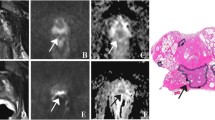
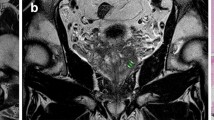
Abstract
The purpose of this study was to determine whether endorectal coil magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) enables accurate assessment of pathologic tumor volume in patients with clinically localized prostate carcinoma. Twenty-four patients with biopsy-proved prostate carcinoma underwent MRI at 0.5 T before radical prostatectomy. Tumor volumes were determined independently on axial fast-spin-echo (SE) T2-weighted MR images and whole-mount pathology slides of the surgical specimens. At pathology, tumor volumes ranged from 0.17 to 9.42 cm3 (mean±SD, 3.11±2.99 cm3). A strong correlation (r=.944) was found between measurements of tumor volume based on MR images and pathological specimens. The error was less than 0.5 cm3 in 14 cases, in the range of 0.5–1 cm3 in 7 cases, and more than 1 cm3 in 3 cases. By using an MR tumor volume of 2 cm3 as cutoff value, extracapsular tumor spread could be predicted with a sensitivity of 81.2%, a specificity of 100%, and an accuracy of 87.5%. Tumor volume determinations based on MR images seem to be accurate enough to be helpful in clinical decision-making.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
McNeal JE, Villers AA, Redwine EA, Freiha FS, Stamey TA (1990) Histologic differentiation, cancer volume, and pelvic lymph node metastasis in adenocarcinoma of the prostate.Cancer 66: 1225–1233.
McNeal JE (1991) Cancer volume and site of origin of adenocarcinoma in the prostate: relationship to local and distant spread.Hum Pathol 23: 258–266.
Stamey TA, Freiha FS, McNeal JE, Redwine EA, Whittemore AS, Schmid HP (1993) Localized prostate cancer: relationship of tumor volume to clinical significance for treatment of prostate cancer.Cancer 71: 933–938.
Spigelman SS, McNeal JE, Freiha FS, Stamey TA (1986) Rectal examination in volume determination of carcinoma of the prostate: clinical and anatomical correlations.J Urol 126: 1228–1230.
Palken M, Cobb OE, Warren BH, Hoak DC (1990) Prostate cancer: correlation of digital rectal examination, transrectal ultrasound, and prostate specific antigen levels with tumor volumes in radical prostatectomy specimens.J Urol 143: 1155–1161.
McSherry SA, Levy F, Schiebler ML, Keefe B, Dent GA, Mohler (1991) Preoperative prediction of pathological tumor volume and stage in clinically localized prostate cancer: comparison of digital rectal examination, transrectal ultrasonography, and magnetic resonance imaging.J Urol 146: 85–89.
Quint LE, Van Erp JS, Bland PH, Mandel SH, Del Buono EA, Grossman HB, Glazer GM, Gikas PW (1991) Carcinoma of the prostate: MR images obtained with body coils do not accurately reflect tumor volume.AJR Am J Roentgenol 156: 511–516.
Sommer FG, Nghiem HV, Herfkens R, McNeal J, Low RN (1993) Determing the volume of prostatic carcinoma: value of MR imaging with an external-array coil.AJR Am J Roentgenol 161: 81–86.
Humphrey PA, Baty J, Keetch D (1995) Relationship between serum prostate specific antigen, needle biopsy findings, and histopathologic features of prostatic carcinoma in radical prostatectomy tissues.Cancer 75: 1842–1849.
Martin JF, Hajek P, Baker L, Gylys-Morin V, Fitzmorris-Glass R, Mattrey RR (1988) Inflatable surface coil for MR imaging of the prostate.Radiology 167: 268–270.
Schnall MD, Lenkinski RE, Pollack HM, Imai Y, Kressel HY (1989) Prostate: MR imaging with an endorectal surface coil.Radiology 172: 570–574.
Schnall MD, Imai Y, Tomaszewski J, Pollack HM, Lenkinski RE, Kressel HY (1991) Prostate cancer: local staging with endorectal surface coil MR imaging.Radiology 178: 797–802.
