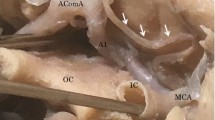
Summary
Both the Heubner's artery and the perforating branches of the anterior cerebral artery (ACA) were present in all thirty-three examined brains. Heubner's arteries varied in number from 1 to 3. They originated from the distal (A2) segment of the ACA in 34% of the cases, from the proximal (A1) segment of the ACA in 17%, at the level of the anterior communicating artery in 21%, from the fenestration of the ACA in 8%, and in all the other cases (20%) from the azygous anterior cerebral artery, accessory middle cerebral artery, frontopolar artery and, finally, by the common stem with the medial orbitofrontal artery. Heubner's artery most commonly terminated dorsal and lateral to the carotid bifurcation, at an average distance of 4.8 mm. The mean diameter of Heubner's artery was 662 μm, that of its extracerebral collateral branches 205 μm, of the terminal branches 462 μm, and of the intracerebral segments 354 μm. Perforating branches varied in number from 1 to 12 with an average of 6.6. The majority of the branches originated from the initial 6.1 mm of the A1 segment. These vessels terminated close to the carotid bifurcation, at an average distance of 3.8 mm. All the perforating branches were divided into small (average 122 μm in diameter) and large (average 325 μm). The mean diameter of intracerebral segments was 276 μm, and that of terminal branches 259 μm. It was concluded that the anatomical characteristics of both the recurrent artery and the perforating branches can be of a great significance in cerebrovascular diseases.
Résumé
L'artère de Heubner et les rameaux perforants de l'artère cérébrale antérieure (ACA) ont été observés sur les 33 cerveaux examinés. L'artère de Heubner varie en nombre de 1 à 3 par hémisphère; cette artère prend naissance de la portion distale (A2) de l'ACA dans 34% des cas, de la portion proximale (A1) dans 17%, du niveau de l'artère communicante antérieure dans 21%, d'une fenestration de l'ACA dans 8%; dans les 20% des cas restants l'artère est issue du tronc azygos de l'ACA, de l'artère cérébrale moyenne accessoire, de l'artère fronto-polaire ou d'un tronc commun avec l'artère orbito-frontale médiale. La terminaison habituelle de l'artère de Heubner se situe en arrière et en dehors de la carotide interne à une distance moyenne de 4,8 mm. Le diamètre moyen de l'artère de Heubner est de 662 μm, des collatérales extracérébrales de 205 μm, des branches terminales de 462 μm, et des branches intracérébrales de 354 μm. Le nombre de rameaux perforants de l'ACA varie de 1 à 12 (6,6 en moyenne); la plupart d'entre eux naissent de la partie initiale du segment A1 qui mesure 6,1 mm, et se terminent près de la carotide interne à une distance moyenne de 3,8 mm.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Choudhury, AR (1976) Proximal occlusion of the dominant anterior cerebral artery for anterior communicating aneurysm. J Neurosurg 45: 484–490
Crompton MR (1962) The pathology of ruptured middle-cerebral aneurysms with special reference to the differences between the sexes. Lancet 2: 421–425
Fisher CM (1982) Lacunar strokes and infarcts: A review. Neurology (Ny) 32: 871–876
Gomes F, Dujovny M, Umansky F, Ausman JI, Diaz FG, Ray WJ, Mirchandani HG (1984) Microsurgical anatomy of the recurrent artery of Heubner. J Neurosurg 60: 130–139
Hamby WE (1969) Intracranial surgery for aneurysms. In: Krayenbühl H, Maspes PE, Sweet WH (eds) Progress in neurological surgery, Vol. 3, Karger, Basel
Hockley AD (1975) Proximal occlusion of the anterior cerebral artery for anterior communicating aneurysm. J Neurosurg 43: 426–431
Kaplan HA (1965) The lateral perforating branches of the anterior and middle cerebral arteries. J Neurosurg 23: 305–310
Kaplan HA (1975) The anatomy of the perforating arteries of the basal ganglia. In: Salamon G (ed) Advances in cerebral angiography. Springer Verlag, Berlin
Krayenbühl H, Yasargil MG (1979) Zerebrale Angiographie für Klinik und Praxis, 3rd ed. Georg Thieme Verlag, Stuttgart
Lazorthes G, Salamon G, Gouazé A, Zadeh J (1975) The central arteries of the brain. Classification and territories of vascular supply. In: Salamon G (ed) Advances in cerebral angiography. Springer Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York, Tokyo
Lazorthes G, Gouazé A, Salamon G (1976) Vascularisation et circulation de l'encéphale. Masson, Paris
Leeds NE (1974) The striate (lenticulostriate) arteries and the artery of Heubner. In: Newton, TH, Potts DG (eds) Radiology of the skull and brain, Vol. 2, Book 2. CV Mosby Co, Saint Louis
Lin JP, Kricheff II (1974) The anterior cerebral artery complex. Normal anterior cerebral artery complex. In: Newton TH, Potts DG (eds) Radiology of the skull and brain, Vol. 2, Book 2. CV Mosby Co, Saint Louis
Mohr JP (1982) Progress in cerebrovascular disease. Lacunes. Stroke 13: 3–10
Ostrowski AZ, Webster JE, Gurdjian ES (1960) The proximal anterior cerebral artery: an anatomic study. Arch Neurol 3: 661–664
Perlmutter D, Rhoton AL (1976) Microsurgical anatomy of the anterior cerebral-anterior communicating-recurrent artery complex. J Neurosurg 45: 259–272
Rascol A, Clanet M, Manelfe C, Guiraud B, Bonafe A (1982) Pure motor hemiplegia: CT study of 30 cases. Stroke 13: 11–17
Rosner SS, Rhoton AL, Ono M, Barry M (1984) Microsurgical anatomy of the anterior perforating arteries. J Neurosurg 61: 468–485
Sundt TM, Kobayashi SH, Fode NC (1982) Results and complications of surgical management of 809 intracranial aneurysms in 722 cases. Related and unrelated to grade of patient, type of aneurysms, and timing surgery. J Neurosurg 56: 753–765
Weisberg LA (1982) Lacunar infarcts. Clinical and computed tomographic correlations. Arch. Neurol 39: 37–40
Westberg G (1963) The recurrent artery of Heubner and the arteries of the central ganglia. Acta Radiol (diagn) 1: 949–954
Wollschlaeger G, Wollschlaeger PB (1974) The circle of Willis. In: Newton TH, Potts DG (eds) Radiology of the skull and brain, Vol 2, Book 2. CV Mosby Co, Saint Louis
Yasargil MG, Smith RD, Young PH, Teddy PJ (1984) Microneurosurgery, Vol 1. Georg Thieme Verlag, Stuttgart.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marinković, S., Milisavljević, M. & Kovačević, M. Anatomical bases for surgical approach to the initial segment of the anterior cerebral artery. Surg Radiol Anat 8, 7–18 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02539703
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02539703