Summary
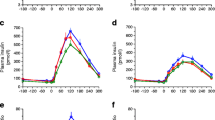
Plasma glucose, insulin and C-peptide responses to a test meal were studied in 7 nonobese patients with type II diabetes mellitus (NIDDM) treated with diet alone and after 6 months of gliclazide therapy, as well as in 6 matched controls. The glycemic levels were significantly higher (p<0.05) in patients under diet alone than in controls and after gliclazide treatment (peak: 12.8±1.0; 7.9±0.4 and 10.0±0.5 mmol/l, respectively;\(\bar x\)±SEM). Diet and gliclazide treated patients showed a reduced B-cell response during the first hour after the meal as indicated by insulin and C-peptide values and areas (insulin areas 0–60 min: controls 57.9 ± 10.9; p<0.01vs diet alone 14.2 ± 2.7 andvs gliclazide 22.1 ± 2.8 µU/ml/min). The hypoinsulinemic phase lasted from 20 to 60 min before gliclazide, and from 20 to 45 min after gliclazide. The first significant C-peptide increase, detected at 10 min in controls and at 30 min under diet alone, was advanced to 15 min after gliclazide treatment. In conclusion: patients with mild, diet-treated NIDDM show a sluggish and attenuated B-cell response to a physiologic challenge (test meal); this secretory impairment is present even after a complete post-prandial glycemic normalization, supporting the idea of a persistent defect. Nevertheless, the slight improvement observed in insulin secretion after gliclazide treatment may be promoting, at least partially, the normalization of prandial hyperglycemia. The benefits of this normalization in diabetic patients previously controlled by diet only await further investigation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Buysschaert M., Marchand E., Grigorescu F., De Metys P., Ketelslegers J. M., Lambert A. E.: Effect of gliclazide on insulin effectiveness and insulin binding to erythrocyte in Type 2 (non-insulin-dependent) diabetic patients — Diabetologia23, 159, 1982; abstract # 48.
Calles-Escandon J., Robbins D. C.: Loss of early phase of insulin release in humans impairs glucose tolerance and blunts thermic effect of glucose — Diabetes36, 1167, 1987.
DeFronzo R. A., Ferrannini E., Koivisto V.: New concepts in the pathogenesis and treatment of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus — Amer. J. Med.74, 52, 1983.
Dimitriadis G., Cryer P., Gerich J.: Prolonged hyperglycaemia during infusion of glucose and somatostatin impairs pancreatic A- and C-cell responses to decrements in plasma glucose in normal man: evidence for induction of altered sensitivity to glucose — Diabetologia28, 63, 1985.
Efendic S., Luft R., Wajngot A.: Aspects of the pathogenesis of Type 2 diabetes — Endocrinol. Rev.5, 395, 1984.
Elkeles R. S., Heding L. G., Paisley R. B.: The long-term effects of chlorpropamide on insulin, C-peptide, and proinsulin secretion — Diabet. Care5, 427, 1982.
Greenfield M. S., Doberne L., Rosenthal M., Schultz B., Windstrom A., Reaven G. M.: Effect of sulfonylurea treatment onin vivo insulin secretion and action in patients with noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus — Diabetes31, 307, 1982.
Halter J. B., Graf R. J., Porte D. Jr.: Potentiation of insulin secretory responses by plasma glucose levels in man: evidence that hyperglycemia in diabetes compensates for impaired glucose potentiation — J. clin. Endocrinol.48, 946, 1979.
Holman R. R., Turner R. C.: Maintenance of basal plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in maturity-onset diabetes — Diabetes28, 227, 1979.
Kolterman O. G., Gray R. S., Griffin J., Burnstein P., Insel J., Scarlett J. A., Olefsky J. M.: Receptor and post-receptor defects contribute to the insulin resistance in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus — J. clin. Invest.68, 957, 1981.
Kolterman O. G., Olefsky J. M.: The impact of sulfonylurea treatment upon the mechanisms responsible for the insulin resistance in type II diabetes — Diabet. Care7 (Suppl. 1), 81, 1984.
Liu G., Coulston A., Chen Y.-D. I., Reaven G. M.: Does day-long absolute hypoinsulinemia characterize the patient with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus? — Metabolism32, 754, 1983.
Mandarino L. J., Gerich J. E.: Prolonged sulfonylurea administration decreases insulin resistance and increases insulin secretion in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: evidence for improved insulin action at a postreceptor site in hepatic as well as extrahepatic tissues — Diabet. Care7 (Suppl. 1), 89, 1984.
National Diabetes Data Group: Classification and diagnosis of diabetes mellitus and other categories of glucose intolerance — Diabetes28, 1039, 1979.
Pfeifer M. A., Graf R. J., Halter J. B., Porte D. Jr.: The regulation of glucose-induced insulin secretion by pre-stimulus glucose level and tolbutamide in normal man — Diabetologia21, 198, 1981.
Pfeifer M. A., Halter J. B., Porte D. Jr.: Insulin secretion in diabetes mellitus — Amer. J. Med.70, 579, 1981.
Reaven G. M.: Insulin secretion and insulin action in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: which defect is primary? — Diabet. Care7 (Suppl. 1), 17, 1984.
Reaven G. M., Shen S. W., Silvers A., Farquhar J. W.: Is there a delay in the plasma insulin response of patients with chemical diabetes mellitus? — Diabetes20, 416, 1971.
Scarlett J. A., Gray R. S., Griffin J., Olefsky J. M., Kolterman O. G.: Insulin treatment reverses the insulin resistance of type II diabetes mellitus — Diabet. Care5, 353, 1983.
Turner R. C., Mc Carthy S. T., Holman R. R., Harris E.: Beta-cell function improved by supplementary basal insulin secretion in mild diabetes — Brit. med. J.i, 1252, 1971.
Varsano-Aharon N., Echemendia E., Yalow R. S., Berson S. A.: Early insulin responses to glucose and to tolbutamide in maturity-onset diabetes — Metabolism19, 409, 1970.
Ward W. K., Beard J. C., Halter J. B., Pfeifer M. A., Porte D. Jr.: Pathophysiology of insulin secretion in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus — Diabet. Care7, 491, 1984.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sinay, I.R., Arias, P., Schnitman, M.A. et al. Diet only or diet and sulfonylureas in mild type II diabetes (niddm)? Pathophysiologic and therapeutic implications. Acta diabet. lat 25, 289–297 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02581127
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02581127