Abstract
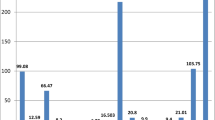
In this study sodium, potassium and chloride concentrations were analysed in the nucleus and crust parts of various kinds of urinary tract calculi. Concentrations of these elements in the nucleus were found to be higher than those in the outer crust part. Moreover, some intra- and inter-correlations were established among the elements mentioned in these two parts of the stones. It was also determined that sodium, potassium and chloride concentrations in the nucleus and crust of various urinary tract stones exhibited statistically significant differences.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Durak, I., Yasar, A., Yurtarslani, Z., Akpoyraz, M., Tasman, S.: Analysis of magnesium and trace elements in urinary calculi by atomic absorption spectrometry.Br. J. Urol., 62, 203 (1988).
Durak, I., Kilic, Z., Perk, H., Sahin, A., Yurtarslani, Z., Yasar, A., Kupeli, S., Akpoyraz, M.: Iron, copper, cadmium, zinc and magnesium contents of urinary tract stones and hairs from men with stone disease.Eur. Urol., 17, 243 (1990).
Elliot, S. J.: Structure and composition of urinary calculi.J. Urol., 109, 82 (1973).
Schales, O., Schales, S. S.: A simple and accurate method for the determination of chloride in biologic fluids.J. Biol. Chem., 140, 879 (1941).
Meyer, J. L., Smith, L. H.: Growth of calcium oxalate crystals. II: Inhibition by natural urinary crystal growth inhibitors.Invest. Urol., 13, 36 (1975).
Meyer, J. L., Thomas, W. J.: Trace metal-citric acid complexes as inhibitors of calcification and crystal growth. I: Effects of Fe(III), Cr(III) and Al(III) complexes on calcium phosphate crystal growth.J. Urol., 128, 1376 (1982).
Meyer, J. L., Thomas, W. J.: Trace metal-citric acid complexes as inhibitors of calcification and crystal growth. II: Effects of Fe(III), Cr(III), and Al(III) complexes on calcium oxalate crystal growth.J. Urol. 128, 1379 (1982).
Robertson, W. G.: Urolithiasis Research. Plenum Press, New York, 1976, pp. 5–25.
Levinson, A. A., Nosal, M., Davidman, M., Prien, E. L. Sr., Prien, E. L. Jr., Stevenson, M. G.: Trace elements in kidney stones from three areas in the United States.Invest. Urol., 15, 270 (1978).
Meyer, J. L., Angino, E. F.: The role of trace metals in calcium urolithiasis.Invest. Urol., 14, 374 (1977).
Wand, M. A. E., Pougnet, M. A. B., Rodgers, A. L.: Determination of calcium, magnesium and phosphorus in human stones by inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectroscopy.Analyst, 109, 1071 (1984).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Durak, I., Akpoyraz, M. & Sahin, A. Sodium, potassium and chloride concentrations in the inner nucleus and outer crust parts of urinary tract calculi. International Urology and Nephrology 23, 221–226 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02550415
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02550415