Summary
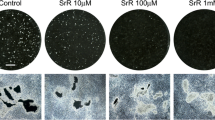
We have compared the effects of thiophene 2-carboxylic acid (TCA) and a number of sulfur-and nitrogen-containing analogs for their ability to inhibit bone resorption in organ cultures of fetal rat long bones. Four compounds,—thionapthene-2-carboxylic acid (TNCA), dibenzo-thiophene-4-carboxylic acid, indole-2-carboxylic acid and carbazole-1-carboxylic acid—caused a doserelated inhibition of PTH-stimulated bone resorption, although TCA was ineffective in this system. TNCA at 3×10−4 M or 10−4 M was the most potent inhibitor of PTH-stimulated bone resorption and was selected for further study. TNCA also inhibited stimulation of resorption by prostaglandin E2 and 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D. Unlike calcitonin, the effect of TNCA was persistent and did not show escape. Moreover, TNCA could inhibit resorption in bones that had previously escaped from calcitonin. TNCA did not appear to be a nonspecific toxin, since it did not decrease incorporation of [3H] thymidine or [3H]proline into fetal rat long bones. The fact that resorption in unstimulated cultures was only decreased when the control rates were high also argues against nonspecific toxicity. Moreover, this suggests that TNCA will be most effective under conditions of accelerated bone resorption when an inhibiting effect is most desirable. heterocyclic sulfur-containing compound, thiophene-2 carboxylic acid (TCA) in the rat. Subsequent studies showed that this compound could inhibit bone resorption in organ cultures of neonatal mouse calvaria [3]. We have compared TCA with a number of analogs for their ability to inhibit PTH stimulated bone resorption in organ culture. TCA itself was found to be relatively ineffective, whereas several of the analogs were inhibitory at concentrations of 3×10−4 or 10−5 M. One of the most potent compounds, thionapthene 2-carboxylic acid (TNCA) was selected for further study. TNCA was a potent inhibitor not only of PTH stimulated bone resorption, but of resorption stimulated by prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) and 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D (1,25-(OH)2D3). It was less effective in inhibiting resorption in control unstimulated cultures. TNCA did not appear to act as a nonspecific toxin in that it did not decrease [3H]-thymidine or [3H]-proline incorporation into bones. The inhibitory effect of TCA was persistent, unlike that of calcitonin, which shows escape after initial inhibition. Moreover, TNCA had a powerful inhibitory effect when it was added to bones that had previously escaped from CT.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alander CB, Onkelinx C, Rodan GA, Raisz LG (1984) Inhibition of bone resorption by 2-thionapthene carboxylic acid. Calcif Tisue Int 36:450 (Abstract)
Lloyd W, Fang VS, Wells H, Tashjian AH (1969) 2-Thiophenecarboxylic acid: A hypoglycemic, antilipolytic agent with hypocalcemic and hypophospatemic effects in rats. Endocrinology 85:763
Fang VS, Minin C, Goldhaber P (1971) 2-Thiophencarboxylic acid: Inhibitor of bone resorption in tissue culture. Science 172:163
Raisz LG, Niemann I (1969) Effect of phosphate, calcium and magnesium on bone resorption and hormonal responses in tissue culture. Endocrinology 85:446–452
Wener JA, Gorton SJ, Raisz LG (1972) Escape from inhibition of resorption in cultures of fetal bone treated with calcitonin and parathyroid hormone. Endocrinology 90:752
Robin JC, Frances K, Roseinstein M, Ambus JL (1980) Studies on osteoporosis. IV. Effect on 2-thiophenecarboxylic acid on heparin accelerated osteoporosis. J Med 1:15–27
Robin JC, Brown MJ, Weinfeld N, Dziak RM (1984) Benzo(B)thiophene-2-carboxylic acid: Calsium uptake and cyclic AMP production in isolated bone cells. Calcif Tissue Int 36:194–199
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Raisz, L.G., Alander, C., Onkelinx, C. et al. Effects of thionapthene 2-carboxylic acid and related compounds on bone resorption in organ culture. Calcif Tissue Int 37, 556–559 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02557841
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02557841