Abstract
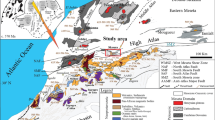
A brief account is presented for the Lebombo volcanic succession which crops out in Natal, South Africa. The volcanic belt is of late Karoo age and is composed of a thick sequence of basaltic lavas (Sabie River Formation) overlain by an equally voluminous succession of acid-flows (Jozini Formation) erupted over a period of about 70 m.y. Field relationships indicate that the Lebombo basalt pile consists of simple and compound flow units. The rhyolite succession consists of thick (80–284 m) flows units characterised by features found in both ignimbrites and rhyolitic lavas respectively. It is postulated that they were extruded as high temperature, low volatile pyroclastic flows. The Bumbeni volcanic complex which crops out near the southern termination of the Lebombo mountains, disconformably overlies the Jozini Formation and is characterised by a suite of rocks that includes rhyolite lavas, air-fall and ash-flow tuffs, syenite intrusions and basic-intermediate lavas. Dolerite dykes are ubiquitous throughout the succession and an extremely dense concentration of basic intrusions located along the western margin of the belt gives rise to the Rooi Rand dyke swarm. Rare sill-forms are found associated with the mafic volcanies. Acid intrusives are represented by simple and composite quartz-porphyry intrusions and rhyolite dykes. The structure of the Lebombo is that of a faulted monocline, tilted to the east, developed prior to the fragmentation of eastern Gondwanaland. The volcanic belt is located at the tectonic contact between two major Precambrian elements, the 3,000 m.y. Kaapvaal craton to the west and the southerly extension of the 550 m.y. Mozambique belt to the east. It is bounded to the south by the 1,000 m.y. old Natal-Namaqua mobile belt.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allsopp, H. L., Bristow, J. W., Manton, W. I. andCleverly, R. W., 1981,Rb-Sr Geochronology of the Lebombo Volcanism Geokong. 81, Abstr. 19 tb Cong. Geol. Soc. S. Afr.
Agashe, L. V. andGupte, R. B., 1972,Mode of Eruption of the Decean Trap Basalts. Bull. Vulcanol.,35, p. 501–601.
Anderson, W.A., 1904,Second Report of the Geological Survey of Natal and Zululand. Surv. Gen. Dept., Natal. West, Newman and Co., London, 169 pp.
Armstrong, R. A., 1978,A Geological and Geochemical Appraisal of the Rooi Rand Dyke Swarm. M. Sc. thesis (unpubl.), Univ. Natal, 135 pp.
-----,Bristow, J. W. andCox, K. G., 1983.The Geochemistry and Petrogenesis of the Rooi Rand Dyke Swarm. Trans. Geol. Soc. S. Afr., Spec. Publ., in preparation.
Betton, P. J., 1978,Geochemistry of Karoo Volcanic Rocks in Swaziland. D.Phil. thesis (unpubl.), Univ. Oxford.
Boyd, F. R., 1961,Welded Tuffs and Flows in the Rhyolite Plateau of Yellowstone Park, Wyoming. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull.,72, p. 387–426.
Bristow, J. W., 1976,The Geology and Geochemistry of the Southern Lebombo. M.Sc. thesis (unpubl.), Univ. Natal, 331 pp.
—————, 1978,Petrographic and Chemical Trends in Relation to the Eruptive Mode of Southern Lebombo Acid Flows. Petros,8, p. 20–25.
-----, 1980,The Geochronology and Geochemistry of Karoo Volcanics in the Lebombo and Adjacent Areas. Ph.D. Thesis (unpubl.), Univ. Cape Town, 257 pp., appendices 74 pp.
----- andCleverly, R. W., 1979,Volcanology of the Lebombo Rhyolites. Geokong. 79, 18th Cong. Geol. Soc. S.Afr., p. 60–63.
----- andSaggerson, E. P. Intrusive Rocks of the Lebombo and Their Relationship to the Structural Evolution of the Volcanic Belt. In preparation.
Cleverly, R. W., 1977,The Structural and Magmatic Evolution of the Lebombo Monocline, Southern Africa, with particular Reference to Swaziland. D. Phil. thesis (unpubl.), Univ. Oxford.
