Abstract
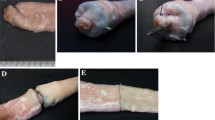
The reason for the higher leakage frequency after low anterior resection compared with high resection is unexplained. With the development of stapling devices, we have a unique opportunity to investigate anastomotic healing during standardized conditions. In female pigs, six in each group, a high anterior resection was performed by resection of a 5-cm colon segment, 10 cm above the peritoneal fold, and low anterior resection was performed after resection of a 5-cm segment at the peritoneal fold and downward. Differences in healing parameters,i.e., blood flow, breaking strength, and radiologic and histologic appearance between low and high anterior resection, were evaluated. Two leakages occurred after low and none after high anterior resection. The anastomotic index was 0.37 (high) and 0.26 (low) (P<0.05). The breaking strength was higher in low resections; this might be due to the thicker wall. There were no differences in blood circulation between high and low anastomoses, but the blood flow was significantly higher in the anastomotic area in both groups. This is probably due to the inflammatory reaction taking place in the healing anastomoses. This study, performed in a standardized fashion with a stapler adjusted to wall thickness and size of the intestine, cannot, on the basis of microcirculation, explain why leakage is more common in lower anastomoses.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Goligher JC, Lee PWG, Simpkins C, Lintott DJ. A controlled comparison of one- and two-layer techniques of suture for high and low colorectal anastomoses. Br J Surg 1977;64:609–14.
Schrock TR, Deveney CW, Dunphy JE. Factors contributing to leakage of colonic anastomoses. Ann Surg 1973;177:513–8.
Tagart REB. Colorectal anastomosis: factors influencing success. J Royal Soc Med 1981;74:111–7.
Goligher JC. Surgery of the anus, rectum and colon. London: Baillière Tindall, 1975:740–1.
Goligher JC, Lee PWR, Macfie J, Simpkins KC, Lintott DJ. Experience with the Russian model 249 suture gun for anastomosis of the rectum. Surg Gynecol Obstet 1979;148:517–24.
Keane FB, Moore DJ, Byrne PJ, Hennessy TP. A comparison of circular stapling devices for rectal anastomoses: a study in dogs. Dis Colon Rectum 1982;25:285–8.
Graffner H, Andersson L, Löwenhielm P, Walther B. The healing process of anastomoses of the colon. Dis Colon Rectum 1984;27:767–71.
Sundqvist K, Hafström L, Persson B. Measurements of total and regional tumor blood flow and organ blood flow using99Tcm labelled microspheres: an experimental study in rats. Eur Surg Res 1978;10:433–43.
Löwenhielm P. Dynamic strain tolerance of blood vessels at different post mortem conditions. J Bioengineering 1978;2:509–15.
Jiborn H, Ahonen J, Zederfeldt B. Healing of experimental colonic anastomoses. Am J Surg 1978;136:587–94.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Grant support from the Segerfalk Foundation.
About this article
Cite this article
Graffner, H., Löwenhielm, P. & Walther, B. The healing process in high and low anterior resection of the rectum. Dis Colon Rectum 27, 772–774 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02553936
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02553936