Summary
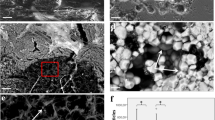
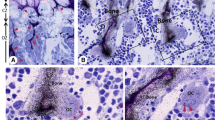
The localization of acid phosphatase (ACPase) activity in and near parathyroid hormone (PTH) activated osteoclasts was investigated using electron microscopic cytochemical methods. At 3 hours after oviposition in Japanese Quail hens, medullary bone osteoclasts were highly reactive for ACPase but lacked ruffled borders. There was no evidence of extracellular ACPase activity associated with these osteoclasts. At 20 minutes after PTH administration, osteoclasts had developing ruffled borders and ACPase activity was found in the matrix and extracellular space adjacent to most of these ruffled borders. ACPase activity was seldom observed beyond the resorption zone delineated eated by the osteoclast clear zones. These results provide direct cytochemical evidence that the ruffled border functions in the release and/or activation of ACPase. In addition, these results show that ACPase localization is rapidly responsive to exogenous PTH.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lucht U (1972) Osteoclasts and their relationship to bone as studied by electron microscopy. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk anat 135:211–228
Holtrop ME, GJ King (1977) The ultrastructure of the osteoclast and its functional implications. Clin Orthop 123:177–196
Lucht U (1971) Acid phosphatase of osteoclasts demonstrated by electron microscopic histochemistry. Histochemie 28:103–117
Doty SB, Schofield BH (1972) Electron microscopic localization of hydrolytic enzymes in osteoclasts. Histochem J 4:245–258
Lucht U, JO Norgaard (1976) Export of protein from the osteoclast as studied by electron microscopic autoradiography. Cell Tissue Res 168:89–99
Miller SC (1977) Osteoclast cell-surface changes during the egg-laying cycle in Japanese quail. J Cell Biol 75:104–118
Miller SC (1981) Osteoclast cell-surface specializations and nuclear kinetics during egg-laying in Japanese quail. Am J Anat 162:35–43
Miller SC (1978) Rapid activation of the medullary bone osteoclast cell-surface by parathyroid hormone. J Cell Biol 76:615–618
Miller SC, MB Bowman, RL Myers (1984) Morphological and ultrastructural aspects of the activation of avian medullary bone osteoclasts by parathyroid hormone. Anat Rec 208:223–231
Mueller WJ, R Schraer, H. Schraer (1964) Calcium metabolism and skeletal dynamics of laying pullets. J Nutr 84: 20–26
Dacke CG, AD Kenny (1973) Avian bioassay method for parathyroid hormone. Endocrinology 92:463–470
Gomori G (1950) An improved histochemical technique for acid phosphatase. Stain Technol 23:81–85
Gothlin G, JLE Ericsson (1971) Fine structural localization of acid phosphomonoesterase in the brush border region of osteoclasts. Histochemie 28:337–344
Thyberg J, S Nilsson, U Friberg (1975) Electron microscopic and enzyme cytochemical studies on the guniea pig metaphysis with special reference to the lysosomal system of different cell types. Cell Tissue Res 156:273–299
Marks SC Jr (1973) Studies of the mechanism of the spleen cell cure for osteopetrosis inia rats: Appearance of osteoclasts with ruffled borders. Am J Anat 146:331–338
Schofield BH, Levin LS, Doty SB (1974) Ultrastructure and lysosomal histochemistry of ia rat osteoclasts. Calc Tissue Res 14:153–160
Kallio DM, PR Garant, C Minkin (1971) Evidence of coated membranes in the ruffled border of the osteoclast J Ultrastruct Res 37:169–177
Schenk R, D Spiro, J Weiner (1967) Cartilage resorption in tibial epiphyseal plate of growing rats. J Cell Biol 34: 275–291
Malkani K, MM Luxembourger, A. Rebel (1973) Cytoplasmic modifications at the contact zone of osteoclasts and calcified tissue in the diaphyseal growing plate of foetal guinea pig tibia. Calcif Tissue Res 11:258–264
Goldhaber P (1961) Oxygen-dependent bone resorption in tissue culture. In: Greep RO, Talmage RV (eds) The parathyroids. CC Thomas, Springfield, IL, pp 243–255
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miller, S.C. The rapid appearance of acid phosphatase activity at the developing ruffled border of parathyroid hormone activated medullary bone osteoclasts. Calcif Tissue Int 37, 526–529 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02557836
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02557836