Summary
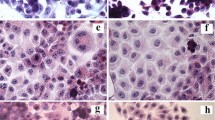
The hepatoblastoma cell line HepG2 has been a matter of many investigations; most of them include biochemical studies of lipoprotein and other hepatic protein metabolism. However, the accurate cellular features of these cells have not been emphasized. We studied the cellular histologic, histochemical, and ultrastructural characteristics of this cell line. In addition, we investigated by immunoenzymatic methods the cellular biosynthesis of several proteins: apolipoproteins-AI,-B,-D, and-E, albumin, alpha-fetoprotein, transferrin, alpha-1-antitrypsin, C-reactive protein, fibronectin, and collagens I, III and IV. The rates of accumulation, in the medium of HepG2 cells, of albumin, alpha-1-antitrypsin, transferrin, and alpha-fetoprotein were 13.2±1.9; 4.9±1.5; 3.2±0.4; and 10.7±1.7 μg/106 cells/24 h, respectively. Our results show that HepG2 cells exhibited most cellular features of normal human hepatocytes. Bile canaliculi as well as Golgi apparatus complexes were particularly developed. Except for the C-reactive protein, HepG2 cells have all retained the ability to synthesize hepatic proteins but with some variable intensity from cell to cell. This hepatoblastoma cell line seems to represent a useful tool in the understanding of hepatic protein biosynthesis, particularly for the investigation on the secretory pathway of plasma proteins.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aden, D. P.; Fogel, A.; Plotkin, S., et al. Controlled synthesis of HBsAg in a differentiated human liver carcinoma-derived cell line. Nature 282:615–616; 1979.
Archer, T. K.; Tam, S. P.; Deugau, K. V., et al. Apolipoprotein CII mRNA levels in primate liver. Induction by estrogen in the human hepatocarcinoma cell line, HepG2. J. Biol. Chem. 260:1676–1681; 1985.
Ballet, F.; Bouma, M. E.; Wang, S. R., et al. Isolation, culture and characterization of adult human hepatocytes from surgical liver biopsies. Hepatology 4:849–854; 1984.
Boström, K.; Wettesten, M.; Boren, J., et al. Pulse-chase studies of the synthesis and intracellular transport of apolipoprotein B100 in HepG2 cells. J. Biol. Chem. 261:13800–13806; 1986.
Bouma, M. E.; Pessah, M.; Renaud, G., et al. Synthesis and secretion of lipoproteins by human hepatocytes in culture. In Vitro 24:85–90; 1988.
Cassio, D.; Rogier, E.; Feldman, G., et al. Plasma-protein production by rat hepatoma cells in culture, their variants and revertants. Differentiation 30:220–228; 1986.
Chiquoine, A. D. The distribution of glucose-6-phosphatase in the liver and in the kidney of the mouse. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 1:429–435; 1953.
Ciechanover, A.; Schwartz, A. L.; Lodish, H. F. The asialoglycoprotein receptor internalizes and recycles independently of the transferrin and insulin receptors. Cell 32:267–275; 1983.
Dashti, N.; Wolfbauer, G. Secretion of lipids, apolipoproteins, and lipoproteins by human hepatoma cell line, HepG2: effects of oleic acid and insulin. J. Lipid Res. 28:423–436; 1987.
Davis, R. A.; Engelhorn, S. C.; Pangburn, D. B. Very low density lipoprotein synthesis and secretion by cultured rat hepatocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 254:2010–2016; 1979.
Ellsworth, J. L.; Erickson, S. K.; Cooper, A. D. Very low and low density lipoprotein synthesis and secretion by the human hepatoma cell line HepG2: effects of free fatty acid. J. Lipid Res. 27:858–874; 1986.
Everson, G. T.; Polokoff, M. A. HepG2. A human hepatoblastoma cell line exhibiting defects, in bile acid synthesis and conjugation. J. Biol. Chem. 261:2197–2201; 1986.
Fair, D. S.; Bahnak, B. R. Human hepatoma cells secrete single chain factor X, prothrombin and antithrombin III. Blood 4:194–204; 1984.
French, R. W. Azure C as tissue stain. Stain Technol. 1–79; 1926.
Geuze, H. J.; Slot, J. W.; Strous, G. J. A. M., et al. The pathway of the asialoglycoprotein-ligand during receptor-mediated endocytosis: a morphological study with colloidal gold/ligand in the human hepatoma cell line, HepG2. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 32:38–44; 1983.
Goldman, N. D.; Liu, T. Y. Biosynthesis of human C-reactive protein in cultured hepatoma cells is induced by a monocyte factor(s) other than interleukin-1. J. Biol. Chem. 262:2363–2368; 1987.
Gomori, G. Distribution of acid phosphatase in the tissue under normal and pathological conditions. Arch. Pathol. 32:189–199; 1942.
Graham, R. C.; Karnovsky, M. J. The early stage of absorption of injected horseradish peroxidase in the proximal tubule of mouse kidney: ultrastructural cytochemistry by a new technique. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 14:291–295; 1960.
Grases, P. J.; Millard, P. R.; O'D McGee, J. The ultrastructure of alcoholic liver disease: a review and analysis of 100 biopsies. Histol. Histopathol. 2:19–29; 1987.
