Summary
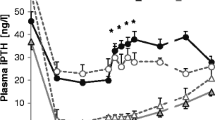
The influence of postprandial-like plasma insulin levels on intestinal calcium absorption (CaA) was studied in 9 health men. On separate occasions, they received either an i.v. infusion of 40 mU/m2 minute synthetic human insulin as well as a variable glucose infusion in order to clamp the plasma glucose at the baseline level (=glucose clamp), or insulin- and glucose-free vehicle infusions (=vehicle). During these infusions, an oral load containing 326 mg Ca in the form of Ca chloride was administered and CaA was determined thereafter with a47Ca/85Sr double tracer method. During glucose clamp, mean plasma insulin was 172 ±(1 SEM) 10 as compared to 6±1 μU/ml during vehicle infusions. During the clamp, 3-hour cumulative CaA rose significantly by 14% as compared to vehicle (39.2±2.5 vs. 34.4±2%,P<0.02). At the same time, serum potassium and phosphorus dropped significantly, whereas serum parathyroid hormone (PTH) and 1,25(OH)2D levels were unchanged as compared to vehicle. The urinary excretions of potassium, sodium, and inorganic phosphorus as well as the urinary specific activity of47Ca, dropped significantly during glucose clamp, whereas the urinary excretion of cAMP was unchanged as compared to vehicle. The results suggest that, under the conditions of euglycemic hyper-insulinemic clamp, insulin stimulates CaA of healthy humans in a PTH- and 1,25(OH)2D-independent manner. Insulin may thus possibly be regarded as a factor participating in the regulation of CaA in humans.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
De Fronzo RA, Cooke CR, Andres R, Faloona GR, Davis PI (1975) The effect of insulin on renal handling of sodium, potassium, calcium and phosphate in man. J Clin Invest 55: 845–855
Willis RG, Green R, Gordon C, Blacklock NJ (1985) The influence of glucose and insulin on calcium excretion in the urine. In: Schwille PO, Smith LH, Robertson WG, Vahlensieck W (eds) Urolithiasis and related clinical research. Plenum Press, New York, London, pp 209–212
Weiss RE, Reddi AH (1980) Influence of experimental dia-betes and insulin on matrix-induced cartilage and bone differentiation. Am J Physiol 230: E200-E207
Puche RC, Romano MC, Locatto ME, Ferretti JL (1973) The effect of insulin on bone resorption. Calcif Tissue Res 12: 8–15
Rosenbloom AL, Lezotte DC, Weber FT, Gudat J, Heller DR, Weber ML, Klein S, Kennedy BB (1977) Diminution of bone mass in childhood diabets. Diabetes 26: 1052–1055
Levin ME, Boisseau VC, Avioli LV (1976) Effects of diabetes mellitus on bone mass in juvenile and adult-onset diabetes. N Engl J Med 294: 241–245
Ishida H, Seino Y, Matsukura M, Ikeda M, Yawata M, Yamashita G, Ishizuka S, Imura H (1985) Diabetic osteopenia and cirulating levels of vitamin D metabolites in type 2 (noninsulin-dependent) diabetics. Metabolism 34: 797–801
Albright F, Reifenstein EC (1948) Parathyroid glands and metabolic bone disease: selected studies. Williams and Wilkins Company, Baltimore, p 150
Schneider LE, Nowosielski JM, Schedl HP (1977) Insulin treatment of diabetic rats: effects on duodenal calcium absorption. Endocrinology 100: 67–73
Rümenapf G, Issa S, Schwille PO (1987) The influence of progressive hyperinsulinemia on duodenal calcium absorption of the rat. Metabolism 36: 60–65
Scholz D, Schwille PO, Sigel A (1981) Response of gastro-intestinal hormones and intestinal calcium absorption during an oral carbohydrate meal. In: Smith LH, Robertson WG, Finlayson B (eds) Urolithiasis: clinical and basic research. Plenum Press, New York, London, pp 795–800
Schwille PO, Rümenapf G, Köhler R (in press) Blood levels of glucometabolic hormones and urinary saturation with stone forming phases after an oral test meal in patients with recurrent idiopathic calcium urolithiasis and in healthy controls. J Am Coll Nutr
