Abstract
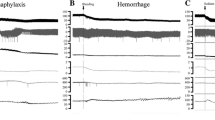
The role of substance P (SP) in cholesterol-induced anaphylactoid reaction was investigated in 13 Landrace pigs. Pigs were anesthetized with sodium thiopental and ventilation was controlled with 70% nitrous oxide in oxygen. A Swan-Ganz catheter and a carotid arterial line were placed to monitor the hemodynamic data. Group 1 pigs (control group,n=5) each received 20 ml of intravenous (IV) colloid infusion solution (Haemaccel) and group 2 pigs (cholesterol group,n=8) each received an IV injection of pure cholesterol emulsion (12 mg/kg) in 20 ml of Haemaccel. Blood samples for SP and histamine (H) levels were taken just before and for 10 min following the placebo, Haemaccel, and cholesterol injections. Urine samples were also collected just before and at 60 min following the injections for methyl histamine (MH) levels. Group 2 pigs (cholesterol) developed an anaphylactoid reaction as indicated by marked and significant hemodynamic changes. None of the group 1 (placebo) pigs developed an anaphylactoid reaction. Significant increases in blood SP and H levels (P<0.05), and urine MH levels (P<0.05) were seen in cholesterol-treated pigs (group 2), whereas no significant changes were seen in control pigs (group 1). Our results suggest that SP is involved in the cholesterol-induced anaphylactoid reaction in pigs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bienenstock J, Tomioka M, Matsuda H (1987) The role of mast cells in inflammatory processes: evidence for nerve/mast cell interactions. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 82:238–243
Caulfield JP, El-Lati S, Thomas G, Church M (1990) Dissociated human foreskin mast cells degranulate in response to anti-IgE and substance P. Lab Invest 63:502–510
Church MK, Lowman MA, Reese PH, Benyon RC (1989) Mast cells, neuropeptides and inflammation. Agents Actions 27:8–16
Church MK, Lowman MA, Robinson C, Holgate SC, Benyon RC (1989) Interaction of neuropeptides with human mast cells. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 88:70–78
Hagermark O, Hökfelt T, Pernow B (1978) Flare and itch induced by substance P in human skin. J Invest Dermatol 71:233–235
Johnson AR, Erdos EG (1973) Release of histamine from mast cells by vasoactive peptides. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 142:1252–1256
Laurindo FR, Goldstein RE, Davenport NJ, Ezra D, Feuerstein GZ (1989) Mechanisms of hypotension produced by platelet-activating factor. J Appl Physiol 66:2681–2680
Levy JH (1992) Anaphylactic reactions in anesthesia and intensive care. Butterworth-Heinemann, Boston
Parris WCV, Kambam JR, Naukam RJ, Sastry RBV (1990) Immunoreactive substance P is decreased in saliva of patients with chronic back pain syndromes. Anesth Anal 970:63–67
Payan DG, Substance P (1989) A modulator of neuroendocrine-immune function. Hosp Pract 24:63–76
Pernow B, Rosell S (1975) Effect of substance P on blood flow in canine adipose tissue and skeletal muscle. Acta Physiol Scand 93:139–141
Pierau FR-K, Ernst R, Sann H, Bartho L (1992) Endogenous opioids and ruthenium red inhibit the flare reaction in the pig skin by different mechanisms. Ann N Y Acad Sci 632:460–464
Vogt W, Zabern I von, Damerau D, Hesse B, Luhmann B, Nolte R (1985) Mechanisms of complement activation by crystalline cholesterol. Mol Immunol 22:101–108
Wassef NM, Johnson SH, Graber GM, Swartz GM, Schultz CL, Hailey J (1989) Anaphylactoid reactions mediated by autoantibodies to cholesterol in miniature pigs. J Immunol 143:2990–2995
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kambam, J.R., Janicki, P.K., Franks, J.J. et al. Substance P level is increased in the cholesterol induced anaphylactoid reaction in the pig. Res. Exp. Med. 195, 327–332 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02576803
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02576803