Abstract
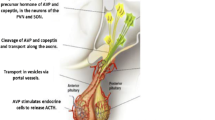
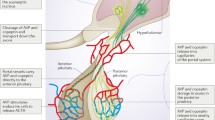
The pathogenesis of active renal stone disease (ARSD) is still not fully elucidated. In the present study the role of atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) and arginine-vasopressin (AVP) as potential pathogenetic factors in ARSD were examined. Thirty patients with ARSD and 21 healthy subjects (HS) were examined both under bed rest (BR) and head-out water immersion (WI) conditions. Serum concentrations of electrolytes (Na, Ca, Mg), ANP and AVP were assessed before (0′), and after 60 and 120 minutes of BR or WI, respectively. Urinary excretions of Na, Ca, Mg, and oxalates were also estimated during BR and WI.
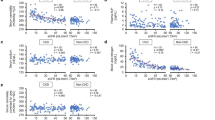
Patients with ARSD showed higher basal plasma levels of ANP and a greater response of ANP secretion, but a lower suppression of plasma AVP to WI induced hypervolaemia as compared with the controls. In addition, in patients with ARSD the physiological relationship between plasma AVP concentration and urinary excretion of Ca and Mg (positive correlation), between plasma ANP level and urinary excretion of Ca and Mg (negative correlation), and between plasma ANP and AVP concentration (negative correlation), respectively, were absent. In addition, patients with ARSD showed a positive correlation between plasma ANP and urinary oxalate excretion. From the results obtained in this study we conclude that both AVP and ANP may be involved in the pathogenesis of ARSD.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anand-Srivastava, M. B., Cantin, M., Genest, I.: Inhibition of pituitary adenylate cyclase by atrial natriuretic factor.Life Sci., 36, 1873 (1985).
Anderson, J. V., Donckier, J., Payne, N. N., Beacham, J., Slater, J. D., Bloom, S. R.: Atrial natriuretic peptide: Evidence of action as a natriuretic hormone at physiological plasma concentrations in man.Clin. Sci., 72, 305 (1987).
Biollaz, J., Nussberger, J., Porchet, M., Brunner-Ferber, F., Otterbein, E. S., Gomez, H., Waeber, B., Brunner, H. R.: Four-hour infusions of synthetic atrial natriuretic peptide in normal volunteers.Hypertension, 8, Suppl. 2, II96 (1986).
Broadus, A. E., Horst, R. L., Lang, L., Liftledike, E. T., Rasmussen, H.: The importance of circulating 1,25 dihydroxyvitamin D in the pathogenesis of hypercalciuria and renal-stone formation in primary hyperparathyroidism.N. Engl. J. Med., 302, 421 (1980).
Coe, F. L., Parks, J. H., Asplin, J. R.: The pathogenesis and treatment of kidney stones.N. Engl. J. Med., 327, 1141 (1992).
Dillingham, M. A., Anderson, R. J.: Inhibition of vasopressin action by atrial natriuretic factor.Science, 231, 1572 (1986).
Fujio, M., Ohasi, M., Nawata, M., Kato, K., Ibayashi, H., Kangawa, K., Matsuo, H.: Alpha-human atrial natriuretic polypeptide reduces the plasma arginine vasopressin concentration in human subjects.Clin. Endocrinol., 25, 181 (1986).
Gerbes, A. L., Vollmar, A. M.: Degradation and clearance of atrial natriuretic factors (ANF).Life Sci., 47, 1173 (1990).
Greenleaf, J. E., Shvartz, E., Keil, L. C.: Hemodilution, vasopressin suppression, and diuresis during water immersion in man.Aviat. Space Environ. Med., 52, 329 (1981).
Kiersztejn, M., Kuczera, M., Kokot, F.: Verhalten der Prolaktinsekretion und des 25-Hydroxy-cholecalciferolspiegels bei Kranken mit aktiver Nierensteinkrankheit.Z. Urol. Nephrol., 81, 431 (1988).
