Abstract
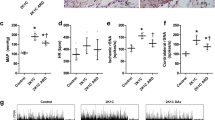
Rats had been given intraventricular injection of 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA) before clipping the unilateral renal artery (2K-1C) that caused selective ablation of the central noradrenergic neurons. Central catecholamines and thein vivo incorporation of3H-proline into vascular non-collagen protein were determined in 2K-1C rats in the acute hypertensive stage.
It is suggested that increased non-collagen protein synthesis in the mesenteric artery and the low level of hypothalamic norepinephrine concentration may participate in the development of 2K-1C hypertension in rats.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benarroch, E. E., Balda, M. S., Finkelman, S., Nahmod, V. E.: Neurogenic hypertension after depletion of norepinephrine in anterior hypothalamus induced by 6-hydroxydopamine administration into the ventral pons: role of serotonin.Neuropharmacol., 22, 29 (1983).
Bloom, F. E., Algeri, S., Groppetti, A., Revuelta, A., Costa, E.: Lesions of central norepinephrine terminals with 6-hydroxydopamine on catecholamine-containing neurons in the rat brain.J. Neurochem., 17, 269 (1970).
Bravo, E. L., Tarazi, R. C., Dustan, H. P., Fouad, F. M.: The sympathetic nervous system and hypertension in primary aldosteronism.Hypertension, 7, 90 (1985).
Brody, M. J., Barron, K. W., Berecek, K. H., Faber, J. E., Lappe, R. W.: Neurogenic mechanism of experimental hypertension. In: J. Genest, O. Kuchel, P. Hamet, M. Cantin (eds): Hypertension, Physiology and Treatment, second edition. McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York-St. Louis-San Francisco-Auckland-Bogotá-Guatemala-Hamburg-Lisbon-London-Madrid-Mexico-Montreal-New Delhi-Panama-Paris-San Juan-São Paulo-Singapore-Sydney-Tokyo-Toronto 1983, p. 117.
Chalmers, J. P., Reid, J. L.: Participation of central noradrenergic neurons in arterial baroreceptor reflexes in the rabbit. A study with intracisternally administered 6-hydroxydopamine.Circ. Res., 26, 789 (1972).
Clark, D. W. J., Jones, D. R., Phelan, E. L., Devine, C. E.: Blood pressure and vascular resistance in genetically hypertensive rats treated at birth with 6-hydroxydopamine.Circ. Res., 293 (1978).
Day, M. D., Roach, A. G.: β-adrenergic receptors in the central nervous system of the cat concerned with control of arterial blood pressure and heart rate.Nature, 242 (1973).
Finch, L., Leach, G. D. H.: The contribution of the sympathetic nervous system to the development and maintenance of experimental hypertension in the rat.Br. J. Pharmacol., 39, 317 (1970).
Folkow, B.: Physiological aspect of primary hypertension.Physiol. Rev., 62, 347 (1982).
Garrigues, A.-M., Cazala, P.: Central catecholamine metabolism.Brain Res., 265, 265 (1983).
Haeusler, G., Finch, L., Thoenen, H.: Central adrenergic neurons and the initiation and development of experimental hypertension.Experientia, 28, 1200 (1972).
Hjemdahl, P., Daleskog, M., Kahn, T.: Determination of plasma catecholamines by high performance liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection: comparison with a radioenzymatic method.Life Sci., 25, 131 (1979).
Katholi, R. E., Winternitz, S. R., Oparil, S.: Decrease in peripheral sympathetic nervous system activity following renal denervation or unclipping in the one-kidney one-clip Goldblatt hypertensive rat.J. Clin. Invest., 69, 55 (1982).
Katholi, R. E., McCann, W. P., Woods, W. T.: Intrarenal adenosine produces hypertension via nerves in the one-kidney, one-clip rat.Hypertension, 7 (Suppl. 1), 1 (1985).
Lowry, O. H., Rosenbrough, N. J., Farr, A. L., Randall, R. J.: Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent.J. Biol. Chem., 193, 265 (1951).
Maruyama, Y., Oshima, T., Nakajima, E.: Simultaneous determination of catecholamines in rat brain by reversed-phase liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection.Life Sci., 26, 1115 (1980).
Nagatsu, T., Ikuta, K., Numata, Y., Kato, T., Sano, M.: Vascular and brain dopamine β-hydroxylase activity in young genetically hypertensive rats.Science, 191, 290 (1975).
Nakada, T., Loevenberg, W.: Lysine incorporation in vessels of spontaneously hypertensive rats: effects of adrenergic drugs.Eur. J. Pharmacol., 48, 87 (1978).
Nakada, T., Yamori, Y.: The role of vascular protein and renin in chronic two-kidney, one-clip Goldblatt hypertension.Clin. Exper. Hypertension, A4(3), 477 (1982).
Nakada, T., Koike, H., Katayama, T.: Participation of central norepinephrine in the development of two-kidney, one-clip Goldblatt hypertension.J. Urol., 135, 1066 (1986).
Palkovits, M.: Isolated removal of hypothalamic or other brain nuclei of the rat.Brain Res., 59, 449 (1973).
Rascher, W., Schömig, A., Dietz, R., Weber, J., Gross, F.: Plasma catecholamine, noradrenaline metabolism and vascular response in desoxycorticosterone acetate hypertension of rats.Eur. J. Pharmacol., 75, 255 (1981).
Saavedra, J., Grobecker, H., Axelrod, J.: Changes in central catecholaminergic neurons in the spontaneously (genetic) hypertensive rat.Circ. Res., 42, 522 (1978).
Skosey, J. L., Zak, R., Martin, A. F., Aschenprenner, V., Rabinowitz, M.: Biochemical correlates of cardiac hypertrophy. V. Labeling of collagen, myosin and nuclear DNA during experimental myocardial hypertrophy in the rat.Circ. Res., 31, 145 (1972).
Virtanen, R., MacDonald, E.: Comparison of the effects of detomidine and exylazine on some α2-adrenoceptor-mediated responses in the central and peripheral nervous systems.Eur. J. Pharmacol., 115, 277 (1985).
Wagner, J., Vitali, P., Palfreyman, M. G., Zraika, M., Huot, S.: Simultaneous determination of 3,4-dihydroxyphenylamine, 5-hydroxytryptophan, dopamine, 4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenylalanine, norepinephrine, 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid, homovanillic acid, serotonin, and 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid in rat cerebrospinal fluid and by high-performance liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection.J. Neurochem., 38, 1241 (1982).
Yamabe, H., Lovenberg, W.: Increased incorporation of14C-lysine into vascular proteins of the spontaneously hypertensive rat.Eur. J. Pharmacol., 29, 109 (1974).
Yamori, Y., Nakada, T., Lovenberg, W.: Effect of antihypertensive therapy on lysine incorporation into vascular protein of the spontaneously hypertensive rat.Eur. J. Pharmacol., 38, 349 (1976).
Zimmerman, B. G., Mommsen, C., Kraft, E.: Sympathetic and renin-angiotensin system influence on blood pressure and renal blood flow of two-kidney, one-clip Goldblatt hypertensive dog.Hypertension, 2, 53 (1980).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nakada, T., Koike, H. & Katayama, T. Central noradrenergic neurons and vascular non-collagen protein in the initial phase of two-kidney, one-clip renovascular hypertension. International Urology and Nephrology 20, 439–447 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02549578
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02549578