Abstract
Air-flow works on the lake's water body which results in winddriven water circulation and wind waves This is a summary of work done by LHYDREP on the physical limnological aspect of the Leman. General information on the basin of the Leman is given in chapter 1. Subsequently in chapter 2 the measuring programme is presented, discussing the measuring positions, the measuring installations and the instruments used of the three campaigns. The data obtained during these campaigns are subsequently interpreted.
In chapter 3 the atmospheric dynamics over the lake is discussed. It deals mainly with the mechanical energy transfer process which is represented here (as usually) by the drog coefficient, Cy. It is shown that the airflow velocity, the fetch Reynolds number and the air stability play important roles.
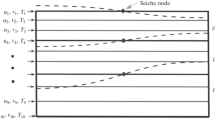
In chapter 4 the hydrodynamics of the lake is presented. Predictions of numerical hydrodynamical models of steady-state circulation (chapter 4.2), of storm surges and of seiches (chapter 4.3) and of inertial currents (chapter 4.4) are compared with available data of the Leman during the homogeneous season. In addition a preliminary study of wind waves (chapter 4.5) is given.
Zusammenfassung
Zur Hydrodynamik des Genfersees Diese Schrift ist eine Zusammenfassung von physikalisch-limnologischen Arbeiten des LHYDREP am Genfersee. Das Windfeld über dem See treibt die Strömungen im See und erzeugt Oberflächenwellen. Allgemeines über den See und sien Becken wird in Kapitel 1 vorgestellt. Darauf folgend ist in Kapitel 2 das Messprogramm erklärt: Messpunkte, Messinstallation und Messinstrumente der drei ausgeführten Messkampagnen.
In Kapitel 3 ist die atmosphärische Dynamik behandelt. Diese beschäftigt sich mit der Energieübertragung von der Luft ins Wasser; wie üblich, ist dies auch hier mit dem Schubspannungs-Koeffizienten, Cy, ausgedrückt. Gezeigt wird, dass Windgeschwindigkeit, “fetch”-Reynolds-Zahl und Luftstabilität eine wichtige Rolle spielen.
In Kapitel 4 wird die Hydrodynamik des Sees betrachtet. Die folgenden vereinfachten Modelle wurden mit vorhandenen Daten verglichen: a) numerisch-hydrodynamische Modelle für stationäre Zirkulation (Kap. 4.2), für Windanstau und Seiches (Kap. 4.3) und b) analytische Lösungen für Inertie-Ströme (Kap. 4.4). Eine vorläufige Studie über Oberflächenwellen ist im Kapitel 4.5 angefügt.
Résumé
L'hydrodynamique du Léman Ces lignes résument succinctement le travail relatif à la limnologie physique du Léman, fait par le LHYDREP. Les vents agissant sur le lac génèrent des courants et des vagues. Une description “orientée” du bassin lémanique fait l'objet du chapitre 1. Au chapitre 2 est présenté le programme de mesures, incluant une discussion sur les emplacements des stations, les installations de mesure et les instruments utilisés dans les trois campagnes exécutées. Les résultats obtenus sont commentés.
Au chapitre 3 est analysée la dynamique atmosphérique sur le lac. Ce chapitre traite principalement des transferts d'énergie mécanique habituellement groupés dans le coefficient de traînée, Cy. Est démontrée l'importance de la vitesse du vent, du nombre de Reynolds, du fetch et de la stabilité atmosphérique.
Au chapitre 4 est discutée l'hydrodynamique du lac. Les résultats, obtenus à l'aide de modèles hydrodynamiques de circulation stable (ch. 4.2), de “storm surges”, de seiches (ch. 4.3) et de courants d'inertie (ch.4.4) sont comparés aux mesures faites en lac homogène (thermiquement). Une étude préliminaire des vagues de vent (ch.4.5) est aussi présentée.
Similar content being viewed by others
Bibliography Contributions of LHYDREP
Prost, J.-P., Bauer, S.W., Graf, W.H., and Girod, H.: campagne de mesures des courants dans le Léman. Bull. tech. Suisse romande103/19 (1977).
Bauer, S.W., Graf, W.H., and Tischer, E.: Les courants dans le Léman en saison froide—une simulation mathématique. Bull. tech. Suisse romande103/19 (1977).
Bruschin, J., and Schneiter, L.: Caractéristiques des vagues dans les lacs profonds. Bull. tech. Suisse romande104/19 (1978).
Bauer, S.W., and Graf, W.H.: Wind induced water circulation of Lake Geneva. In: Nihoul, J.C.J. (ed.): Marine Forecasting. Elsevier Scientific Publishing Company, Amsterdam 1979.
Graf, W.H., Perrinjaquet, C., Bauer, S.W., Prost, J.P., and Girod, H.: Measuring on Lake Geneva. In: Graf, W.H., and Mortimer, C.H. (ed): Hydrodynamics of Lakes. Elsevier Scientific Publishing Company, Amsterdam 1979.
Bauer, S.W., and Perrinjaquet, C.: Data band and-visualization for sequential data with special reference to Lake Geneva. In: Graf, W.H., and Mortimer, C.H. (ed): Hydrodynamics of Lakes. Elsevier Scientific Publishing Company, amsterdam 1979.
Graf, W.H., and Prost, J.P.: The aerodynamic drag; first experiments on Lake Geneva. In: Graf, W.H., and Mortimer, C.H. (ed.): Hydrodynamics of Lakes, Elsevier Scientific Publishing Company, Amsterdam 1979a.
