Summary
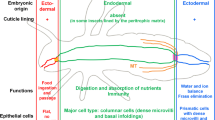
The number of insect midgut cells is maintained homeostatically in vivo and in vitro. However, during starvation, the midgut shrinks and the rate of cell replacement appears to be suppressed. When they undergo metamorphosis, the internal organs of insects are drastically remodeled by cell proliferation, differentiation, and apoptotic processes, and the net number of cells usually increases. An extract of 1650 midguts ofPeriplaneta americana was fractionated by highperformance liquid chromatography (HPLC) to obtain the peptides that regulate these processes. The HPLC fractions were tested for myotropic activity in the foregut and for effects on cell proliferation or loss in primary cultures of larvalHeliothis virescens midgut cells and in a cell line derived from the last-instar larval fat body ofMamestra brassicae. Some fractions stimulated midgut stem cell proliferation and differentiation, while others caused loss of differentiated columnar and goblet cells. Other fractions stimulated cell proliferation in the larval fat body cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Day, M. F.; Powning, R. F. A study of the processes of digestion in certain insects. Aust. J. Biol. Sci. 2:175–221; 1949.
Dow, J. A.; Harvey, W. R. Role of midgut electric K+pump potential difference in regulating lumen K+ and pH in larval Lepidoptera. J. Exp. Biol. 140:455–463; 1988.
Endo, Y.; Iwanaga, T.; Fujita, T., et al. Localization of pancreatic polypeptide (PP)-like immunoreactivity in the central and visceral nervous systems of the cockroachPeriplaneta. Cell Tissue Res. 227:1–9; 1982.
Ferkovich, S. M.; Oberlander, H. Growth factors in invertebrate in vitro culture. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. 27A:483–486; 1991.
Homma, K.; Matsushita, T.; Natori, S. Purification, characterization, and cDNA cloning of a novel growth factor from conditioned medium of NIH-Sape-4, an embryonic cell line ofSarcophaga perigrina (flesh fly). J. Biol. Chem. 271:13,770–13,775; 1996.
Kawamura, K.; Shibata, T.; Saget, O., et al. A new family of growth factors produced by the fat body and activate onDrosophila imaginal discs. Development 126:211–219; 1999.
Loeb, M. J.; Hakim, R. S. Insect midgut epithelium in vitro: an insect stem cell system. J. Insect Physiol. 42:1103–1111; 1996.
Loeb, M. J.; Hakim, R. S. Cultured midgut cells ofHeliothis virescens (Lepidoptera): fibronectin and integrin β 1 immunoreactivity during differentiation in vitro. Invertebr. Reprod. Dev. 35:95–102; 1999.
Loeb, M. J.; Hakim, R. S.; Martin, P., et al. Apoptosis in cultured cells fromHeliothis virescens larvae exposed to various conditions. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 45:12–23; 2000.
Loeb, M. J.; Jaffe, H.; Gelman, D. B., et al. Two polypeptide factors that promote differentiation of insect midgut stem cells in vitro. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 40:129–140; 1999.
Mitsuhashi, J.; Inoue, H. Obtainment of a continuous cell line from the larval fat bodies of the mulberry tiger moth,Spilosoma imparilis (Lepidoptera: Arctiidae). Appl. Entomol. Zool. 23:488–490; 1988.
Mitsuhashi, J.; Oshiki, T. Preliminary attempts to rear an endoparasitic fly, Exorista sorbilans (Diptera, Tachinidae) in vitro. Jpn J. Entomol. 61:459–464.
Neal, J. J.; Reuveni, M. Separation of cytochrome P-450 containing vesicles from the midgut microsomal fraction ofManduca sexta. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 102C:77–82; 1992.
Nishiitsutsuji-Uwo, J.; Endo, Y.; Takeda, M. Insect brain-midgut endocrine system: with special reference to paraneurons. In: Kobayashi, H., et al. ed. Neurosecretion and the biology of neuropeptides. New York: Springer; 1985:410–417.
Nishiitsutsuji-Uwo, J.; Endo, Y.; Takeda, M. Brain-gut peptides in the cockroach with special reference to midgut. In: Stefano, J., ed. CRC handbook of comparative opioid and related neuropeptide mechanisms. Vol. 2. New York: CRC Press, 1986:81–91.
Palli, S. R.; Locke, M. The synthesis of hemolymph proteins by the larval midgut of an insectCalpodes ethlius (Lepidoptera: Hesperiidae). Insect Biochem. 17:561–572; 1987.
Sehnal, F.; Zitnan, D. Endocrines of insect midgut. In: Progress in comparative endocrinology. New York: Wiley-Liss; 1990:510–515.
Strand, M. R.; Hayakawa, Y.; Clark, K. D. Plasmatocyte spreading peptide (PSP1) and growth blocking peptide (GBP) are multifunctional homologs. J. Insect Physiol. 46:817–824; 2000.
Takeda, M.; Yoshida, Y.; Endo, Y. Serotonin is “the midgut regeneration stimulating factor (MRSF)” inPeriplaneta. Physiol. Zool. 68:111; 1995.
Taylor, C. W. Calcium absorption by the midgut of the Blowfly,Calliphora vicina. J. Exp. Biol., 114:551–561; 1985.
Teo, L. H.; Woodring, J. P. The invertase of the house cricketAcheta domesticus L. (Orthoptera: Gryllidae). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 93B:643–646; 1989.
Valaitis, A.P. Gypsy moth midgut proteinases: purification and characterization of luminal trypsin, elastase, and the brush border membrane leucine aminopeptidase. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 25:139–149; 1995.
Valaitis, A. P.; Boweres, D. F. Purification and properties of the soluble midgut trehalase from the gypsy moth,Lymantria dispar. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 23:599–606; 1993.
Veenstra, J. A.; Lau, G. W.; Agricola, H.-J., et al. Immunohistological localization of regulatory peptides in the midgut of the female mosquitoAedes aegypti. Histochem. Cell Biol. 104:337–347; 1995.
Verhaert, P.; Huybrechts, R.; Schols, D., et al. Characterization of vertebrate peptide hormone-like materials in the American cockroach: different methods employed to investigate these substances and their results. In: Borkovec, D. B.; Gelman, A. B., ed. Insect neurochemistry and neurobiology. New Jersey: Humana Press; 1986:229–233.
Wagner, R. M.; Loeb, M. J.; Kochansky, J. P., et al. Identification and characterization of an ecdysiotropic peptide from brain extracts of the Gypsy moth,Lymantria dispar. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 34:175–189; 1997.
Weirich, G. Ecdysone 20-hydroxylation inManduca sexta (Lepidoptera: Sphingidae) midgut: development-related changes of mitochondrial and microsomal ecdysone 20-monooxygenase activities in the fifth larval instar. Eur. J. Entomol. 94:57–65; 1997.
Weirich, G.; Thompson, M. J.; Svoboda, J. A. In vitro ecdysteroid conjugation by enzymes ofManduca sexta midgut cytosol. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 3:109–126; 1986.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Mention of products in this article does not imply endorsement by the U.S. Department of Agriculture.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Takeda, M., Sakai, T., Fujisawa, Y. et al. Cockroach midgut peptides that regulate cell proliferation, differentiation, and death in vitro. In Vitro Cell.Dev.Biol.-Animal 37, 343–347 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02577568
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02577568