Abstract
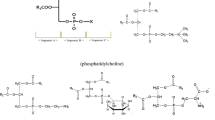
A method for the simultaneous determination of the main molecular species of soybean phosphatidylcholine or phosphatidylethanolamine and their corresponding hydroperoxides is described. Hydroperoxides were formed by incubation of phospholipids with lipoxygenase at pH 9.2. Silicic acid column chromatography (silica Sep-Pak column) was used to separate the phospholipids into phosphatidylcholine and phosphatidylethanolamine. A single C−18 reverse-phase column was employed to separate the main molecular species of soybean phosphatidylcholine or phosphatidylethanolamine and their hydroperoxides by high-performance liquid chromatography. The mobile phase consisted of 5% 10 mM ammonium acetate at pH 5 and 95% methanol. The molecular species of phosphatidylcholine and phosphatidylethanolamine were detected at 205 nm; the eluate was mixed with a chemiluminescence reagent (isoluminol and microperoxidase) and monitored by fluorometry. Under the experimental conditions used, three individual molecular species of both soybean phosphatidylethanolamine and phosphatidylcholine (18∶3/18∶2, 18∶2/18∶2 and 16∶0/18∶2), together with their corresponding hydroperoxides, were identified and quantitated.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CL:
-
chemiluminescence
- GLC:
-
gas-liquid chromatography
- 15-HPETE:
-
15-hydroperoxyeicosatetraenoic acid
- HPLC:
-
high-performance liquid chromatography
- MTBE:
-
methyl tertiarybutyl ether
- PC:
-
phosphatidylcholine
- PCOOH:
-
phosphatidylcholine hydroperoxides
- 16∶0/18∶2 PC:
-
1-palmitoyl-2-linoleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine
- 18∶0/20∶4 PC:
-
1-stearoyl-2-arachidonoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine
- 18∶2/18∶2 PC:
-
1,2-dilinoleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine
- 18∶3/18∶2 PC:
-
1-linolenoyl-2-linoleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine
- PE:
-
phosphatidylethanolamine
- PEOOH:
-
phosphatidylethanolamine hydroperoxides
- RP:
-
reverse-phase
- UV:
-
ultraviolet
References
Yagi, K. (1976)Biochem. Med. 15, 212–216.
Bird, R.P., Hung, S.S.O., Hadley, M., and Draper, H.H. (1983)Anal. Biochem. 128, 240–244.
Therasse, J., and Lemonnier, F. (1987)J. Chromatogr. (Biomed. Appl.) 413, 237–241.
Lepage, G., Munoz, G., Champagne, J., and Roy, C. (1991)Anal. Biochem. 197, 277–289.
Janero, D.R. (1990)Free Rad. Biol. Med. 9, 515–540.
Gutteridge, J.M.C., and Halliwell, B. (1990)Trends Biochem. Sci. (TIBS) 15, 129–135.
Valenzuela, A. (1991)Life Sciences 48, 301–309.
Corongiu, F.P., and Milia, A. (1983)Chem. Biol. Interact. 44, 289–292.
Thomas, P.D. (1990)Anal. Biochem. 188, 228–232.
Jlang, Z.Y., Woollard, A.C.S., and Wolff, S.P. (1991)Lipids 26, 853–856.
Yamamoto, Y., Brodsky, M.H., Baker, J.C., and Ames, B.N. (1987)Anal. Biochem. 160, 7–13.
Miyazawa, T., Yasuda, K., and Fujimoto, K. (1987)Anal. Lett. 20, 904–925.
Miyazawa, T. (1989)Free Rad. Biol. Med. 7, 209–217.
Müllertz, A., Schmedes, A., and Hølmer, G. (1990)Lipids 25, 415–418.
Patton, G.M., Fasulo, J.M., and Robins, S.J. (1982)J. Lipid Res. 23, 190–196.
Hullin, F., Kim, H.Y., and Salem, N., Jr. (1989)J. Lipid Res. 30, 1963–1975.
Glass, R.L. (1990)J. Agric. Food Chem. 38, 1684–1686.
Eskola, J., and Laaskso, S. (1983)Biochim. Biophys. Acta 751, 305–311.
Hamilton, J.G., and Comai, K. (1988)Lipids 23, 1146–1149.
Picard, J., Veissiere, D., Voyer, F., and Bereziat, G. (1972)Clin. Chim. Acta 36, 247–250.
Brash, A.R., Ingram, C.D., and Harris, T.M. (1987)Biochemistry 26, 5465–5471.
Yamamoto, Y. (1990)Methods Enzymol. 186, 371–380.
Crawford, C.G., Plattner, R.D., Sessa, D.J., and Rackis, J.J. (1980)Lipids 15, 91–94.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Therond, P., Couturier, M., Demelier, JF. et al. Simultaneous determination of the main molecular species of soybean phosphatidylcholine or phosphatidylethanolamine and their corresponding hydroperoxides obtained by lipoxygenase treatment. Lipids 28, 245–249 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02536647
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02536647