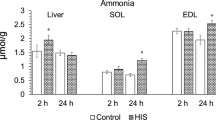
Abstract
Transient hyperammonemia was observed in rats after inhalation anesthesia with ether. The elevation of blood ammonia concentration induced by ether anesthesia was greatest in carbon tetrachloride injured and indomethacin-treated rats, but not observed in phenobarbital-treated rats. The results suggest interaction between ether metabolism and ammonia metabolism in the liver.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen SI, Conn HO (1960) Observations on the effect of exercise on blood ammonia concentration in man. Yale J Biol Med 33: 133–144
Hobara N, Watanabe A (1980) Altered pharmacodynamics of 1-(2-tetrahydrofuryl)-5-fluorouracil by pretreatment of rats with phenobarbital, indomethacin, diclofenac sodium and carbon tetrachloride. Pharmacology 21:323–326
Jones JG (1987) Mechanisms of some pulmonary effects of general anaesthesia. Br J Hosp Med 38:472–476
Kato R, Onoda K (1970) Studies on the regulation of the activity of drug oxidation in rat liver microsomes by androgen and estrogen. Biochem Pharmacol 19:1649–1660
Leeuwen PAM van, Bogaard EJM v.d., Janssen MA, Boer JEG de, Eyck HMA v, Soeters PB (1984) Ammonia production and glutamine metabolism in the small and large intestine of the rat and the influence of lactulose and neomycin. In: Kleinberger G, Ferenci P, Riederer P, Thaler H (eds). Advance in hepatic encephalopathy and urea cycle diseases. Karger, Basel, pp 154–162
Lumb AB, Nunn JF (1991) Respiratory function and ribcage contribution to ventilation in body positions commonly used during anesthesia. Anesth Analg 73:422–426
Ross WT, Cardell RR (1978) Proliferation of smooth endoplasmic reticulum and induction of microsomal drug-metabolizing enzymes after ether or halothene. Anesthesiology 48: 325–331
Sasame HA, Castro JA, Gillette JR (1986) Studies on the destruction of liver microsomal cytochrome P-450 by carbon tetrachloride administration. Biochem Pharmacol 17:1759–1768
Weber FL, Veach GL (1970) The importance of the small intestine in gut ammonia production in the fasting dog. Gastroenterology 77:235–240
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Watanabe, A., Kuwabara, Y. Hyperammonemia induced in rats by inhalation anesthesia with ether. Res. Exp. Med. 194, 157–164 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02576376
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02576376