Guguen-Guillouzo, C.; Campion, J. P.; Brissot, P., et al. High field preparation of isolated human adult hepatocytes by enzymatic perfusion of the liver. Cell. Biol. Int. Rep. 6:625–628; 1982.
Havekes, L.; Van Hinsbergh, V.; Kempen, H. J., et al. The metabolism in vitro of human low density lipoprotein by the human hepatoma cell line HepG2. Biochem. J. 214:951–958; 1983.
Hoeg, J. M.; Demosky, S. J.; Edge, S. B., et al. Characterization of a human hepatic receptor for high density lipoproteins. Arteriosclerosis 5:228–237; 1985.
Knowles, B. B.; Howe, C. C.; Aden, D. P. Human hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines secrete the major plasma proteins and hepatitis B surface antigen. Science 209:497–499; 1980.
Kushner, I.; Feldmann, G. Control of the acute phase response. Demonstration of C-reactive protein synthesis and secretion by hepatocytes during acute inflammation in the rabbit. J. Exp. Med. 148:466–477; 1978.
Lodish, H. F.; Kong, N.; Hirani, S., et al. A vesicular intermediate in the transport of hepatoma secretory proteins from the rough endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi complex. J. Cell Biol. 104:221–230; 1987.
Lodish, H. F.; Kong, N.; Snider, M., et al. Hepatoma secretory proteins migrate from rough endoplasmic reticulum to Golgi at characteristic rates. Nature 304:80–83; 1983.
Ma, M. H.; Biempica, L. The normal human liver cell. Cytochemical and ultrastructural studies. Am. J. Pathol. 62:353–389; 1971.
Marinari, L.; Lenich, C. M.; Ross, A. C. Production and secretion of retinol-binding protein by a human hepatoma cell line, HepG2. J. Lipid Res. 28:941–948; 1987.
Mc Manus, J. F. A. Histological demonstration of mucin after periodic acid. Nature 158:202; 1946.
Parent, J. B.; Bauer, H. C.; Olden, K. Three secretory rates in human hepatoma cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 846:44–50; 1985.
Redman, C. M.; Avellino, G. Effects of canavanine on the secretion of plasma proteins by HepG2 cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 847:198–206; 1985.
Remy, L. The intracellular lumen: origin, role and implications of a cytoplasmic neostructure. Biol. Cell 56:97–106; 1986.
Rogier, E.; Cassio, D.; Weiss, M. C., et al. An ultrastructural study of rat hepatoma cells in culture, their variants and revertants. Differentiation 30:229–236; 1986.
Sternlieb, I. Electron microscopy of mitochondria and peroxisomes of human hepatocytes. In: Popper, H.; Schaffner, F., eds. Progress in liver diseases, vol. 6. New York: Grune and Stratton; 1979:81–104.
Strous, G. J. A. M.; Willemsen, R.; Van Kerkhof, P., et al. Vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein, albumin and transferrin are transported to the cell surface via the same Golgi vesicles. J. Cell Biol. 97:1815–1822; 1983.
Tam, S. P.; Archer, T. K.; Deeley, R. G. Effects of estrogen on apolipoprotein secretion by the human hepatocarcinoma cell line, HepG2. J. Biol. Chem. 260:1670–1675; 1985.
Tam, S. P.; Archer, T. K.; Deeley, R. G. Biphasic effects of estrogen on apolipoprotein synthesis in human hepatoma cells: mechanism of antagonism by testosterone. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 83:3111–3115; 1986.
Thrift, R. N.; Forte, T. M.; Cahoon, B. E., et al. Characterization of lipoproteins produced by the human liver cell line, HepG2, under defined conditions. J. Lipid Res. 27:236–250; 1986.
Uchino, R.; Nohara, T.; Okamoto, E., et al. Biosynthesis of various types of collagen by human hepatoma cells in vitro. Virchows Arch. (Cell Pathol.) 48:229–236; 1985.
Vega-Salas, D. E.; Salas, P. J. I.; Rodriguez-Boulan, E. Modulation of the expression of an apical plasma membrane protein of Madin-Darby canine kidney epithelial cells: cell-cell interactions control the appearance of a novel intracellular storage compartment. J. Cell Biol. 104:1249–1259; 1987.
Verspohl, J.; Roth, R. A.; Vigneri, R., et al. Dual regulation of glycogen metabolism by insulin and insulin-like growth factors in human hepatoma cells (HepG2). Analysis with an antireceptor monoclonal antibody. J. Clin. Invest. 74:1436–1443; 1984.
Wanson, J. C.; Drochmans, P.; Mosselmans, R., et al. Adult rat hepatocytes in primary monolayer culture. Ultrastructural characteristics of intercellular contacts and cell membrane differentiations. J. Cell Biol. 74:858–877; 1977.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bouma, ME., Rogier, E., Verthier, N. et al. Further cellular investigation of the human hepatoblastoma-derived cell line HepG2: Morphology and immunocytochemical studies of hepatic-secreted proteins. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol 25, 267–275 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02628465
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02628465