Abstract
As the only lithotripsy centre at a University Hospital in the most crowded city of Turkey, we have a big number of patients with urinary stones. Between April 1990 and August 1993, 2680 sessions of treatment were done to 1257 renal units.
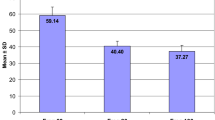
Our study reveals that the results obtained by the performance of an experienced technician are just as reliable as those obtained by an experienced urologist.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chaussy, C., Brendel, W., Schmiedt, E.: Extracorporeally induced destruction of kidney stones by shock waves.Lancet, 2, 1265 (1980).
Chaussy, C., Schmiedt, E., Joacham, D., Brendel, W., Forssmann, B., Walther, V.: First clinical experience with extracorporeally induced destruction of kidney stones by shock waves.J. Urol., 127, 417 (1982).
Andersen, J. T., Mogensen, P.: Extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy of urinary calculi.Scand. J. Urol. Nephrol., Suppl. 138, 19 (1991).
Drach, G. W., Dretler, S., Fair, W.:Report of the United States cooperative study of extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy.J. Urol., 135, 1127 (1986).
Grace, P. A., Gillen, P., Smith, J. M., Fitzpatrik, J. M.: Extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy with the Lithostar lithotriptor.Br. J. Urol., 64, 117 (1989).
Talati, J., Shah, T., Memon, R., Sidhwa, M., Adil, S., Aamir, O.: Extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy for urinary tract stones using MPL 9000 spark gap technology and ultrasound monitoring.J. Urol., 146, 1482 (1991).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ilker, Y., Erton, M., Şimşek, F. et al. Extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL) for urinary tract stones using Dornier MFL 5000, performed by the technician. International Urology and Nephrology 27, 511–513 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02564733
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02564733