThoma, H. (1994): ‘Hypoglycaemia unawareness is associated with an early decrease in vigilance during hypoglycaemia’,Diabetol.,37, p. A47 (abstract)
Ipp, E., andForster, B. (1987): ‘Sparing of cognitive function in mild phypoglycemia: dissociation from the neuroendocrine response’,J. Clin. Endocr. Metab.,65, pp. 806–810
Jasper, H. H. (1958): ‘The ten-twenty electrode system of the international federation of electroencephalography,’Neurophysiol.,10, pp. 371–375
Johansen, K., Ellegaard, S., andWex, S. (1986): ‘Detection of nocturnal hypoglycemia in insulin-treated diabetics by a skin temperature-skin conductance meter’,Acta Med. Scand.,220, pp. 213–217
Macdonald, I. A., Bennett, T., Gale, E. A. M., Green, J. H., andWalford, S. (1982): ‘The effect of propranolol or metoprolol on thermoregulation during insulin-induced hypoglycemia in man’,Clin. Sci.,63, pp. 301–310
Pramming, S., Thorsteinsson, B., Stigsby, B., andBinder, C. (1988): ‘Glycaemic threshold for changes in electroencephalograms during hypoglycaemia in patients with insulin dependent diabetes’,Br. Med. J.,296, pp. 665–667
Pramming, S., Thorsteinsson, B., Thailgaard, A., Pinner, E. M., andBinder, C. (1986): ‘Cognitive function during hypoglycaemia in Type I diabetes mellitys’,Br. Med. J.,229, pp. 647–650
Siesjoe, B. K. (1988): ‘Hypoglycaemia brain metabolism and brain daunage’,Diab. Metab. Rev.,4, pp. 113–144
Tallroth, G., Lindgren, M., Stenberg, G., Rosen, I., andAgakdh, C.-D. (1990): ‘Neurophysiological changes during insulin-induced hypoglycaemia and in the recovery period following glucose infusion in type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus and in normal man’,Diabetol.,33, pp. 319–323
Tamburrano, G., Lala, A., Locturatolo, N., Leonetti, F., Sbraccia, P., Giaccari, A., Busco, S., andPorcu, S. (1988): ‘Electroencephalography and visually evoked potentials during moderate hypoglycemia’,J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab.,66, pp. 1301–1306
Wilkins, E. S. (1989): ‘Towards implantable glucose sensors: a review’,J. Biomed. Eng.11, pp. 354–361
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Heger, G., Howorka, K., Thoma, H. et al. Monitoring set-up for selection of parameters for detection of hypoglycaemia in diabetic patients. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 34, 69–75 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02637024
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02637024