Abstract
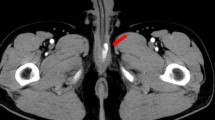
A patient with high-flow priapism was treated by transcatheter embolization of a posttraumatic left cavernosal arteriovenous fistula using N-butyl-cyanoacrylate (NBCA), resulting in complete detumescence. Erectile function has been preserved during a 3-month follow-up. Only two patients with NBCA embolization for high-flow priapism have been reported previously.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hauri D, Spycher M, Brühlmann W (1983) Erection and priapism: A new physiopathological concept. Urol Int 38:138–141
Burt FR, Schirmer HK, Scott WW (1960) A new concept in the management of priapism. J Urol 83:60–61
Witt MA, Goldstein I, De Tejada IS, Greenfield A, Krane RJ (1990) Traumatic laceration of intracavernosal arteries: The pathophysiology of nonischemic, high flow, arterial priapism. J Urol 143:129–134
Lue TF, Hellstrom WJG, McAninch JW, Tanagho EA (1986) Priapism: A refined approach to diagnosis and treatment. J Urol 136:104–108
Walker TG, Crant PW, Goldstein I, Krane RJ, Greenfield AJ (1990) “High-flow” priapism: Treatment with superselective transcatheter embolization. Radiology 174:1053–1056
Visvanathan K, Burrows PE, Schillinger JF, Khoury AE (1992) Posttraumatic arterial priapism in a 7-year-old boy: Successful management by percutaneous transcatheter embolization. J Urol 148:382–383
Ricciardi R, Bhatt GM, Cynamon J, Bakal CW, Melman A (1993) Delayed high flow priapism: Pathophysiology and management. J Urol 149:119–121
Brock G, Breza J, Lue TF, Tanagho EA (1993) High flow priapism: A spectrum of disease. J Urol 150:968–971
Wear JB, Crummy AB, Munson BO (1977) A new approach to the treatment of priapism. J Urol 117:252–254
Crummy AB, Ishizaka J, Madsen PO (1979) Posttraumatic priapism: Successful treatment with autologous clot embolization. AJR 133:329–332
Gudinchet D, Fournier D, Jichlinski P, Meyrat B (1992) Traumatic priapism in a child: Evaluation with color flow Doppler sonography. J Urol 148:380–383
Bastuba MD, De Tejada IS, Dinlenc CZ, Sarazen A, Krane RJ, Goldstein I (1994) Arterial priapism: Diagnosis, treatment and long-term followup. J Urol 151:1231–1237
Bookstein JJ (1988) Penile angiography: The last angiographic frontier. AJR 150:47–51
Wheeler GW, Simmons CR (1973) Angiography in posttraumatic priapism: A case report. AJR 119:619–620
Harding JR, Hollander JB, Bendick PJ (1993) Chronic priapism secondary to a traumatic arteriovenous fistula of the corpus cavernosum. J Urol 150:1504–1506
Carmignani G, Belgrano E, Puppo P, Cichero A, Quattrini S (1980) Idiopathic priapism successfully treated by unilateral embolization of internal pudendal artery. J Urol 124:553–556
McLeod RE, Clayden GR, Bonnell G (1981) Post-traumatic priapism: Successful treatment by percutaneous catheter embolization. J Can Assoc Radiol 32:238–240
Puppo P, Belgrano E, Quattrini S, Fabbro V, Rebetto U, Giuliani L (1983) Treatment of priapism by transcatheter embolization of internal pudendal arteries. Urol Radiol 5:261–263
Belgrano E, Puppo P, Quattrini S, Trombetta C, Bottino P, Giuliani L (1984) Percutaneous temporary embolization of the internal pudendal arteries in idiopathic priapism: 2 additional cases. J Urol 131:756–758
Steers WD, Selby JB (1991) Use of methylene blue and selective embolization of the pudendal artery for high flow priapism refractory to medical and surgical treatments. J Urol 146:1361–1363
Gonzalez EA, Pamplona M, Rodriguez A, Garcia-Hidalgo E, Nunez V, Levia O (1994) High flow priapism after blunt perineal trauma: Resolution with bucrylate embolization. J Urol 151:426–428
Ming-Xian J, Neng-Shu H, Ping W, Gui C (1994) Use of selective embolization of the bilateral cavernous arteries for posttraumatic arterial priapism. J Urol 151:1641–1642
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Numan, F., Çakirer, S., Işlak, C. et al. Posttraumatic high-flow priapism treated by N-butyl-cyanoacrylate embolization. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 19, 278–280 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02577650
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02577650