Bruschin, J., and Schneiter, L.: Wind waves in the bay of Geneva. In: Graf, W.H., and Mortimier, C.H. (ed.): Hydrodynamics of Lakes. Elsevier Scientific Publishing Company, Amsterdam 1979.
Bauer, S.W.: Three-dimensional simulation of time dependent elevations and currents in a homogeneous lake of arbitrary shape using an irregular-grid finite-difference model. In: Graf, W.H., and Mortimer, C.H. (ed.): Hydrodynamics of Lakes. Elsevier Scientific Publishing Company Amsterdam 1979a.
Graf, W.H., and Prost, J.P. Frottement aérodynamique sur un lac. Seminar paper; XVIII Congr. int. Ass. Hydr. Res.6, Cagliary, Italy (1979).
Bauer, S.W.: Three-dimensional irregular-grid finite-difference model of wind induced water level fluctuations and currents in a homogeneous lake with applications to the Lake of Geneva. Thèse de doctorat No. 335, Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale, Lausanne, Suisse 1979 (also appeared as: Communication du Laboratoire d'hydraulique No. 41. 1980).
Graf, W.H., and Prost, J.P.: Aerodynamic drag and its relation to the sea-state; with data from Lake Geneva. Arch. Met. Geoph. Biokl. (A)29 (1980)
Prost, J.P., Perrinjaquet, C., and Beguin, Ph.: Campagne de mesures de la basse couche atmosphérique sur le Léman. Bull. tech. Suisse romande106/23 (1980).
Bauer, S.W., Graf, W.H., Mortimer, C.H., and Perrinjaquet, C.: Inertial Motion in Lake Geneva. Arch. Met. Geoph. Biokl. (A)30 (1981).
Bauer, S.W., Graf, W.H., Mortimer, C.H., and Perrinjaquet, C.: Courants d'inertie dans le Léman. Bull. tech. Suisse romande106/6 (1981).
References
Boullery, B.: Etude expérimentale du coefficient de frottement pour un fetch court et en régime de vent faible. Bull. Dir. Etudes Rech. Electricité France (A)1 (1977).
Businger, J.: Turbulent Transfer in the Atmospheric Surface Layers. In: Hangen, D. (ed.): Workshop of Micrometerology. Am. Meteor. Soc. (1973).
Coantic, M.F.: An Introduction to Turbulence in Geophysics and Air-Sea Interaction. Agardograph232, AGARD-NATO (1978).
Forel, F.A.: Le Léman; monographie limnologique, tome 2. Ed. F. Rougé, Lausanne (1895).
Hamblin, P.F.: Seiches, Circulation and Storm Surges of an Ice-Free Lake Winnipeg. J. Fish. Res. Bd. Canada33 (1976).
Kitaigorodskii, S.A.: The Physics of Air-Sea Interactions15, Israel Progr. Sci. Transl, Jerusalem 1973.
Kraus, E.B.: Atmosphere-Ocean Interaction. Oxford Monographs in Meteorology. Clarendon Press, Oxford 1972.
Mortimer, C.H.: Strategies for Coupling of Data Collection and Analysis with Dynamic Modelling of Lake Motion. In: Graf, W.H., and Mortimer, C.H. (ed.): Elsevier Scientific Publishing Company, Amsterdam 1979.
Neumann, G., and Pierson, W.: Principles of Physical Oceanography. Prentice-Hall Inter., Inc., N. J., USA 1966.
Plate, E.J.: Aerodynamic Characteristics of Amtospheric Boundary Layers. US Atomic Energy Commission, TID-25465 (1971).
Schlichting, H., Boundary Layer Theory. McGraw Hill, New York. 1968.
Schwind, J.J.: Geophysical Fluid Dynamics for Oceanographers. Prentice-Hall Inc., Englewood Cliffs, N.J., USA 1954.
Service Fédéral des eaux (SFdE): Les dénivellations du Lac Léman Dépt. féd. des ports et des chemins de fer, Bern 1954.
Simons, T.J.: Circulation Models of Lakes and Inland Waters. Can. Bull. Fish. Aquat. Sci.203 (1980).
Smith, S.D.: Wind Stress and Heat Flux over the Ocean in Gale Force Winds. J. Phys. Oceanogr.10/5 (1980).
Stewart, R.W.: The Air-Sea Momentum Exchange. Boundary-Layer Meteorology6, 151–167 (1974).
Sündermann, J.: Numerical Modelling of Circulation in Lakes., In: Graf, W.H., and Mortimer, C.H. (ed.): Hydrodynamics of Lakes, Elsevier Scientific Publishing Company, Amsterdam 1979.
Tennekes H., and Lumley, J.: A First Course in Turbulence MIT-Press, Cambridge 1972.
US Army Coastal Engineering Research Center: Shore Protection Manual1. Dpt. of Army, Corps of Engineers (1975).
Wiegel, R.L.: Oceanographical Engineering. Prentice-Hall, N.J., USA (1964).
Wu, J.: Wind Stress Coefficient over Sea Surface near Neutral Conditions—A Revisit. J. Phys. Oceanogr.10/5 (1980).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Graf, W.H. Hydrodynamics of the Lake of Geneva. Schweiz. Z. Hydrologie 45, 62–100 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02538152
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02538152