Abstract
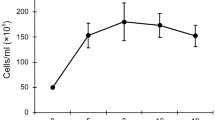
The chlorellavorus bacterium (Bdellovibrio chlorellavorus Gromov and Mamkaeva 1972) attaches to (but does not enter) cells of the unicellular green alga,Chlorella, which is killed and the cell contents of which are digested. The bacterium is pleomorphic (vibrios 0.3 μm wide; cocci 0.6 μm wide), and it has a Gram-negative cell wall structure pili, and a single, unsheathed, polar flagellum. Division may occur only in bacterial cells attached to algal cells, an attachment mediated by a pad (245×36 nm) of unknown composition. Bacterial growth occurs only in the presence of liveChlorella cells, and not on various bacteriological culture media, killedChlorella cells, 4 strains ofPrototheca, or 24 strains of Gram-negative bacteria. The chlorellavorus bacterium may not require algal protein synthesis, since the bacterium grows on algae in the presence of cycloheximide (30 μg/ml). Although the DNA base composition of the chlorellavorus bacterium (50 mol % G+C) is in the same range asBdellovibrio bacteriovorus, its ultrastructure, developmental cycle, host range, and format of its intermicrobial association all distinguish the chlorellavorus bacterium from members of the genusBdellovibrio.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Allen, R. D., Baumann, P. 1971. Structure and arrangement of flagella in species of the genusBeneckea andPhotobacterium fischeri. Journal of Bacteriology107:295–302.
Gromov, B. V., Mamkaeva, K. A. 1972. [Electron microscopic examination ofBdellovibrio chlorellavorus parasitism on cells of the green algaChlorella vulgaris]. Tsitologiya14:256–260. [In Russian.]
Harris, R. H., Mitchell, R. 1973. The role of polymers in microbial aggregation. Annual Review of Microbiology27:27–50.
Kraus, S. J., Glassman, L. H. 1974. Scanning electron microscope study ofNeisseria gonorrhoeae. Applied Microbiology27:584–592.
Jephcott, A. E., Reyn, A., Birch-Andersen, A. 1971.Neisseria gonorrhoeae. III. Demonstration of presumed appendages to cells from different colony types. Acta Pathologica et Microbiologica Scandinavica Section B79:437–439.
Mamkaeva, K. A. 1966. [Observations on the lysis of cultures of the genusChlorella]. Mikrobiologiya35:853–859. [In Russian.]
Marchant, H. J. 1973. Processing small delicate biological specimens for scanning electron microscopy. Journal of Microscopy97:369–371.
Seidler, R. J., Mandel, M., Baptist, J. N. 1972. Molecular heterogeneity of the bdellovibrios: Evidence of two new species. Journal of Bacteriology109:209–217.
Seidler, R. J., Starr, M. P. 1968. Structure of the flagellum ofBdellovibrio bacteriovorus. Journal of Bacteriology95:1952–1955.
Starr, M. P. 1975. A generalized scheme for classifying organismic associations. Symposia of the Society for Experimental Biology24:1–20.
Starr, M. P. 1975.Bdellovibrio as symbiont: The association of bdellovibrios with other bacteria interpreted in terms of a generalized scheme for classifying organismic associations. Symposia of the Society for Experimental Biology24:93–124.
Starr, M. P., Baigent, N. L. 1966. Parasitic interaction ofBdellovibrio bacteriovorus with other bacteria. Journal of Bacteriology91:2006–2017.
Starr, M. P., Seidler, R. J. 1971. The bdellovibrios. Annual Review of Microbiology25:649–678.
Starr, M. P., Stolp, H. 1976.Bdellovibrio methodology. Methods in Microbiology9:217–244.
Stolp, H. 1973. The bdellovibrios: Bacterial parasites of bacteria. Annual Review of Phytopathology11:53–76.
Stolp, H., Starr, M. P. 1963.Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus gen. et sp. n., a predatory, ectoparasitic, and bacteriolytic microorganism. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek29:217–248.
Wanka, F., Schrauwen, P. J. A. 1971. Selective inhibition by cycloheximide of ribosomal RNA synthesis in chlorella. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta254:237–240.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Coder, D.M., Starr, M.P. Antagonistic association of the chlorellavorus bacterium (“Bdellovibrio” chlorellavorus) withChlorella vulgaris . Current Microbiology 1, 59–64 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02601710
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02601710