Summary
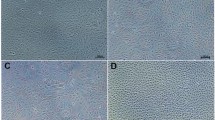
A continuous line of epithelioid cells was established from explant skin tissues of the green sea turtle,Chelonia mydas. These cells, designated GTS, have been subcultured more than 60 times in commercially available mammalian cell culture medium supplemented with 5% bovine calf serum. Of those temperatures tested, optimal growth was achieved at 30°C although replication occurred between 16 and 37°C. These cells may be held as monolayers at 8°C or stored frozen in growth medium containing 10% dimethylsulfoxide at −70 or −196°C. The modal number of 55 chromosomes per cell is in agreement with the heterogametic female diploid number of this species. The GTS line represents the first established culture of normal epithelioid skin cells to be reported for a poikilothermic species.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wolf, K.; Quimby, M. C.; Pyle, E. A.; Dexter, R. P.. Preparation of monolayer cell cultures from tissues of some lower vertebrates. Science 132: 1890–1891; 1960.
Clem, L. W.; Moewus, L.; Sigel, M. M.: Studies with cells from marine fish in tissue culture. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 108: 762–766; 1961.
Wolf, K.; Quimby, M. C. Established eurythermic line of fish cells in vitro. Science 13: 1065–1066; 1962.
Wolf, K.; Mann, J. A. Poikilotherm vertebrate cell lines and viruses: a current listing for fishes. In Vitro 16: 168–179; 1980.
Wolf, K.; Quimby, M. C. Amphibian cell culture: permanent cell line from the bullfrog (Rana catesbeiana). Science 144: 1578–1580; 1964.
Clark, H. F.; Karzon, D. T. Terrapene heart (TH-1), a continuous cell line from the heart of the box turtleTerrapene carolina. Exp. Cell Res. 48: 263–268; 1967.
Koment, R. W.; Haines, H. G. A new reptilian herpesvirus isolated from the green sea turtle,Chelonia mydas. Abstracts Ann. Meeting Am. Soc. Microbiol. 1977: 347.
Rebell, G.; Rywlin, A.; Haines, H. A herpes-type agent associated with skin lesions of green sea turtles in aquaculture. Am. J. Vet. Res. 36: 1221–1224; 1975.
Koment, R. W.; Duman, R. G. Preparation of metaphase chromosomes in cell cultures derived from an aquatic reptile. J. Tissue Cult. Methods 6: 75–78; 1980.
Geary, L. E.; Lazarides, E.; Goetz, I; Roberts, E. Actin filaments in human skin fibroblasts are similar in normal persons and patients with Huntington's disease. Ann. Neurol. 4: 554–556; 1978.
Kleinfeld, R.; Melnick, J. L. Cytological aberrations in cultures of “normal” monkey kidney epithelial cells. J. Exp. Med. 107: 599–608; 1958.
Donnelly, G. M.; Newcomer, E. H. Autoradiographic patterns in cultured leukocytes of the domestic fowl. Exp. Cell Res. 30: 363–368; 1963.
Makino, S. The chromosomes of the sea turtle,Chelonia japonica, with evidence of female heterogamety. Annot. Zool. Jap. 25: 250–257; 1952.
Stephenson, N. G. Effects of temperature on reptilian and other cells. J. Embryol. Exp. Morphol. 16: 455–467; 1966.
Freeman, A. E.; Igel, H. J.; Herrman, B. J.; Kleinfeld, F. L. Growth and characterization of human skin epithelial cell cultures. In Vitro 12: 352–362; 1976.
Worton, R. G.; Duff, C. Karyotyping. Methods Enzymol. 58: 322–344; 1979.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koment, R.W., Haines, H. Characterization of a reptilian epithelioid skin cell line derived from the green sea turtle,Chelonia mydas . In Vitro 18, 227–232 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02618575
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02618575