Summary
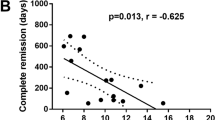
A remission defmed by the possibility of temporarily discontinuing insulin therapy while blood glucose remains normal is not infrequently observed after intensive insulin therapy in newly diagnosed acute type I diabetes in the South of France. In order to analyze possible factors of such a remission, 47 newly diagnosed ketotic diabetics under 35 years of age of Caucasian origin were enrolled in a prospective study. They were given continuous s.c. insulin infusion for two weeks and oral agents were introduced on day 8. In 16 patients insulin could not be withdrawn. In 31 insulin was stopped for more than 3 months (mean 12.3, range 3.35) while blood glucose remained below 6 mmol/l fasting (mean 5.3) and 7.8 post-prandial (mean 5.1) and glycosylated Hb below 8.5% (mean 6). At presentation, diabetics who later went into remission and those who did not, showed no difference in age (22.3vs 23.1 years), sex ratio, apparent duration of symptoms (1.4vs 1.6 months), glycosylated hemoglobin (12.0vs 13.1%) and basal or post-prandial C-peptide values or presence of islet cell antibodies. No differences were observed in the frequency of DR3 and DR4 antigens in the two groups but diabetics who developed a remission bore the A 19.2 antigen (9/31vs 1/16) and the B18 one (11/31vs 1/16) more frequently, A 19.2 and B18 being associated in 7 cases of this group. This increased frequency in the remission group of HLA antigens, more often observed in diabetics of Mediterranean origin, suggests that differences in the genetic background may be associated with a difference in the evolution of the disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barrett E. J., DeFronzo R. A., Bevilacqua S., Ferranini E.: Insulin resiscance in diabetic ketoacidosis — Diabetes31, 923, 1982.
Bottazzo G. F., Florin-Cristiensen A., Doniach D.: Islet cell antibodies in diabetes mellitus with autoimmune polyendocrine deficiencies — Lancetii, 1279, 1974.
Brush J. M.: Initial stabilization of diabetic children — Amer. J. Dis. Child.67, 429, 1944.
Contu L., Deschamps I., Lestradet M., Hors J., Schmid M., Busson M., Nadajam A., Marcelli-Barse A., Duasset J.: HLA haplotype study of 53 juvenile insulin dependent diabetic families — Tiss. Antigens20, 123, 1982.
Contu L., Puligheddu A., Mura C., Gabbas A.: HLA antigens in Sardinian patients with diabetes mellitus — Diabète et Métabol.3, 263, 1977.
DeFronzo R. A., Hendler R., Simonson D.: Insulin resistance is a prominent feature of insulin-dependent diabetes — Diabetes31, 795, 1982.
De Mouzon A., Ohayon E., Ducos J., Hauptmann G.: Bf and C4 markers for insulin dependent diabetes in basques — Lancetii, 1364, 1979.
Heinze E., Beischer W., Keller L., Winkler G., Teller W. M., Pfeiffer E. F.: C-peptide secretion during the remission phase of juvenile diabetes — Diabetes27, 670, 1978.
Irvine W. J., McCallum C. J., Gray R. S., Campbell C. J., Duncan L. J. P., Farquhar J. W., Vaughan H., Morris P. J.: Pancreatic islet-cell antibodies in diabetes mellitus correlated with the duration and type of diabetes, coexistent autoimune disease, and HLA type — Diabetes26, 138, 1977.
Jackson R. L., Boyd J. D., Smith R. E.: Stabilization of the diabetic children — Am. J. Dis. Child.59, 332, 1940.
Knip M., Puukkar R., Kaar M. M., Akerblom H. D.: Remission phase, endogenous insulin secretion and metabolic control in diabetic children — Acta diabetol. lat.19, 243, 1982.
Lernmark Å., Hägglöf B., Freedman Z., Irvine J., Ludvigsson J., Holmgren G.: A prospective analysis of antibodies reacting with pancreatic islet cells in insulin-dependent diabetic children — Diabetologia20, 471, 1981.
