Abstract
Background
RCAS1 (receptor-binding cancer antigen expressed on SiSo cells) is a cancer cell-surface antigen and has been identified as a prognostic factor in several cancers. It is thought that tumor cells escape from immune attack by expressing RCAS1, which induces apoptosis in receptor-positive immune cells. We investigated the relationship between RCAS1 expression and clinicopathologic features and clinical outcome in patients with extrahepatic bile duct carcinoma (EBDC) who underwent curative resection.
Methods
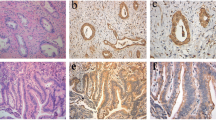
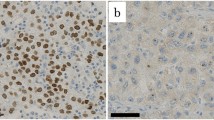
RCAS1 expression was determined by immunohistochemistry in 60 patients with EBDC who underwent curative resection from 1992 to 1999. The patients were divided into two groups on the basis of the extent of RCAS1 expression: a low-expression group (immunoreactivity in <25% of cells) and a high-expression group. Expression was correlated with clinicopathologic features and prognosis.
Results
RCAS1 was expressed in 52 (86.7%) of 60 tumors and at a high frequency in all histopathologic stages. High expression of RCAS1 was detected in 46 (76.7%) of 60 cases. No correlation existed between the pattern of RCAS1 expression and any clinicopathologic feature, although high expression did correlate with poor prognosis. High RCAS1 expression was an independent negative predictor for survival.
Conclusions
RCAS1 expression predicts poor outcome in resectable EBDC.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Langer JC, Langer B, Taylor BR, Zeldin R, Cummings B. Carcinoma of the extrahepatic bile ducts: results of an aggressive surgical approach.Surgery 1985;98:752–9.
Reding R, Buard JL, Lebeau G, Launois B. Surgical management of 552 carcinomas of the extrahepatic bile ducts (gallbladder and periampullary tumors excluded): results of the French Surgical Association Survey.Ann Surg 1991;213:236–41.
Schoenthaler R, Philips TL, Castro J, Efird JT, Better A, Way LW. Carcinoma of the extrahepatic bile ducts: the University of California at San Francisco experience.Ann Surg 1994;219:267–74.
Doglietto GB, Alfieri S, Pacelli F, et al. Extrahepatic bile duct carcinoma: a western experience with 118 consecutive patients.Hepatogastroenterology 2000;47:349–54.
Tompkins RK, Saunders K, Roslyn JJ, Longmire WP Jr. Changing patterns in diagnosis and management of bile duct cancer.Ann Surg 1990;211:614–21.
Bhuiya MR, Nimura Y, Kamiya J, et al. Clinicopathologic studies on perineural invasion of bile duct carcinoma.Ann Surg 1992;215:344–9.
Nishida T, Nakao K, Hamaji M, Nakahara MA, Tsujimoto M, Prognostic significance of proliferative cell nuclear antigen in carcinoma of the extrahepatic bile duct.World J Surg 1997;21: 634–9.
Hui AM, Cui X, Makuuchi M, Li X, Shi YZ, Takayama T. Decreased p27(Kip1) expression and cyclin D1 overexpression, alone and in combination, influence recurrence and survival of patients with resectable extrahepatic bile duct carcinoma.Hepatology 1999;30:1167–73.
Suto T, Sugai T, Nakamura S, et al. Assessment of the expression of p53, MIB-1 (Ki-67 antigen), and argyrophilic nucleolar organizer regions in carcinoma of the extrahepatic bile duct.Cancer 1998;82:86–95.
Yokoyama Y, Hiyama E, Murakami Y, Matsuura Y, Yokoyama T. Lack of CD44 variant 6 expression in advanced extrahepatic bile duct/ampullary carcinoma.Cancer 1999;86:1691–9.
Hida Y, Morita T, Fujita M, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor expression is an indeendent negative predictor in extrahepatic biliary tract carcinomas.Anticancer Res 1999;19:2257–60.
Li X, Hui AM, Takayama T, Cui X, Shi Y, Makuuchi M. Altered p21 (WAF1/CIP1) expression is associated with poor prognosis in extrahepatic bile duct carcinoma.Cancer Lett 2000;154:85–91.
Sonoda K, Nakashima M, Saito T, et al. Establishment of a new human uterine cervical adenocarcinoma cell line, SiSo, and its reactivity to anticancer reagents.Int J Oncol 1995;6:1099–104.
