Summary
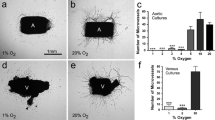
Human arterial endothelial cells were cultured in vitro for up to 40 cumulative population doublings. Culture conditions similar to those required for long-term propagation of human umbilical vein endothelial cells were employed. These included fibronectin-coated culture vessels, 5 to 20% fetal bovine serum, endothelial cell growth factor, and heparin. Thoracic aorta endothelial cells were larger than iliac artery endothelial cells. Both cell types stained positively for Factor VIII antigen by immunofluorescence. A decrease in confluent density as a function of population doubling level was correlated with the appearance of large, senescent cells in the cultures. Serum growth factors to which the arterial endothelial cells responded included insulin, transferrin, epidermal growth factor, thrombin, and somatomedins. The effect of thrombin did not require the availabilty of the active site of the protease. The effect of the somatomedins was only seen in the presence of heparin. Neither platelet-derived growth factor nor hydrocortisone induced arteiral endothelial cell proliferation. These growth factor responses were also observed on the part of human umbilical vein endothelial cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Awbrey, B. J.; Hoak, J. C.; Owen, W. G. Binding of human thrombin to cultured human endothelial cells J. Biol. Chem. 254;4092–4095; 1979.
Bar, R. S.; Goldsmith, J. C.; Rechler, M. M., et al. Interactions of multiplication-stimulating activity with bovine endothelium: Comparative studies in primary, passaged, and cloned cultures from the pulmonary and systemic circulations. Endocrinology 110:990–996; 1982.
Bar, R. S.; Peacock, M. L.; Rechler, M. M., et al. Receptors for multiplication-stimulating activity on human arterial and venous endothelial cells. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 52:814–816; 1981.
Bar, R. S.; Stueck, S. S.; Dake, B., et al. Multiplication-stimulating activity (MSA) stimulates proteoglycan synthesis in cultured endothelial cells Endocrinology 115:2487–2489; 1984.
Chamley-Campbell, J.; Campbell, G.; Ross, R. The smooth muscle cell in culture Physiol. Rev. 59:1–61; 1979.
Clemmons, D. R.; Underwood, L. E.; Chatelain, P. G. et al. Liberation of immunoreactive somatomedin-C from its binding proteins by proteolytic enzymes and heparin J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 56:384–389; 1983.
Engvall, E.; Ruoslahti, E. Binding of soluble form of fibroblast surface protein, fibronectin, to collagen. Int. J. Cancer 20:1–5; 1977.
Gimbrone, M. A., Jr.; Cotran, R. S. Human vascular smooth muscle in culture. Growth and ultrastructure. Lab. Invest. 33:16–27; 1975.
Gimbrone, M. A., Jr.; Cotran, R. S.; Fokman, J. Human vascular endothelial cells: Growth and DNA synthesis J. Cell Biol. 60:673–684; 1974.
Glassberg, M. K.; Bern, M. M.; Coughlin, S. R., et al. Cultured endothelial cells derived from the human iliac arteries. In Vitro 18:859–866; 1982.
Gordon, P. B.; Sussman, I. I.; Hatcher, V. B. Long-term culture of human endothelial cells. In Vitro 19:661–671; 1983.
Gospodarowicz, D.; Brown, K. D.; Birdwell, C. R., et al. Control of proliferation of human vascular endothelial cells. Characterization of the response of human umbilical vein endothelial cells to fibroblast growth factor, epidermal growth factor, and thrombin. J. Cell Biol. 77:774–788; 1978.
Heldin, C.-H.; Westermark, B.; Wasteson, A. Specific receptors for platelet-derived growth factor on cells derived from connective tissue and glia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 78:3664–3668; 1981.
Jaffe, E. A.; Nachman, R. L.; Becker, C. G., et al. Culture of human endothelial cells derived from umbilical veins. Identification by morphologic and immunologic criteria. J. Clin. Invest. 52:2745–2756; 1973.
Johnson, A. R. Human pulmonary endothelial cells in culture. Activities of cells from arteries and cells from veins. J. Clin. Invest. 65:841–850; 1980.
Knauer, D. J.; Cunningham, D. D. A reevaluation of the response of human umbilical vein endothelial cells to certain growth factors. J. Cell Physiol. 117:397–406; 1983.
Knauer, D. J.; Smith, G. L. Inhibition of biological activity of multiplication-stimulating activity by binding to its carrier protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 77:7252–7256; 1980.
Maciag, T. Angiogenesis. In: Spaet, T., ed. Progress in Hemostasis and Thrombosis, vol. 7, Orlando, FL: Grune and Stratton, Inc.; 1984:167–182.
Maciag, T.; Cerundolo, J.; Ilsley, S., et al. An endothelial cell growth factor from bovine hypothalamus: identification and partial characterization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 76:5674–5678; 1979.
Maciag, T.; Hoover, G. A.; Weinstein, R. High and low molecular weight forms of endothelial cell growth factor J. Biol. Chem. 257:5333–5336; 1982.
Maciag, T.; Hoover, G. A.; Stemerman, M. B., et al. Serial propagation of human endothelial cells in vitro J. Cell Biol. 91:420–426; 1981.
Maciag, T.; Hoover, G. A.; van der Spek, J., et al. Growth and differentiation of human umbilical vein endothelial cells in culture. In: Sato, G.; Sirbasku, D.; Pardee, A., eds. Cold Spring Harbor Conferences on Cell Proliferation, vol. 9: Growth of cells in hormonally defined media. New York: Cold Spring Harbor Press; 1982:525–538.
Repin, V. S.; Dolgov, V. V.; Zaikina, O. E., et al. Heterogeneity of endothelium in human aorta. A quantitative analysis by scanning electron microscopy. Atherosclerosis 50:35–52; 1984.
Thronton, S. C.; Mueller, S. N.; Levine, E. M. Human endothelial cells: Use of heparin in cloning and long-term serial cultivation Science 222:623–625; 1983.
Weinstein, R.; Stemerman, M. B.; Maciag, T. Hormonal requirements for growth of arterial smooth muscle cells in vitro: An endocrine approach to atherosclerosis Science 212:818–820; 1981.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was supported in part by Public Health Service grants HL01030, HL01734, and AG00599.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weinstein, R., Wenc, K. Growth factor responses of human arterial endothelial cells in vitro. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol 22, 549–556 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02621142
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02621142