Summary
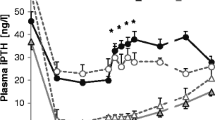
To investigate the effect of low doses of intranasal salmon calcitonin on plasma cyclic AMP (cAMP) and serum ionized calcium, 40 healthy postmenopausal women were randomized to receive a single dose of either placebo or 50, 100, or 200 IU of salmon calcitonin as a nasal spray. Blood samples were collected throughout an 8-hour period. None of the doses could provoke detectable hypocalcemia, whereas 100 and 200 IU of salmon calcitonin were associated with an increase in plasma cAMP after 15 minutes. Measurable plasma levels of salmon calcitonin were demonstrated in all active treatment groups, and the calculated areas under the curves showed a dose-dependent increase.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gruber HE, Ivey J, Baylink DJ, Matthews J, Nelp WB, Sisom K, Chesnut CH III (1984) Longterm calcitonin therapy in postmenopausal osteoporosis. Metabolism 33:295–303
Pontiroli AE, Alberetto M, Pozza G (1985) Intranasal calcitonin and plasma calcium concentrations in normal subjects. BMJ 290:1390–1391
Reginster JY, Albert A, Franchimont P (1985) Salmoncalcitonin nasal spray in Paget's disease of bone: preliminary results in five patients. Calcif Tissue Int 37:577–580
Kurose H, Seino Y, Shima M, Tanaka H, Ishida H, Yamaoka K, Yabuuchi H (1987) Intranasal absorption of salmon calcitonin. Calcif Tissue Int 41:249–251
Buclin T, Randin JP, Jacquet AF, Azria M, Attinger M, Gomez F, Burckhardt P (1987) The effect of rectal and nasal administration of salmon calcitonin in normal subjects. Calcif Tissue Int 41:252–258
Austin LA, Heath H (1981) Calcitonin. Physiology and pathophysiology. N Engl J Med 304:269–278
Talmage RV, Cooper CW, Toverud SU (1983) The physiological significance of calcitonin. In: Peck WA (ed) Bone and mineral research. Annual 1. Excerpta Medica, Amsterdam Oxford Princeton, p 74
Caniggia A, Gennari C, Lore' F, Nuti R, Galli M (1980) Effects of parathyroid hormone and calcitonin on plasma and nephrogenous cyclic adenosine-3′,5′-monophosphate in normal subjects and in pathological conditions. Eur J Clin Invest 10:99–105
Markowitz M, Rotkin L, Rosen JF (1981) Circadian rhythms of blood minerals in humans. Science 213:672–674
Pujol-Amat P, Davi E, Martin-Comin J (1977) Diurnal variation in cyclic A.M.P. in plasma. Lancet I:489
Nüesch E, Schmidt R (1980) Comparative pharmacokinetics of calcitonins. In: Pecile A (ed) Calcitonin. Excerpts Medica, Amsterdam (ICS Nr 540), p 352
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thamsborg, G., Storm, T.L., Brinch, E. et al. The effect of different doses of nasal salmon calcitonin on plasma cyclic AMP and serum ionized calcium. Calcif Tissue Int 46, 5–8 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02555817
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02555817