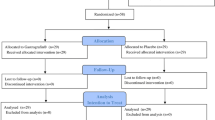
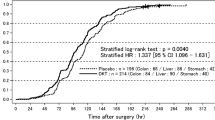
Abstract
Sequential analysis of a placebo-controlled double-blind clinical trial involving 18 patients demonstrated that ceruletide had a statistically significant effect on restoration of peristalsis in intestinal paralysis after abdominal surgery (P<0.05).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Haas W, Rueff FL. Caerulein in der Therapie der postoperativen Darmatonie und des Ileus. Therapiewoche 1978; 28:8939–44.
Waldmann D, Hartung H. Zur konservativen Behandlung des schweren paralytischen Ileus. Fortschr Med 1979; 97:1–3.
Montero VF, Laganga AM, Garcia EA. Usefulness of caerulein in the treatment of post-operative intestinal atony. J Int Med Res 1980; 8:98–104.
Armitage P. Sequential medical trials. Oxford: Blackwell, 1960.
Sommoggy S, Theisinger W, Fraunhofer B. Medikamentoese Beeinflussung der postoperativen Darmatonie. Fortsch Med 1981; 99:13–21.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Madsen, P.V., Lykkegaard-Nielsen, M. & Nielsen, O.V. Ceruletide reduces postoperative intestinal paralysis. Dis Colon Rectum 26, 159–160 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02560160
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02560160