Sonoda K, Nakashima M, Kaku T, Kamura T, Nakano H, Watanabe T. A novel tumor-associated antigen expressed in human uterine and ovarian carcinomas.Cancer 1996;77:1501–9.
Nakashima M, Sonoda K, Watanabe T. Inhibition of cell growth and induction of apoptotic cell death by the human tumor-associated antigen RCAS1.Nat Med 1999;5:938–42.
Sonoda K, Kaku T, Kamura T, Nakashima M, Watanabe T, Nakano H. Tumor-associated antigen 22-1-1 expression in the uterine cervical squamous neoplasias.Clin Cancer Res 1998;4:1517–20.
Kaku T, Sonoda K, Kamura T, et al. The prognostic significance of tumor-associated antigen 22-1-1 expression in adenocarcinoma of the uterine cervix.Clin Cancer Res 1999;5:1449–53.
Iwasaki T, Nakashima M, Watanabe T, et al. Expression and prognostic significance in lung cancer of human tumor-associated antigen RCAS1.Int J Cancer 2000;89:488–93.
Sobin LH, Wittekind C,TNM Classification of Malignant Tumors, 5th ed. New York: Wiley-Liss, Inc., 1997;81–3
Strand S, Hofmann WJ, Hug H, et al. Lymphocyte apoptosis induced by CD95 (APO-1/Fas) ligand-expressing tumor cells—a mechanism of immune evasion?.Nat Med 1996;2:1361–6.
Hahne M, Rimoldi D, Schroter M, et al. Melanoma cell expression of Fas(Apo-1/CD95) ligand: implications for tumor immune escape.Science 1996;274:1363–6.
Niehans GA, Brunner T, Frizelle SP, et al. Human lung carcinomas express. Fas ligand.Cancer Res 1997;57:1007–12.
Ungefroren H, Voss M, Jansen M, et al. Human pancreatic adenocarcinomas express Fas and Fas ligand yet are resistant to Fas-mediated apoptosis.Cancer Res 1998;58:1741–9.
O’Connell J, Bennett MW, O’Sullivan GC, et al. Fas ligand expression in primary colon adenocarcinomas: evidence that the Fas counterattack is a prevalent mechanism of immune evasion in human colon cancer.J Pathol 1998;186:240–6.
Bennett MW, O’Connell J, O’Sullivan GC, et al. Expression of Fas ligand by human gastric adenocarcinomas: a potential mechanism of immune escape in stomach cancer.Cut 1999;44:156–62.
Nagao M, Nakajima Y, Hisanaga M, et al. The alteration of Fas receptor and ligand system in hepatocellular carcinomas: how do hepatoma cells escape from the host immune surveillance in vivo?Hepatology 1999;30:413–21.
Que FG, Phan VA, Phan VH, et al. Cholangiocarcinomas express Fas ligand and disable the Fas receptor.Hepatology 1999;30:1398–404.
Oshikiri T, Hida Y, Miyamoto M, et al. RCAS1 as a tumour progression marker: an independent negative prognostic factor in gallbladder cancer.Br J Cancer 2001;85:1922–7.
Hiraoka K, Hida Y, Miyamoto M, et al. High expression of tumor-associated antigen RCAS1 in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma is an unfavorable prognostic marker.Int J Cancer (in press).
Sturm PD, Rauws EA, Hruban RH, et al. Clinical value of K-ras codon 12 analysis and endobiliary brush cytology for the diagnosis of malignant extrahepatic bile duct stenosis.Clin Cancer Res 1999;5:629–35
Saurin JC, Joly-Pharaboz MO, Pernas P, Henry L, Ponchon T, Madjar JJ. Detection of Ki-ras gene point mutations in bile specimens for the differential diagnosis of malignant and benign biliary strictures.Gut 2000;47:357–61.
Ikeda K, Sato M, Tsutsumi O, et al. Promoter analysis and chromosomal mapping of human EBAG9 gene.Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2000;273:654–60.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suzuoki, M., Hida, Y., Miyamoto, M. et al. RCAS1 expression as a prognostic factor after curative surgery for extrahepatic bile duct carcinoma. Annals of Surgical Oncology 9, 388–393 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02573874
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02573874