Abstract
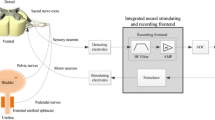
An implantable multiprogrammable microstimulator that is intended to restore normal bladder functions (retention and incontinence) to spinal cord injured patients is presented. The implantable microstimulator circuitry is externally controlled and is powered by a single encoded radio frequency carrier and has four bipolar (eight monopolar) independently controlled channels. It offers a higher degree of reprogrammability and flexibility and can be used in any neuromuscular applications. The implant system is adaptable to the patient's needs and to future developments in stimulation algorithms, without changing the implant. Features of the microstimulator include its capabilities to generate a wide range of waveforms and to combine up to four different programmable frequencies in each wave train. By using a forward error detection and correction communication protocol, the reliability of the implant is increased. The chip has been designed for structural testability by means of a scan-based test approach and uses circuit techniques to reduce power consumption and ensure long-term stability.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arabi, K., andSawan, M. (1994): ‘A multiprogrammable microstimulator dedicated to bladder dysfunctions’. Proc. IEEE-EMBS, 16th Ann. Conf. Baltimore, USA, 3–6 November
Brindly, G. S. (1977): ‘An implant to empty the bladder or close the urethra’,J. Neurol.,40, pp. 358–369
Brocklehurst, J. C. (1982): ‘Noncatheter devices for urinary incontinence in the elderly’,Med. Instrument,16, (3), pp. 167–168
Li, J.-S., Hassouna, M., Duval, F., andElhilali, M. M. (1992): ‘Electrical stimulation induced sphincter fatigue during voiding’,J. Urol.,148, pp. 949–952
Perkins, T. A. (1986): ‘Versatile three-channel stimulation controller for restoration of bladder function in paraplegia’,J. Biomed. Eng.,8, pp. 268–271
Sawan, M., Duval, F., Leclair, M.,et al. (1992): ‘Computerized transcutaneous control of a multichannel implantable urinary prosthesis’,IEEE Trans.,BME-39, (6), pp. 600–609
Sawan, M., Duval, F., Li, J.-S., Hassouna, M., andElhilali, M. M. (1993): ‘A new bladder stimulator—hand-held controller and miniaturized implant: preliminary results in dogs’,Biomed. Instrument. Technol.,27, pp. 143–149
Tanagho, E. A., andSchmidt, R. A. (1988): ‘Electrical stimulation in the clinical management of the neurogenic bladder’,J. Urol.,140, pp. 1331–1339
Walter, J. S., Wheeler, J. S., Robinson, C. J., andWurster, R. D. (1993): ‘Inhibiting the hyperreflexic bladder with electrical stimulation in a spinal animal model’,Neurol. Urodynam.,12, pp. 241–253
Wei, M., Duval, F., Fontaine, R., Mouine, J., Sawan, M., Elhilali, M., andHassouna, M. (1994): ‘A dedicated microprocessor for urinary incontinence stimulator’. 26th Southeastern Symp. on System Theory, Athens, Ohio, USA
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arabi, K., Sawan, M. Implantable multiprogrammable microstimulator dedicated to bladder control. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 34, 9–12 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02637016
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02637016