Abstract
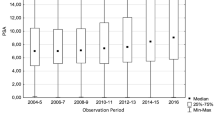
We surveyed the comparative clinical features of patients with stage A1 and stage A2 prostate cancer. Preoperatively, prostate specific antigen (PSA) level was elevated in 50.0% of stage A2 patients as compared to 18.2% of stage A1 patients. Compared to low positivity of prostatic acid phosphatase in 12.5% of stage A2 and in 0% of stage A1, PSA was more sensitive to the presence of incidental carcinoma. During the observation period (mean 35.7 months) no stage A patient died of cancer. No evidence of the disease showed significantly higher rate, and death without cancer was significantly lower in stage A1.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Correa, R., Anderson, R., Gibbons, R., Mason, T.: Latent carcinoma of the prostate: Why the controversy?J. Urol., 107, 450 (1973).
Jewett, H.: The present status of radical prostatectomy for stages A and B prostatic cancer.Urol. Clin. North Am., 2, 105 (1975).
Cantrell, B. B., deKlerk, D. P., Eggleston, J. C., Boitnott, J. K., Walsh, P. C.: Pathologic factors that influence the prognosis of Stage A prostatic cancer—the influence of extent versus grade.J. Urol., 125, 516 (1981).
Hermanek, P., Sobin, L. H.: UICC TNM Classification of Malignant Tumours. Springer-Verlag, Berlin 1987, p. 141.
Beahrs, G. H., Henson, D. E., Hutter, R. V. P., Meyers, M. H.: American Joint Committee on Cancer: Manual for Staging of Cancer. J. B. Lippincott, Philadelphia 1988.
Schroeder, F. H., Bloom, J. H., Hop, W. C., Mostofi, F. K.: The TNM classification of prostatic cancer.Prostate (Suppl.),4, 129 (1992).
Japanese Urological Association and The Japanese Pathological Society: General rule for clinical and pathological studies on prostatic cancer. 2nd ed. Kanehara 1992.
Lorentz, K., Assel, K.: Studies on aryl phosphate hydrolysis by human acid phosphatase.Enzyme, 20, 248 (1975).
Wang, M. C., Papsidero, L. D., Kuriyama, M., Valenzuela, L. A., Murphy, G. P., Chu, T. M.: Prostate antigen: A new potential marker for prostatic cancer.Prostate, 2, 89 (1981).
Ogawa, Y., Morikawa, J., Ohsawa, R., Machida, T., Miki, M., Yanagisawa, M.: Purification and determination of human prostate specific antigen in serum.Radioisotopes, 33, 273 (1984).
Emmett, J. L., Barber, K. W., Jackman, R. J.: Transrectal biopsy to detect prostate carcinoma: A review and report of 203 cases.J. Urol., 87, 460 (1962).
Murphy, W. M., Dean, P. J., Brasfield, J. A., Tatum, L.: Incidental carcinoma of the prostate. How much sampling is adequate?Am. J. Surg. Pathol., 10, 170 (1986).
Thompson, I. M., Zeidman, E. J.: Current urological practice: Routine urological examination and early detection of carcinoma of the prostate.J. Urol., 148, 326 (1992).
Haas, G. P., Montie, J. E., Pontes, J. E.: The state of prostate cancer screening in the United States.Eur. Urol., 23, 337 (1993).
Ercole, C. J., Lange, P. H., Mathisen, M., Chiou, R. K., Reddy, P. K., Vessella, R. L.: Prostatic specific antigen and prostatic acid phosphatase in the monitoring and staging of patients with prostatic cancer.J. Urol., 138, 1181 (1987).
Stamey, T. A., Yang, N., Hay, A. R., McNeal, J. E., Freiha, F. S., Redwine, E.: Prostate-specific antigen as a serum marker for adenocarcinoma of the prostate.N. Engl. J. Med., 317, 909 (1987).
Hudson, M. A., Bahnson, R. R., Catalona, W. J.: Clinical use of prostate specific antigen in patients with prostate cancer.J. Urol., 142, 1011 (1989).
Benson, M. C., Whang, I. S., Pantuck, A., Ring, K., Kaplan, S. A., Olsson, C. A., Cooner, W. H.: Prostate specific antigen density: A means of distinguishing benign prostatic hypertrophy and prostate cancer.J. Urol., 147, 815 (1992).
Benson, M. C., Whang, I. S., Olsson, C. A., McMahon, D. J., Cooner, W. H.: The use of prostate specific antigen density to enhance the predictive value of intermediate levels of serum prostate specific antigen.J. Urol., 147, 817 (1992).
Miller, J. S., Donovan, J. F., Williams, R. D.: Evaluation and treatment of stage A prostate cancer. In: Williams, R. D., Carroll, P. R. (eds): Urological Oncology. Pergamon Press, New York 1989, p. 113.
Blute, M. L., Zincke, H., Farrow, G. M.: Long-term followup of young patients with stage A adenocarcinoma of the prostate.J. Urol., 136, 840 (1986).
McNeal, J. E., Bostwick, D. G., Kindorachuk, R. A., Redwine, E. A., Freiha, F. S., Stamey, T. A.: Patterns of progression in prostate cancer.Lancet, 11, 60 (1986).
McNeal, J. E.: Origin and development of carcinoma in the prostate.Cancer, 23, 24 (1969).
McNeal, J. E.: Normal histology of the prostate.Am. J. Surg. Pathol., 12, 619 (1988).
McIntire, T. L., Murphy, W. M., Coon, J. S., Chandler, R. W., Schwartz, D., Conway, S., Weinstein, R. S.: The prognostic value of DNA ploidy combined with histologic substaging for incidental carcinoma of the prostate gland.Am. J. Clin. Pathol., 89, 370 (1988).
Epstein, J. I., Paull, G., Eggleston, J. C., Walsh, P. C.: Prognosis of untreated stage A1 prostatic carcinoma: A study of 94 cases with extended followup.J. Urol., 136, 837 (1986).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kunimi, K., Amano, T., Lee, S.W. et al. Comparative clinical features of stage A1 and stage A2 prostate cancers. Is the concept of stage a changing from the current status?. International Urology and Nephrology 27, 575–585 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02564744
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02564744