—————, 1978,The Lebombo Rhyolites: Ignimbrites or Lavas? Petros,8, p. 12–14.
————— andBristow, J. W., 1979,Revised Volcanic Stratigraphy of the Lebombo Monocline. Trans. geol. Soc. S.Afr.,82 (2), p. 227–230.
Cox, K. G., 1970,Tectonics and Volcanism of the Karoo Period, and Their Bearing on the Postulated Fragmentation of Gondwonaland. In:Clifford, T. N. andGass, I. D., Eds.,African Magmatism and Tectonics. Oliver and Boyd, Edinburgh, p. 211–236.
—————, 1972,Karoo Lavas and Associated Igncous Rocks of Southern Africa. Bull. Volcanol.,35, p. 867–886.
————— andVail, J. R., 1965,The Geology of the Nuanetsi Igneous Province. Phil. Trans. Roy. Soc. Lond.,257, p. 71–218.
De Toff, A. L., 1929,The Volcanic Belt of the Lebombo: a Region of Tension. Trans. Roy. S.Afr.,18, p. 189–218.
Gibson, I. L., 1970,A Pantelleritic Welded Ash-flow Rift from the Ethiopian Rift Valley. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol.,28, p. 89–111.
Guest, J. E., 1969,Upper Tertiary Ignimbrites in the Andean Cordillera of Port of Antofagasta Province, Northern Chile. Bull. Geol. Soc. Am.,80, p. 337–362.
Halbich, I. W. andCornell, D. H.,Metamorphic Zoning in the Cape Fold Belt. In the press.
Hawthorne, J. B., Carrington, A. J., Clement, C. R. andSkinner, E. W., 1979,Geology of the Dokolwayo Kimberlite and Associated Paleoalluvial Diamond Deposits, p. 59–70. In:Boyd, F. R. andMeyer, H. O. A., Eds.,Kimberlite Diatremes and Diamonds. Proc. Second Int. Kimb. Conf. 1.
Kennedy, W. J. andKlinger, H. C., 1972,Hiatus Concretions and Hardground Horizons in the Cretaceous of Zululand. Palaeontology,15, p. 539–549.
King, L. C., 1970,The Geology of the Hluhluwe Game Reserve. Petros,2, p. 16–19.
Klinger, H. C., 1976,Cretaceous Heteromorph Ammonites from Zululand. Mem. Geol. Surv. S.Afr.,69, 142 pp.
Liu, H. S., 1980,Convection Generated Stress Field and Intra-plate Volcanism. Tectonophysics,65, p. 225–244.
Lock, B. E., 1972,A Lower-Paleozoic Rheoignimbrite from White-Bay, Newfoundland. Can. J. Earth Sci.,9, p. 1495–1503.
————— andBroderick, T. J., 1974,Stratigraphy of the Karoo Volcanic Rocks of the Barkley East District. Trans. geol. Soc. S.Afr.,55, p. 175–198.
Lombard, B. V., 1952,Karoo Dolerites and Lavas. Trans. geol. Soc. S.Afr.,55, p. 175–198.
Maud, R. R., 1962,The Structure and Possible Origin of the Coast of Natal. Ph.D. thesis (unpubl.), Univ. Natal, 266 pp.
Monkman, L. J., 1961,The Geology of the Maose-Malibaugwe River Basin, with Special Reference to the Stormberg Vulcanicity of Southern Rhodesia. Ph.D. thesis (unpubl.), Univ. Leeds.
Myers, J. S., 1980,Structure of the Coastal Dyke Swarm and Associated Plutonic Intrusions of East Griqualand. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett.,46, p. 407–418.
Rhodes, R. C., 1970,Volcanic Rocks Associated with the Western Part of the Mogollan Plateau Volcano-tectonic Complex, Southwestern New Mexico. Ph.D. thesis (unpubl.), Univ. New Mexico.
Rittmann, A., 1962,Volcanoes and Their Activity. Interscience Publishers, New York.
