Abstract
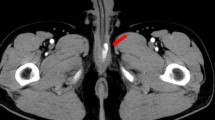
Two subtypes of priapism have been described based on the pathophysiologic mechanism. The more common type, termed stasis priapism, is characterized by a low flow state in which inadequate venous outflow creates an acidotic hypoxic environment leading to a painful prolonged erection. The other less common subtype, high flow priapism, is arteriogenic. We used embolization therapy in one case with long lasting stasis priapism and in the other with high flow priapism due to bilateral arteriosinusoidal fistulae in the penis. In both cases we used polyvinyl alcohol for embolization and sexual potency preservation.
Priapism is the persistence of erection that does not result from sexual desire. Hauri et al. described two variants of priapism [4]. In high flow priapism (non-ischaemic) there is unregulated arterial inflow to the lacunar spaces due to a lacerated cavernous artery associated with previous perineal and penile trauma. In stasis priapism, the second type, the basis abnormality could be due to a more pronounced or prolonged blood entrapment inside the vascular spaces of the corpora cavernosa sustained by an unknown cause [2]. There are many treatment methods especially for low flow ischaemic variant [3]. We report two different kinds of priapism and embolization therapy in both of them with polyvinyl alcohol.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bastuba, M. D., Tejada, I. S., Dinlenc, C. Z. Sarazen, A., Krane, R. J., Goldstein, I.: Arterial priapism: Diagnosis, treatment and long-term follow-up.J. Urol., 151, 1231 (1994).
Belgrano, E., Puppo, P., Quattrini, S., Trombetta, C., Bottina, P., Giuliani, L.: Percutaneous temporary embolization of the internal pudendal arteries in idiopathic priapism: 2 additional cases.J. Urol., 131, 756 (1984).
Gonzales, E. A., Pamplona, M., Rodriguez, A., Garcia-Hidelgo, E., Nuez, V., Leiva, O.: High flow priapism after blunt perineal trauma: Resolution with bucrylate embolization.J. Urol., 151, 426 (1994).
Hauri, D., Spycher, M. A., Bruehlmann, W.: Erection of priapism: A new physiopathological concept.Urol. Int., 38, 138 (1983).
Ravi, R., Baijal, S. S., Roy, S.: Embolotherapy of priapism.Arch. Esp. Urol., 45, 587 (1992).
Spycher, M. A., Hauri, D.: The ultrastructure of the erectile tissue in priapism.J. Urol., 135, 142 (1986).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gökta§, S., Tahmaz, L., Ata¢, K. et al. Embolization therapy in two subtypes of priapism. International Urology and Nephrology 28, 723–727 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02552172
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02552172