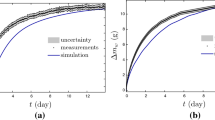
Abstract
There were a number of studies on moisture transfer modelling of wood, but no systematic study for moisture transfer in particleboard with respect to usage or storage. The physical parameters of four kinds of particleboards were determined in this study. The unsteady-state diffusion coefficients and surface emission coefficients of moisture in particleboards were separated in one experimental period by using the method of linear regression. Then the moisture transfer processes in particleboard were analysed by using Finite Element Method (FEM), and the moisture absorption processes of four kinds of particleboards were observed experimentally. By comparing the computed results with the experimental results, it showed that the error was within 10%. Therefore, we came to the conclusion that the processes of moisture transfer in particleboard can be described by using FEM:
Zusammenfassung
Im Gegensatz zum Holz, liegen für Spanplatten noch keine systematischen Untersuchungen des Wassertransports vor. In dieser Arbeit wurden für vier Plattentypen die physikalischen Eigenschaften bestimmt. Diffusions-Koeffizienten und Koeffizienten für den Wasseraustritt aus der Oberfläche wurden über Regressions-analysen getrennt erfaßt. Die Feuchtebewegung innerhalb der Platten wurde darauf nach der Finite-Element-Methode (FEM) simuliert und mit der Wasseraufnahme der vier Plattentypen verglichen. Die Abweichungen der berechneten von den experimentell bestimmten Werten lagen im Bereich von 10%. Die FEM erweist sich daher als geeignet, die Wasserbewegung innerhalb von Spanplatten zu beschreiben.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Avramidis, St. and Siau, J. F.: An investigation of the external and internal resistance to moisture diffusion in wood. Wood Sci. Technol. 21 (1987) 249–256
Choong and Skaar, C.: Diffusivity and surface emissivity in wood drying. Wood Fiber. 4(2) (1972) 80–86
Droin, A.; Taverdet, J. L. and Vergnaud, J. M.: Modelling the kinetics of moisture absorption by wood. Wood Sci. Technol. 22 (1988) 11–20
Droin, A.; Taverdet, J. L. and Vergnaud, J. M.: Modelling the absorption and desorption of moisture by wood in an atmosphere of constant and programmed relative humidity. Wood Sci. Technol. 22 (1988) 299–310
Droin, A.; Taverdet, J. L. and Vergnaud, J. M.: Modelling the process of moisture absorption in three dimensions by wood samples of various shapes: cubic, parallelepipedic. Wood Sci. Technol. 23 (1989) 259–271
Hata, T.; Kawai, S. and Sasaki, H.: Production of particleboard with steam-injection. Wood Sci. Technol. 24 (1990) 65–78
Jaluria, Y. and Torrance, K. E.: Computational heat transfer. Springer, Berlin 1986
Lehmann, W. F.: Moisture-stability relationships in wood-base composition boards. Forest Prod. J. Vol. 22. No. 7 1972
Liu, Jen. Y.: A new method for separating diffusion coefficient and surface emission coefficient, Wood and Fiber Science. 21(2) (1989) 133–141
Siau, J. F. Transport processes in wood. Springer, Berlin 1984
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liping, C., Deku, S. Modelling of the moisture transfer process in particleboards. Holz als Roh- und Werkstoff 50, 395–399 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02627609
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02627609