Abstract
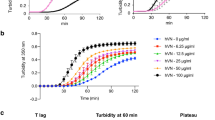
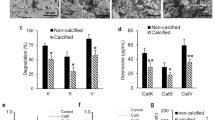
The coacervate of the N-formyl-O-methyl ester derivative of α-elastin was incubated in a calcifying medium containing bovine serum. The lag period observed before calcium phosphate formation was shown to be influenced by the conditions under which the protein matrix was formed. Tropoelastin coacervates, both blocked and unblocked, provide a matrix for calcification. A cross-linked structure is not an obligatory prerequisite for elastin calcification, nor is the pyridinium moiety of desmosine or isodesmosine. A significant advantage of thisin vitro calcifying system for coacervates is that it may be used to study the effect of various factors, such as glycoproteins, mucopolysaccharides and lipids, on the initiation of calcification.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cox, B. A., Starcher, B. C., Urry, D. W.: Coacervation of α-elastin results in fiber formation. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.)317, 209–213 (1973)
Hall, D. A.: The reaction between elastase and elastic tissue. I. The substrate. Biochem. J.59, 459–465 (1955)
Hall, D. A.: The fibrous components of connective tissue with special reference to the elastic fiber. Int. Rev. Cytol.8, 211–251 (1959)
Martin, G. R., Schiffmann, E., Bladen, H. A., Nylen, M.: chemical and morphological studies on thein vitro calcification of aorta. J. Cell Biol.16, 243–252 (1963)
Molinari Tosatti, M. P., Gotte, L., Moret, V.: Some features of the binding of calcium ions to elastin. Calcif. Tiss. Res.6, 329–334 (1971)
Partridge, S. M., Davis, H. F., Smith, D. W.: The chemistry of connective tissue. 2. Soluble proteins derived from partial hydrolysis of elastin. Biochem. J.61, 11–21 (1955)
Rucker, R. B., Goettlich-Riemann, W., Tom, K.: Properties of chick tropoelastin. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.) 193–201 (1973)
Schiffmann, E., Martin, G. R., Corcoran, B. A.: The role of the matrix in aortic calcification. Arch. Biochem. Biophys.107, 284–291 (1964)
Smith, D. W., Brown, D. M., Carnes, W. H.: Preparation and properties of salt-soluble elastin. J. biol. Chem.247, 2427–2432 (1972)
Starcher, B., Hill, C. H., Matrone, G.: Importance of dietary copper in the formation of aortic elastin. J. Nutr.82, 318–322 (1964)
Starcher, B. C., Saccomani, G., Urry, D. W.: Coacervation and ion binding studies on aortic elastin. Biochem. biophys. Acta (Amst.)310, 481–486 (1973)
Starcher, B. C., Urry, D. W.: elastin coacervate as a matrix for calcification. Biochem. biophys. Res. Commun.53, 210–216 (1973)
Sykes, B. C., Partridge, S. M.: Isolation of a soluble elastin from lathyritic chicks. Biochem. J.130, 1171–1172 (1972)
Termine, J. D., Posner, A. S.: Calcium phosphate formationin vitro I. Factors affecting initial phase separation. Arch. Biochem. Biophys.140, 307–317 (1970)
Thomas, J., Elsden, D. F., Partridge, S. M.: Partial structure of two major degradation products from the cross-linkages in elastin. Nature (Lond.)200, 651–652 (1963)
Urry, D. W.: Nautral sites for calcium ion binding to elastin and collagen: A charge neutralization theory for calcification and its relationship to atherosclerosis. Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. (Wash.)68, 810–814 (1971)
Urry, D. W.: In: Advances in experimental medicine and biology (Clarkson, T. V., ed.), vol. 43, p. 211–243, New York: Plenum Publishing Company 1974
Urry, D. W., Cunningham, W. D., Ohnishi, T.: A neutral polypeptide-calcium ion complex. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.)292, 853–857 (1973)
Urry, D. W., Ohnishi, T.: Bioinorganic Chem.3, 305–313, 1974 (in press)
Yu, S. Y., Blumenthal, H. T.: The calcification of elastic fibers. I. Biochemical studies. J. Gerontol.18, 119–126 (1963)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Starcher, B.C., Cox, B.A. & Urry, D.W. Development of anin vitro system for the calcification of tropoelastin and α-elastin coacervates in serum. Calc. Tis Res. 17, 1–7 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02547210
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02547210