Kokot, F., Grzeszczak, W., Więcek, A.: Water immersion induced alterations of atrial natriuretic factor in patients with noninflammatory acute renal failure.Nephrol. Dial. Transplant., 4, 691 (1989).
Kokot, F., Kokot, S.: Renal stone disease—pathogenesis and therapy (in Polish).Przegl. Lek., 45, 469 (1988).
Kokot, F., Stupnicki, R.: Radioimmunological and radiocompetitive methods used in the clinical practice (in Polish), National Medical Publisher Institute, Warsaw 1985.
Kokot, F., Więcek, A., Grzeszczak, W., Szczechowska, E., Dulawa, J.: The water immersion model in nephrology.Contrib. Nephrol., 70, 107 (1989).
Kuczera, M., Kiersztejn, M., Kokot, F.: Endokrine Veränderungen bei Kranken mit aktiver Nierensteinkrankheit.Nieren-und Hochdruckkrankheiten, 22, 13 (1993).
Kuczera, M., Kiersztejn, M., Kokot, F.: Kalzitonin- und Glukagonsekretion bei aktiver Nephrolithiasis.Z. Gesamte Inn. Med., 42, 209 (1987).
Maack, T., Park, C. H., Camargo, M.: Renal filtration, transport, and metabolism of hormones. In: Seldin, D. W., Giebisch, D. (eds). The Kidney: Physiology and Pathophysiology, Raven Press, New York 1985, p. 1773.
McMurray, J., Seidelin, P. H., Struthers, A. D.: Evidence for a proximal and distal nephron action of atrial natriuretic factor in man.Nephron, 51, 39 (1989).
Michell, A. R.: Urolithiasis—historical, comparative and pathophysiological aspects: A review.J. R. Soc. Med., 82, 669 (1989).
Morel, F.: Regulation of kidney functions by hormones: A new approach.Rec. Prog. Hormone Res., 39, 271 (1983).
Preminger, G. M.: The metabolic evaluation of patients with recurrent nephrolithiasis: A review of comprehensive and simplified approaches.J. Urol., 141, 760 (1989).
Robertson, G. L.: Physiology of ADH secretion.Kidney Int., 32, Suppl. 21, 20 (1987).
Seymour, A. A., Blaine, E. H., Mazack, E. K., Smith, S. G., Stabilito, I. I., Haley, A. B., Napier, M. A., Whinnery, M. A., Nutt, R. F.: Renal and systemic effects of synthetic atrial natriuretic factor,Life Sci., 36, 33 (1985).
Smith, L. H.: Calcium-containing renal stones.Kidney Int., 13, 383 (1978).
Takagi, T., Nishikawa, M., Mori, Y., Matsubara, H., Inada, M.: Effects of atrial natriuretic peptide infusion and its metabolism in patients with chronic renal failure.Endocrinol. Jpn., 38, 497 (1991).
Weidmann, P., Hosler, L., Gnädinger, M. P., Lang, R. E., Uehlinger, D. E., Shaw, S., Rascher, W., Reubi, F. C.: Blood levels and renal effects of atrial natriuretic peptide in normal man.J. Clin. Invest., 77, 734 (1986).
Więcek, A.: Osmotyczna i nieosmotyczna regulacja wydzielania wazopresyny.Postępy Hig. Med. Dośw., 39, 195 (1985).
Woolf, A. S., Lyon, T. L., Hoffbrand, B., Cohen, S., Moult, P.: The effects of physiological infusion of atrial natriuretic factor in normal subjects and patients with nephrotic syndrome.Nephron, 54, 244 (1989).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kokot, F., Klimek, D., Wi(ecek, A. et al. Atrial natriuretic peptide and arginine-vasopressin secretion in patients with active renal stone disease. International Urology and Nephrology 30, 357–365 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02550323
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02550323