Abstract
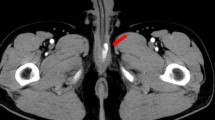
A 22-year-old man suffered a hiking accident with perineal trauma and developed a nonpainful priapism secondary to bilateral arterial-cavernosal fistulas. To minimize the risk of impotence in this young patient, successive selective embolizations with autologous blood clot were performed to close the fistulas. This led to an uncomplicated full recovery. No fistula was detectable on Doppler ultrasonography at 1-year follow-up. Review of the literature confirms the safety of embolization with autologous clot.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ming-Xian J, Neng-Shu H, Ping W, Gui C (1994) Use of selective embolization of the bilateral cavernous arteries for posttraumatic arterial priapism. J Urol 151:1641–1642
Burt FB, Schirmer HK, Scott WW (1960) A new concept in the management of priapism. J Urol 83:60–61
Wheeler GW, Simmons CR (1973) Angiography in post-traumatic priapism: A case report. Am J Roentgenol 119:619–620
Hauri D, Spycher M, Brühlmann W (1983) Erection and priapism: A new physiopathological concept. Urol Int 38:138–145
Ricciardi R Jr, Bhatt GM, Cynamon J, Bakal CW, Melman A (1993) Delayed high flow priapism: Pathophysiology and management. J Urol 149:119–121
Brock G, Breza J, Lue TF, Tanagho EA (1993) High flow priapism: A spectrum of disease. J Urol 150:968–971
McLeod RE, Clayden GR, Bonnell G (1981) Post-traumatic priapism: Successful treatment by percutaneous catheter embolization. J Can Assoc Radiol 32:238–239
Steers WD, Selby JB Jr (1991) Use of methylene blue and selective embolization of the pudendal artery for high flow priapism refractory to medical and surgical treatments. J Urol 146: 1361–1363
Gonzalez EA, Pamplona M, Rodriguez A, Garcia-Hidalgo E, Nunez V, Leiva O (1994) High flow priapism after blunt perineal trauma: Resolution with bucrylate embolization. J Urol 151:426–428
Wear JB Jr, Crummy AB, Munson BO (1977) A new approach to the treatment of priapism. J Urol 117:252–254
Carmignani G, Belgrano E, Puppo P, Cichero A, Quattrini S (1980) Idiopathic priapism successfully treated by unilateral embolization of internal pudendal artery. J Urol 124:553–554
Crummy AB, Ishizuka J, Madsen PO (1979) Posttraumatic priapism: Successful treatment with autologous clot embolization. Am J Roentgenol 133:329–330
Puppo P, Belgrano E, Quattrini S, Fabbro V, Repetto U, Giuliani L (1983) Treatment of priapism by transcatheter embolization of internal pudendal arteries. Urol Radiol 5:261–265
Belgrano E, Puppo P, Quattrini S, Trombetta C, Bottino P, Giuliani L (1984) Percutaneous temporary embolization of the internal pudendal arteries in idiopathic priapism: 2 additional cases. J Urol 131:756–758
Witt MA, Goldstein I, Saenz de Tejada I, Greenfield A, Krane RJ (1990) Traumatic laceration of intracavernosal arteries: The pathophysiology of nonischemic, high flow, arterial priapism. J Urol 143:129–132
Visvanathan K, Burrows PE, Schillinger JF, Khoury AE (1992) Posttraumatic arterial priapism in a 7-year-old boy: Successful management by percutaneous transcatheter embolization. J Urol 148:382–383
Bastuba MD, Saenz de Tejada I, Dinlenc CZ, Sarazen A, Krane RJ, Goldstein I (1994) Arterial priapism: Diagnosis, treatment and long-term followup. J Urol 151:1231–1237
Schwartz AN, Wang KY, Mack LA, Lowe M, Berger RE, Cyr DR, Feldman M (1989) Evaluation of normal erectile function with color flow Doppler sonography. Am J Roentgenol 153:1155–1160
Saenz de Tejada I, Goldstein I, Krane RJ (1988) Local control of penile erection: Nerves, smooth muscle, and endothelium. Urol Clin North Am 15:9–15
Saenz de Tejada I, Blanco R, Goldstein I, Azadzoi K, de las Morenas A, Krane RJ, Cohen RA (1988) Cholinergic neurotransmission in human corpus cavernosum. I. Responses of isolated tissue. Am J Physiol 254(3 Pt 2):H459-H467
Lue TF, Hellstrom WJ, McAninch JW, Tanagho A (1986) Priapism: A refined approach to diagnosis and treatment. J Urol 136:104–108
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lazinger, M., Beckmann, C.F., Cossi, A. et al. Selective embolization of bilateral arterial cavernous fistulas for posttraumatic penile arterial priapism. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 19, 281–284 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02577651
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02577651