Abstract
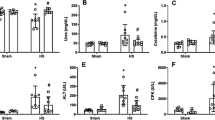
We have investigated the effect of two doses of allopurinol (ALL) (100 and 50 mg/kg) administered i.v. on liver function after 1 h of normothermic ischemia. ALL given in a concentration of 100 mg/kg significantly improved bile output after 1 and 24 h of reperfusion. Hepatocyte injury reflected by alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and lactic dehydrogenase (LDH) in plasma was also significantly reduced at 24 h, but not at 1 h of reperfusion compared with controls. ALL administered at a concentration of 50 mg/kg had some protective effect. Significant correlation between circulating liver enzymes and bile output at 24 h after reperfusion indicates an important pathophysiologic link between hepatocyte function and injury in this time window.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Godin DV, Bhimji S (1987) Effects of allpurinol on myocardial ischemic injury induced by coronary artery ligation and reperfusion. Biochem Pharmacol 36: 2101–2107
Kmetec E, Mendoza AR, Stanley EL (1978) Effects of allopurinol on purine metabolism in cultured heart cells. Biochem Pharmacol 27: 1297–1300
Bowers BA, Branum GD, Rotolo FS, et al (1987) Bile flow—an index of ischemic injury. J Surg Res 42: 565–569
Kamiike W, Nakahara M, Nakao K, et al (1985) Correlation between cellular ATP level and bile excretion in the rat liver. Transplantation 39: 50–55
Karwinski W, Farstad M, Ulvik R, Søreide O (1991) Sixty-minute normothermic liver ischemia in rats. Evidence that allopurinol improves liver cell energy metabolsim during reperfusion but that timing of drug administration is important. Transplantation 52: 231–234
Karwinski W, Bolann B, Ulvik R, Farstad M, Søreide O (1993) Normothermic liver ischemia in rats. Xanthine oxidase is not the main source of oxygen free radicals. Res Exp Med 193: 275–283
Hickman R, Rose-Innes C, Tyler M, et al (1992) Energy charge as an indicator of liver viability. A comparison of changes in livers that remained intact with those subjected to autografting. Transplantation 53: 540–545
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karwinski, W., Garcia, R. & Scott Helton, W. Allopurinol dose is important for attenuation of liver dysfunction after normothermic ischemia: Correlation between bile flow and liver enzymes in circulation. Res. Exp. Med. 194, 321–327 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02576394
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02576394