Wootton R, Reeve J (1980) The relative merits of various techniques for measuring radiocalcium absorption. Clin Sci 58: 287–293
Chen PS, Toribara TY, Warner H (1956) Microdetermination of phosphorus. Anal Chem 18: 1756–1758
Brown BL, Ekins RP, Albano JDM (1972) Saturation assay for cyclic AMP using endogenous binding protein. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res 2: 25–34
Herbert V, Lau L, Gottlieb WC, Bleicher SJ (1965) Coated charcoal immunoassay of insulin. J Clin Endocrinol Metabol 25: 1375–1384
Schwille PO (1979) Bestimmung von Parathormon. In: Domschke W, Koch H (eds) Diagnostik in der Gastroenterologie, Thieme, Stuttgart, pp 324–330
Reinhardt TA, Horst RL, Orf JW, Hollis BW (1984) A microassay for 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D not requiring high performance liquid chromatography: application to clinical studies. J Clin Endocrinol Metabol 58: 91–98
Raymakers JA, Roelofs JMM, Duursma SA, Visser WJ (1975) Measurement of three-hour calcium absorption by double isotope technique. Neth J Med 18: 191–204
Crabbé J (1981) Stimulation by insulin of transepithelial sodium transport. In: Scott WN, Goodman DBP (eds) Hormonal regulation of epithelial transport of ions and water. Ann NY Acad Sci, vol 372, New York, pp 220–234
Zierler KL (1966) Possible mechanisms of insulin action on membrane potential and ion fluxes. Am J Med 40: 735–739
Sing-Cross H, Peterlik M (1981) Effects of vitamin D and on phosphate transport across biomembranes. Academic, Orlando FL, pp 293–296
Hough S, Russell JE, Teitelbaum SL, Avioli LV (1982) Calcium homeostasis in chronic streptozotocin-induced diabetes mellitus in the rat. Am J Physiol 242: E451-E456
Ishida H, Seino Y, Nishi S, Kitano N, Sano M, Taminato T, Matsukura S, Ishizuka S, Imura H (1985) Effects of insulin on altered mineral and vitamin D metabolism in streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Acta Endocrinol 108: 231–236
avioli LV, McDonald JE, Singer RA, Henneman PM (1965) A new oral isotope test of calcium absorption. J Clin Invest 47: 2239–2252
Klein H, Trost M, Seidlin E (1964) A pilot study of lamellar bone physiology in diabetes mellitus. Henry Ford Hosp Med Bull 12: 55–62
McNair P, Madsbad S, Christensen MS, Christiansen C, Faber OK, Binder C, Transbøi I (1979) Bone mineral loss in insulin-treated diabetes mellitus: studies on pathogenesis. Acta Endocrinol 90: 463–472
Stolar MW (1988) Atherosclerosis in diabetes: the role of hyperinsulinemia. Metabolism 37 (suppl 1): 1–9
Flodin NW (1986) Atherosclerosis: an insulin-dependent disease? J Am Coll Nutr 5: 417–427
Ferranini E, Buzzigoli G, Bonadonna R, Giorico MA, Olegini M, Graziadei L, Pedrinelli R, Brandi L, Bevillacqua S (1988) Insulinresistez bei essentieller Hypertonie. Münch Med Wschr 130: 3–10
Rao PN, Gordon C, Davies D, Blacklock NJ (1982) Are stone formers maladapted to refined carbohydrates? Br J Urol 54: 575–577
Fernandez-Moreno MD, Serrano-Rios M, Prieto JC (1987) Characterization of specific insulin, receptors along the rat small and large intestinal epithelial tract. Front Horm Res 16: 83–91
Guthmann HM II, Palmieri GMA, Hinton AB, Guthmann AL (1982) The mechanism of insulin-induced hypercalcemia in the chick. Endocrinology 110: 571–574
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rümenapf, G., Schmidtler, J. & Schwille, P.O. Intestinal calcium absorption during hyperinsulinemic euglycemic glucose clamp in healthy humans. Calcif Tissue Int 46, 73–79 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02556090
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02556090