Ross, C. S. andSmith, R. L., 1961,Ash Flow Tuffs: Their Origin, Geologic Relations and Identification. Geol Soc. Am. Prof. Paper366, 81 pp.
Rutten, M. G. andVan Everdingen, R. O., 1961,Rheoignimbrites of the Rammes Volcano, Peruvian, Oslo Graben. Geol. Mjinb.,40, p. 49–57.
Saggerson, E. P. andLogan, C. T., 1970,Distribution controls of Layered and Differentiated Intrusions in the Lebombo Volcanic Subprovince. Geol. Soc. S.Afr. Spec. Publ.,1, p. 721–733.
Schmincke, H. U., 1974,Volcanological Aspects of Peralkaline Silicic Welded Ashflow Tuffs. Bull. Volcanol.,38, p. 549–631.
Scrutton, R. A. andDingle, R. V., 1976,Observations in the Processes of Sedimentary Basin Formation at the Margins of Southern Africa. Tectonophysics,36, p. 143–156.
Smith, R. L., 1960,Ash-flows. Bull. Geol. Soc. Am.,71, p. 795–842.
Sparks, R. S. J., 1975.Stratigraphy and Geology of the Ignimbrites of Vulsini Volcano, Central Italy. Geol. Rundsch.,64, p. 497–523.
—————, andWilson, L., 1976,A Model for the Formation of Ignimbrite by Gravitational Column Collapse. J. Geol. Soc. Lond.,132, p. 441–451.
————— andWalker, G. P. L., 1973,Products of Ignimbrite Eruptions. Geol.,1, p. 115–118.
Stockley, G. M., 1947,Report on the Geology of Basutoland. Basutoland Gov. Printer, Maseru.
Stratten, T., 1965,The Pyroclastic and Associated Igneous Rocks of the Lebombo Mountain Range, South of the Great Usutu River, Zululand. M.Sc. thesis (unpubl.), Univ. Potchefstroom.
—————, 1970,Late Karoo Igneous Rocks of the Southern Lebombo Mountain Range, p. 441–445. In:Haughton, S. H., Ed.,Proceedings and Papers, 2nd Gondwana Symposium. CSIR, Pretoria, 689 pp.
Tazieff, H., 1970,Mechanisms of Ignimbrite Eruption. In:Newall, G. andRast, N., Eds.,Mechanisms of Igneous Intrusion. Gallery Press, Liverpool.
Tyndale-Biscoe, R. M., 1949,Notes on a Geological Reconnaissance of the Country East of Beitbridge, Southern Rhodesia. Trans. geol. Soc. S.Afr.,52, p. 403–413.
Tyrrell, G. W., 1937,Flood Basalts and Fissure Eruptions. Bull. Volcanol., 1, p. 94–99.
Urie, J. G. andHunter, D. R., 1963,The Geology of the Stormberg Volcanics. Bull. Geol. Surv. Swaziland,3, p. 28–44.
Van wyk, W.L., 1963,Ground-Water Studies in Northern Natal, Zululand and Surrounding Areas. Geol. Surv. S.Afr. Mem.,52, 135 pp.
Wachendorf, H., 1971,Die rhyolite und Basalte der Lebombos in hinterland van Lourenco Marques (Mocambique). Getekt, Forsch.,40, p. 1–86.
Wachendorf, H., 1973,The Rhyolitic Flows of the Lebombos (S.E. Africa). Bull. Volcanol.,37, p. 515–529.
Wager, L. R. andDeer, W. A., 1938,A Dyke Swarm and Crustal Flexure in East Greenland. Geol. Mag.,75, p. 39–46.
Walker, G. P. L., 1959,Some Observations on the Antrim Basalts and Associated Dolerite Intrusions. Proc. Geol. Assoc.,70, p. 179–205.
Wheelock, G., 1979,The Geochemical Distribution of Zeolites from Basalts of the Mfolozi Formation. Petros,8, p. 6–11.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saggerson, E.P., Bristow, J.W. The geology and structural relationships of the southern Lebombo volcanic and intrusive rocks, South Africa. Bull Volcanol 46, 161–181 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02597583
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02597583