Abstract
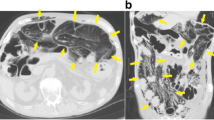
Breathing high concentrations of oxygen at atmospheric pressure has been effective in achieving prompt objective and subjective relief in pneumatosis coli. A 22-year-old man was treated with 40% oxygen—a smaller concentration than used by previous physicians—supplied through a nonrebreathing mask. During meals, oxygen was given at 5 1/minute by nasal cannula. Oxygen therapy was maintained for seven days. A year after treatment the patient was still asymptomatic and free from disease. Using this therapeutic measure the benefit/risk ratio of oxygen therapy could be increased.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Du Vernoi JG. Cited by Mackenzie EP. Pneumatosis intestinalis; review of the literature with report of 13 cases. Pediatrics 1951;7:537–49.
Mayer J. Cited by Matthews FJ. Enteric pneumatosis. Br Med J 1954;1:851–2.
Tsiftsis D, Wastell C. Pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis: report of two cases involving the descending colon. Am J Surg 1979; 137:679–82.
Marshak RH, Blum SD, Eliashop J. Pneumatosis involving the left side of the colon. JAMA 1956;161:1626–8.
Wertkin MG, Wetchler BB, Waye JD, Brown LK. Pneumatosis coli associated with sigmoid volvulus and colonoscopy. Am J Gastroenterol 1976;65:209–14.
Koss LG. Abdominal gas cysts (pneumatosis cystoides intestinorum hominis): an analysis with a report of a case and a critical review of the literature. Arch Pathol 1952;53:523–49.
Keyting WS, Maclarver RP, Kovarik JL, Daywitt AL. Pneumatosis intestinalis: a new concept. Radiology 1961;76:733–41.
Yale CE, Balish E, Wu JP. The bacterial etiology of pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis. Arch Surg 1974;109:89–94.
Leonidas JC, Hall RT. Neonatal pneumatosis coli: a mild form of neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis. J Pediatr 1976;89:456–9.
Gillon J, Tadesse K, Logan RFA, Holt S, Sircus W. Breath hydrogen in pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis. Gut 1979;20:1008–11.
Holt S, Stewart IC, Heading RC, MacPherson AI. Resolution of primary pneumatosis coli. J R Coll Surg Edinb 1978;23:297–9.
Wandtke J, Skucas J, Sparato R, Bruneau RJ. Pneumatosis intestinalis as a complication of jejunoileal bypass. AJR 1977;129:601–4.
Forgacs P, Wright PH, Wyatt AP. Treatment of intestinal gas cysts by oxygen breathing. Lancet 1973;1:579–82.
Simon NM, Nyman KE, Divertie MB, Rovelstad RA, King JE. Pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis: treatment with oxygen via close-fitting mask. JAMA 1975;231:1354–6.
Watson RD. Successful treatment of pneumatosis coli with oxygen. Br Med J 1976;1:199.
Down RHL, Castleden WM. Oxygen therapy for pneumatosis coli. Br Med J 1975;1:493–4.
Wyatt AP. Prolonged symptomatic and radiological remission of colonic gas cysts after oxygen therapy. Br J Surg 1975;62:837–9.
Holt S, Gilmour HM, Buist TAS, Marwick K, Heading RC. High flow oxygen therapy for pneumatosis coli. Gut 1979;20:493–8.
Gruenberg JC, Batra SK, Priest RJ. Treatment of pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis with oxygen. Arch Surg 1977;112:62–4.
Höflin F, Van der Linden W. Pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis treated by oxygen breathing. Scand J Gastroentetrol 1974;9;427–8.
Clark JM, Lambertsen CJ. Pulmonary oxygen toxicity: a review. Pharmacol Rev 1971;23:37–133.
Clark JM, Lambertsen CJ. Rate of development of pulmonary O2 toxicity in man during O2 breathing at 2.0 Ata. J Appl Physiol 1971;30:739–52.
Van der Linden W. Reapparence of intestinal gas cysts after oxygen treatment. Lancet 1974;2:1388–9.
Bloch C. The natural history of pneumatosis coli. Radiology 1977;123:311–4.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Miralbés, M., Hinojosa, J., Alonso, J. et al. Oxygen therapy in pneumatosis coli. Dis Colon Rectum 26, 458–460 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02556526
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02556526