Ludvigsson J., Heding L. G.: C-peptide in children with juvenile diabetes. A preliminary report — Diabetologia12, 627, 1976.
Ludvigsson J., Säfwenberg J., Heding L. G.: HLA-types, C-peptide and insulin antibodies in juvenile diabetes — Diabetologia13, 13, 1977.
Madsbad S., Binder C., Krarup T., Regeur L.: The effect of strict metabolic control on residual β-cell function — A control study — Diabetes29 (Suppl. 2), 23A, 1980; abstract # 90.
Mirouze J., Seignalet J., Selam J. L., Lapinski M., Jaffiol C.: Antigènes HLA chez les diabétiques insulinodépendants — Nouv. Presse méd.5, 1628, 1976.
Mirouze J., Selam J. L., Pham T. C., Chenon D.: The outcome of juvenile ketotic diabetes following remissions induced by the artificial pancreas: a four-year follow-up. In:Federlin K., Pfeiffer E. F., Raptis S. (Eds): Islet-pancreas transplantation and artificial pancreas. Workshop Vouliagmeni Beach/Athens. Georg Thieme Verlag, Stuttgart-New York and Thieme-Stratton Inc., New York, 1982; Hormone metabol. Res.12 (Suppl.), 238, 1932.
Mirouze J., Selam J. L., Pham T. C., Mendoza E., Orsetti A.: Sustained insulin-induced remissions of juvenile diabetes by means of an external artificial pancreas — Diabetologia14, 223, 1978.
Park B. N., Soeldner J. S., Gleason R. E.: Diabetes in remission. Insulin secretory dynamics — Diabetes23, 616, 1979.
Pinget M., Blickle J. F., Anceau A., Audhuy B., Jacques C., Brogard J. M., Dorner M.: Diabetes insulinodépendants récents: rémissions partielles induites par la pompe à insuline — Nouv. Presse méd.10, 1381, 1981.
Pirart J., Lavaux J. P.: Remissions in diabetes. In:Pfeiffer E. F. (Ed.): Handbuch des Diabetes mellitus. Lehmans Verlag, München, 1972; vol. 2, p. 443.
Serrano-Ríos M., Regueiro J. R., Severino R., López-Larrea C., Arnaiz-Villena A.: HLA antigens in insulin dependent and non-insulin dependent Spanish diabetic patients — Diabète et Métabol.9, 116, 1983.
Stiller C. R., Laupacis A., Dupré J., Jenner M. R., Keown P. A., Rodger W., Wolfe B. M. J.: Cyclosporine for treatment of early type I diabetes. Preliminary results — New Engl. J. Med.308, 1226, 1983.
Svejgaard A., Platz P., Ryder L. P.: 8th Workshop Joint Report on Insulin-dependent Diabetes Mellitus. In:Terasaki P. (Ed.): Histocompatibility testing 1980. UCLA, Los Angeles/CA, 1980; p. 638.
Vague Ph., Vialettes B., Altomare E., Lassmann V., Moulin J. P.: Diabetes insulinodépendants récents. Rémission par insulinothérapie adéquate — Nouv. Presse méd.10, 3724, 1981.
Vague Ph., Vialettes B., Altomare E., Lassmann V., Simonin M. J.: Factors associated with the early remission of insulin dependent diabetes. A prospective study — Diabetologia19, 321, 1980; abstract # 384.
Vialettes B., Di Campo-Rougerie C., Lassmann V., Vague Ph.: Comparaisons de divers types d’anticorps anti-îlots dans le diabète en fonction de la cause et de la durée d’évolution — Nouv. Presse méd.12, 2303, 1983.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vague, P., Vialettes, B., Lassmann, V. et al. Sustained initial remission induced by intensive insulin treatment in type I diabetes. Possible role of the genetic Background. Acta diabet. lat 22, 295–304 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02624748
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02624748