Summary
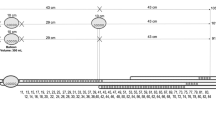
This study was undertaken to determine the pressure profile of the rectum and anal sphincter of healthy persons. Open-tip tubes and tiny balloons of various sizes connected to pressure transducers were withdrawn in stages from the lower part of the sigmoid to the exterior in 11 healthy males in the Sims position. Records of the pressures encountered during the withdrawals were made photokymographically. Mean sigmoid and rectal resting pressures were 2 to 5 cm. of water above ambient pressure. A band of elevated pressure about 4 cm. in width was always detected in the anal sphincter. The mean maximal pressure in the sphincter as detected by open-tip tubes was 45 cm. of water; greater maximal pressures were encountered when balloons were withdrawn through the sphincter. Bands or zones of increased pressure were consistently detected in the rectum during withdrawal of even tiny balloons. These zones have been interpreted as being produced by pressure applied to the balloon as it was withdrawn past a bend in the rectum or over folds in the rectum. The suggestion is made that these structures may act as incomplete or feeble valves resisting the analward movement of rectal contents, just as they resisted the analward movement of the balloons.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atkinson, M., D. A. W. Edwards, A. J. Honour and E. N. Rowlands: Comparison of cardiac and pyloric sphincters: A manometric study. Lancet.2: 918, 1957.
Atkinson, M., D. A. W. Edwards, A. J. Honour and E. N. Rowlands: The oesophagogastric sphincter in hiatus hernia. Lancet.2: 1138, 1957.
Bacon, H. E.: Anus-Rectum-Sigmoid Colon, Diagnosis and Treatment. Ed. 1, Philadelphia, J. B. Lippincott Company, 1938, p. 22.
Code, C. F. and J. F. Schlegel: The pressure profile of the gastroesophageal sphincter in man: An improved method of detection. Proc. Staff Meet., Mayo Clin.33: 406, 1958.
Creamer, Brian, H. A. Anderson and C. F. Code: Esophageal motility in patients with scleroderma and related diseases. Gastroenterologia.86: 763, 1956.
Davidson, M., M. H. Sleisenger, H. Steinberg and T. P. Almy: Studies of distal colonic motility in children: The pathologic physiology of congenital megacolon—(Hirschsprung’s disease). Gastroenterology.29: 803, 1955.
Davidson, Murray, M. H. Sleisenger, T. P. Almy and S. Z. Levine: Studies of distal colonic motility in children. I. Non-propulsive patterns in normal children. Pediatrics.17: 807, 1956.
Davidson, Murray, M. H. Sleisenger, T. P. Almy and S. Z. Levine: Studies of distal colonic motility in children. II. Propulsive activity in diarrheal states. Pediatrics.17: 820, 1956.
Fyke, F. E., Jr. and C. F. Code: Resting and deglutition pressures in the pharyngo-esophageal region. Gastroenterology.29: 24, 1955.
Fyke, F. E., Jr., C. F. Code and J. F. Schlegel: The gastroesophageal sphincter in healthy human beings. Gastroenterologia.86: 135, 1956.
Gauer, O. H. and E. Gienapp: A miniature pressure-recording device. Science.112: 404, 1950.
Lambert, E. H.: Strain gages: Resistance wire. In: Glasser, Otto: Medical Physics. Chicago, The Year Book Publishers, Inc., 1950, vol. 2, p. 1090.
Martin, Edward and V. G. Burden: The surgical significance of the recto-sigmoid sphincter. Ann. Surg.86: 86, 1927.
O’Beirne, James: New Views of the Process of Defecation, and Their Application to the Pathology and Treatment of Diseases of the Stomach, Bowels, and Other Organs, Together With an Analytical Correction of Sir Charles Bell’s Views Respecting the Nerves of the Face. Dublin, Hodges & Smith, 1833, 286 pp.
Spriggs, E. A., C. F. Code, J. A. Bargen, R. K. Curtiss and N. C. Hightower, Jr.: Motility of the pelvic colon and rectum of normal persons and patients with ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology.19: 480, 1951.
Swenson, Orvar, H. F. Rhenilander and Israel Diamond: Hirschsprung’s disease: A new concept of the etiology: Operative results in thirty-four patients. New England J. Med.241: 551, 1949.
Wetterer, E.: Eine neue manometrische Sonde mit elektrischer Transmission. Ztschr. Biol.101: 332, 1943.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Read at the meeting of the American Proctologic Society, Houston, Texas, April 25 to 27, 1960.
The Mayo Foundation, Rochester, Minnesota, is a part of the Graduate School of the University of Minnesota.
About this article
Cite this article
Hill, J.R., Kelley, M.L., Schlegel, J.F. et al. Pressure profile of the rectum and anus of healthy persons. Dis Colon Rectum 3, 203–209 (1960). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02616555
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02616555