Abstract
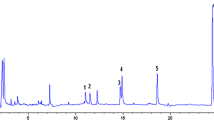
A method for quantitative determination of trace amounts of alkylphenol ethoxylates (APE) in environmental water is described. Levels of 1 to 3 μg/L can be detected and resolved into their complete oligomer distribution (1EO to 18EO) while maintaining integrity of the oligomer distribution. This is a major improvement over previous methods; for the first time distortion of oligomer distribution due to work-up conditions of earlier methods has been prevented.
Isolation of the APE from water is achieved using a simple and rapid dual-column procedure. The first column removes interfering ionic materials, the second traps the APE on alkyl-bonded silica. Assay of the extract employs HPLC with a fluorescence detector.
The method was used for analyzing treated waste-water and river water. A much better picture of the biodegradation behavior of APE in the environment has emerged as a result of keeping APE oligomer distribution intact during sample extraction. There is no accumulation of alkylphenol and the low EO oligomers during wastewater treatment, although the oligomer distribution may become skewed toward these species. Concentrations in the receiving waters examined were very low, in the range of 1–2 μg/L total APE species (OEO to 18EO).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Swisher, R.D.,Surfactant Biodegradation, Surfactant Science Series Vol. 18, Marcel Dekker, 1987, pp. 493, 854.
Synthetic Organic Chemicals, United States Production and Sales, 1988; USITC Publication 2219, Sept. 1989. U.S. International Trade Commission, Washington, DC 20436.
Giger, W., E. Stephanou and C. Schaffner,Chemosphere 10 (11/12):1253 (1981).
Stephanou, E., and W. Giger,Environ. Sci. Technol. 16 (11): 800 (1982).
Ahel, M., and W. Giger,Anal. Chem. 57 (8): 1577 (1985).
Ahel, M., and W. Giger,:2584 (1985).
Kudoh, M., H. Ozwa, S. Fudano and K. Tsuji,J. Chromatog. 287:337 (1984).
Holt, M.S., E.H. McKerrell, J. Perry and R.J. Watkinson,362:419 (1986).
Yoshimura, K.,J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 63(12):1590 (1986).
Brown, D., H. DeHenau, J.T. Garrigan, P. Gericke, H. Holt, E. Kunkel, E. Matthys, J. Waters and R.J. Watkinson,Tenside 24(1):14 (1987).
Marcomini, A., S. Capri and W. Giger,J. Chromatogr. 403:243 (1987).
Ahel, M., W. Giger and M. Koch,Commun. Eur. Communities [Rep.]: 414 (1986).
Giger, W., P.H. Brunner and C. Schaffner,Science 225:623 (1984).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Kubeck, E., Naylor, C.G. Trace analysis of alkylphenol ethoxylates. J Am Oil Chem Soc 67, 400–405 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02539698
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02539698