Abstract
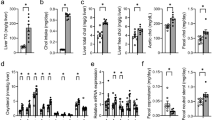
Sterol balance studies, using both isotopic and chromatographic techniques, were carried out in hamsters fed semipurified diets to detect changes in sterol metabolism during the early period of the lithogenic stimulus. The balance studies examined animals in the first two weeks on the experimental lithogenic diets. The variables were as follows: dose of cholesterol (group 1, 0.05% vs. group 2, 0.2%); dietary fat (fatty acid) (group 2, butterfat vs. group 4, palmitic acid); source of hamster [group 2, Sasco (Omaha, NE) vs. group 3, Charles River (Wilmington, MA)]; average weight of animals (group 4, 60 g vs. group 5, 119 g). Animals in groups 1, 2, 3 and 5 maintained almost constant weight throughout the two-week balance study. Liver and plasma cholesterol levels increased in groups 2–5 with increasing dose of dietary cholesterol. The highest levels were found in group 4 (liver cholesterol, 32.7 mg/g; plasma cholesterol, 367 mg/dL). Sterol balance measurements showed that bile acid synthesis remained low (range 0.55–1.01 mg/d) for all groups regardless of the intake of dietary cholesterol (range, 3.27–20.90 mg/d). The dietary cholesterol absorbed from the intestine (range, 2.91–18.91 mg/d) was stored in the liver; this storage was reflected in the negative values for cholesterol balance for all groups (range, −0.70 to −14.97 mg/d). These studies did not reveal any correlations between parameters of sterol balance and cholelithiasis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- GLC:
-
gas-liquid chromatography
- PAD:
-
palmitic acid diet
- SPD:
-
semipurified diet
References
Carey, M.C., and Small, D.M. (1978)J. Clin. Invest. 61, 998–1026.
Redinger, R.N., and Small, D.M. (1972)Arch. Int. Med. 130, 618–630.
Thistle, J., and Schoenfield, L.J. (1971)N. Engl. J. Med. 184, 177–181.
Fromm, H. (1986)Gastroenterology 91, 1560–1567.
Vlahcevic, Z.R., Bell, Jr., C.C., Buhac, I., Farrar, J.T., and Swell, L. (1978)Gastroenterology 59, 165–173.
Pomare, E.W., and Heaton, K.W. (1973)Gut 14, 885–890.
Metzger, A.L., Alder, R., Heymsfield, S., and Grundy, S.M. (1973)N. Engl. J. Med. 288, 333–336.
Williams, N.C., Morse, J.W.I., MacDonald, I.A., Katoor, R., and Riding, M.D. (1977)Am. J. Dig. Dis. 22, 189–194.
Holzbach, R.T., Marsh, M., Olszewski, M., and Holan, K. (1973)J. Clin. Invest. 52, 1467–1479.
Cohen, B.I., Matoba, N., Mosbach, E.H., and McSherry, C.K. (1989)Lipids 24, 151–156.
Cohen, B.I., Matoba, N., Mosbach, E.H., Ayyad, N., Hakam, K., Suh, S.O., and McSherry, C.K. (1990)Gastroenterology 98, 397–405.
Cohen, B.I., Mosbach, E.H., Ayyad, N., Miki, S., and McSherry, C.K. (1992)Lipids 27, 526–532.
Ayyad, N., Cohen, B.I., Mosbach, E.H., and Miki, S. (1992)Lipids 27, 993–998.
Dam, H. (1971)Am. J. Med. 51, 596–613.
Grundy, S.M., Ahrens, Jr., E.H., and Miettinen, T.A. (1965)J. Lipid Res. 6, 397–410.
Quintão, E., Grundy, S.M., and Ahrens, Jr., E.H. (1971)J. Lipid Res. 12, 221–232.
Cohen, B.I., Raicht, R.F., and Mosbach, E.H. (1974)Lipids 9, 1024–1029.
Cohen, B.I., Raicht, R.F., Shefer, S., and Mosbach, E.H. (1974)Biochim. Biophys. Acta 369, 79–85.
Raicht, R.F., Cohen, B.I., Shefer, S., and Mosbach, E.H. (1975)Biochim. Biophys. Acta 388, 374–384.
Grundy, S.M., and Ahrens, Jr., E.H. (1969)J. Lipid Res. 10, 91–107.
Miettinen, T.A., Ahrens, Jr., E.H., and Grundy, s.M. (1965)J. Lipid Res. 6, 411–424.
Kim, D.N., Lee, K.T., Reiner, J.M., and Thomas, W.A. (1974)J. Lipid Res. 15, 326–331.
Singhal, A.K., Finver-Sadowsky, J., McSherry, C.K., and Mosbach, E.H. (1983)Biochim. Biophys. Acta 752, 214–222.
Snedecor, C.W. (1948) inStatistical Methods, pp. 54–81 and 182–184, Iowa State College Press, Ames.
Singhal, A.K., Ayengar, N.K.N., May, P.S., McSherry, C.K., and Mosbach, E.H. (1983) inDietary Fats and Health (Perkins, E.G., and Visek, W.J., eds.) pp. 267–277, American Oil Chemists' Society, Champaign.
Ayyad, N., Cohen, B.I., Mosbach, E.H., Miki, S., Mikami, T., Mikami, Y., and Stenger, R.J. (1993)Lipids 28, 981–986.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Cohen, B.I., Ayyad, N., Mikami, T. et al. Effects of dietary fat and fatty acids on sterol balance in hamsters. Lipids 29, 503–508 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02578248
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02578248