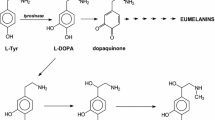
Summary
Crosslinking of [14C]l-tyrosine to at least five hamster melanoma cell surface proteins is reported. This effect was abolished by addition of nonradioactivel-tyrosine,l-phenylalanine, orl-dopa, but not byd-tyrosine, tyramine, dopamine, norepinephrine, or epinephrine. The above proteins can be purified by tyrosine-affinity chromatography. They have molecular weights different from proteins staining for dopa oxidase and proteins that bind anti-tyrosinase antibody in Western blots. It is suggested that they may be a hithergo unrecognized part of the cellular apparatus governing melanogenesis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hadley, M. E., editor. Endocrinology. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall; 1988.
Hayashibe, K.; Mishima, Y.; Ichihashi, M., et al. Melanosomal antigenic expression on the cell surface and intracellular subunit within melanogenic compartments of pigment cell: analysis by antimelanosome-associated monoclonal antibodies. J. Invest. Dermatol. 87:89–94; 1986.
Aubert, C. G.; Ali-Mehdi, S.; Galindo, J. R., et al. Melanogenesis of human melanoma cells cultured in tyrosine-depleted medium. In: Bagnara, J.; Klaus, S.; Paul, E., et al., eds. Pigment cell, biological molecular and clinical aspects. Tokyo: University of Tokyo Press; 1985:477–486.
Lerner, A.; Fitzpatrick, T. B. Biochemistry of melanin of melanin formation. Physiol. Rev. 30:91–126; 1950.
Moellmann, G.; Slominski, A.; Kuklinska, E., et al. Regulation of melanogenesis in melanocytes. Pigment Cell. Res. Suppl. 1:79–87; 1988.
Pawelek, J.; Korner, A. The biosynthesis of mammalian melanin. Am. Sci. 70:136–145; 1982.
Peters, C.; Braun, M.; Weber, B., et al. Targeting of a lysosomal membrane protein: a tyrosine-containing endocytosis signal in the cytoplasmic tail of lysosomal acid phosphatase is necessary and sufficient for targeting to lysosomes. EMBO J. 9:3497–3506; 1990.
Seiji, M. Subcellular particles and melanin formation in melanocytes. Adv. Biol. Skin 8:189–222; 1967.
Slominski, A.; Paus, R. Arel-tyrosine andl-dopa hormone-like bioregulators? J. Theor. Biol. 143:123–138; 1990.
Slominski, A.; Moellmann, G.; Kuklinska, E., et al. Positive regulation of melanin pigmentation by two key substrates of the melanogenic pathway.l-tyrosine andl-dopa. J. Cell Sci. 89:287–296; 1988.
Slominski, A.; Moellmann, G.; Kuklinska, E.l-Tyrosine,l-dopa and tyrosinase as positive regulators of the subcellular apparatus of melanogenesis in Bomirski Ab amelanotic melanoma cells. Pigm. Cell Res. 2:109–116; 1989.
Slominski, A.; Moellmann, G.; Kuklinska, E. MSH inhibits growth in a line of amelanotic melanoma cells and induces increases in cyclic AMP levels and tyrosinase activity without inducing melanogenesis. J. Cell Sci. 92:551–559; 1989.
Slominski, A.l-Tyrosine induces synthesis of melanogenesis related proteins. Life Sci. 45:1799–1803; 1989.
Slominski, A.; Paus, R.; Costantino, R. Differential expression and activity of melanogenesis-related proteins during induced hair growth in mice. J. Invest. Dermatol. 96:172–179; 1991.
Waugh, S. M.; DiBella, E. E.; Pilch, P. F. Isolation of a proteolytically derived domain of the insulin receptor containing the major site of crosslinking/binding. Biochemistry 28:3448–3455; 1989.
Yurkow, E. J.; Laskin, J. Purification of tyrosinase to homogeneity based on its resistance to sodium dodecyl sulfate-proteinase K digestion. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 275:122–129; 1989.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Slominski, A. l-tyrosine-binding proteins on melanoma cells. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol – Animal 27, 735–738 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02633219
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02633219