Abstract
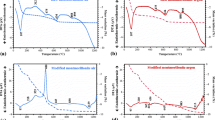
Thomsonite with ideal chemical composition and with an ordered framework structure was synthesised hydrothermally from zeolite Na−A, which was ground to X-ray amorphous, with 0.05 mol dm−3 CaCl2 solution at 200°C. The dehydration behaviour of the prepared thomsonite was examined by TG-DTA. It was revealed that thomsonite lost most of zeolitic water below 450°C in three steps at about 180°, 340° and 390°C. The peak profiles of, the two higher-temperature endotherms were sharp and similar, and the weight loss at each step was approximately equal.
Zusammenfassung
Aus Zeolith Na−A, welches mittels einer 0,05 molaren CaCl2-Lösung bei 200°C röntgenographisch amorph gemahlen wurde, stellte man auf hydrothermischem Wege Thomsonit mit idealer chemischer Zusammensetzung und mit einer geordneten Gitterstruktur her. Das Dehydratationsverhalten des hergestellten Thomsonits wurde mittels TG/DTA untersucht. Es wurde gezeigt, daß Thomsonit unter 450°C, in drei Schritten: bei 180°, 340° und bei 390°C einen Großteil Zeolith-Wasser verliert. Die Peakverläufe der zwei Endothermen bei höheren Temperaturen sind scharf und ähneln sich und der Gewichtsverlust ist bei jedem Schritt etwa gleich.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. Gottardi and E. Galli, Natural Zeolites, Springer-Verlag, Berlin 1985, p1.
W. S. Wise and R. W. Tschernich, Can. Miner., 16 (1978) 487.
R. M. Barrer and P. J. Denny, J. Chem. Soc. (London), (1961) 983.
V. C. Juan and H. J. Lo, Proc. Geol. Soc. China, 12 (1969) 21.
U. Wirsching, Clays and Clay Miner., 29 (1981) 171.
L. P. van Reeuwijk The Thermal Dehydration of Natural Zeolites, Medelingen Landbouwhogeschool Wageningen, Nederland, 1974, p1.
G. Engelhardt and D. Michel, High Resolution Solid-State NMR of Silicates and Zeolites, John Wiley and Sons, New York 1987, p. 213.
J. J. Pluth, J. V. Smith and A. Kvick, Zeolites, 5 (1985) 74.
E. Lippmaa, M. Magi, A. Samoson and G. Engelhardt, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 108 (1981) 4992.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yamazaki, A., Inoue, Y., Koike, M. et al. Preparation and dehydration behaviour of thomsonite with ideal chemical composition. Journal of Thermal Analysis 40, 85–97 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02546558
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02546558