Schiebler ML, Schnall MD, Pollack HM, Lenkinski RE, Tomaszewski JE, Wein AJ, Whittington R, Rauschning W, Kressel HY (1993) Current role of MR imaging in the staging of adenocarcinoma of the prostate.Radiology 189: 339–352.
Quinn SF, Franzini DA, Demlow TA, Rosencrantz DR, Kim J, Hanna RM, Szumowski J (1994) MR imaging of prostate cancer with an endorectal surface coil technique: correlation with whole-mount specimens.Radiology 190: 323–327.
Tempany CM, Zhou X, Zerhouni EA, Rifkin MD, Quint LE, Piccoli CW, Ellis JH, McNeil BJ (1994) Staging of prostate cancer: results of radiology diagnostic oncology group project comparison of three MR imaging techniques.Radiology 192: 47–54.
Outwater EK, Petersen RO, Stegelman ES, Gomella LG, Chernesky CE, Mitchell DG (1994) Prostate carcinoma: assessment of diagnostic criteria for capsular penetration on endorectal coil MR images.Radiology 193: 333–339.
Huch Böni RA, Boner JA, Lütolf UM, Trinkler F, Pestalozzi DM, Krestin GP (1995) Contrast-enhanced endorectal coil MRI in local staging of prostate carcinoma.J Comput Assist Tomogr 19: 232–237.
White S, Hricak H, Forstner R, Kurhanewicz J, Vigneron DB, Zaloudek CJ, Weiss JM, Narayan P, Carroll PR (1995) Prostate cancer: effect of postbiopsy hemorrhage on interpretation of MR images.Radiology 195: 385–390.
Bartolozzi C, Menchi I, Lencioni R, Serni S, Lapini A, Barbanti G, Bozza A, Amorosi A, Manganelli A, Carini M (1996) Local staging of prostate carcinoma with endorectal coil MRI: correlation with whole-mount radical prostatectomy specimens.Eur Radiol 6: 339–345.
UICC International Union against Cancer (1992)TNM atlas, 3rd ed, 2nd rev. pp 241–250. Berlin: Springer-Verlag.
Silvery E, Boring CC, Squires TS (1990) Cancer facts and figures.CA Cancer J Clin 40: 12–15.
Chiarodo A (1991) National Cancer Institute roundtable on prostate cancer: future directions.Cancer Res 51: 2498–2505.
Steinfeld AD (1992) Questions regarding the treatment of localized prostate cancer.Radiology 184: 593–598.
Walsh PC, Lepor H (1989) The role of radical prostatectomy in the management of prostatic cancer.Cancer 60:(Suppl 3): 526–237.
Heiken JP, Forman HP, Brown JJ (1994) Neoplasms of the bladder, prostate, and testis.Radiol Clin North Am 32: 81–98.
McNeal JE, Villers AA, Redwine EA, Freiha FS, Stamey TA (1990) Capsular penetration in prostate cancer: significance for natural history and treatment.Am J Surg Pathol 14: 240–247.
Villers AA, McNeal JE, Redwine EA, Freiha FS, Stamey TA (1990) Pathogenesis and biological significance of seminal vesicle invasion in prostatic adenocarcinoma.J Urol 143: 1183–1187.
McNeal JE, Kindrachuk RA, Freiha FS, Bostwick DG, Redwine EA, Stamey TA (1986) Patterns of progression in prostate cancer.Lancet 1: 60–63.
Stamey TA, McNeal JE, Freiha FS, Redwine EA (1988) Morphometric and clinical studies on 68 consecutive radical prostatectomies.J Urol 139: 1235–1241.
Mirowitz SA, Brown JJ, Heiken JP (1993) Evaluation of the prostate and prostatic carcinoma with gadolinium-enhanced endorectal coil MR imaging.Radiology 186: 153–157.
Schnall MD, Bezzi M, Pollack HM, Kressel HY (1990) Magnetic resonance imaging of the prostate.Magn Reson Q 6: 1–16.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lencioni, R., Menchi, I., Paolicchi, A. et al. Prediction of pathological tumor volume in clinically localized prostate cancer: value of endorectal coil magnetic resonance imaging. MAGMA 5, 117–121 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02592242
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02592242