Abstract
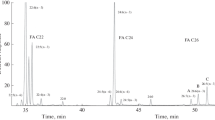
There is a considerable gap in current knowledge of the lipid composition of snails and slugs, both of which belong to the phylum Mollusca. We have therefore analyzed the sterol and fatty acid compositions of three species of slugs and three species of snails. The sterols of slugs included eight different sterols: cholesterol contributed 76–85% of the total sterols, brassicasterol accounted for 4–13%; other sterols we identified were lathosterol, 24-methylene cholesterol, campesterol, stigmasterol, sitosterol and sitostanol. In contrast, snails contained two additional sterols, desmosterol and cholestanol. Of the polyunsaturated fatty acids in slugs, linoleic (18∶2n−6) and arachidonic acids (20∶4n−6) were the major n−6 fatty acids, while linolenic (18∶3n−3) and eicosapentaenoic acids (20∶5n−3) were the predominant n−3 fatty acids. Docosahexaenoic acid (22∶6n−3), the end product in the n−3 fatty acid synthetic pathway and an important membrane fatty acid of mammals, fish and birds, was absent in both slugs and snails. However, the analogous product of n−6 fatty acid synthesis, 22∶5n−6, was found in both snails and slugs. This raises speculation about preference for n−6 fatty acid synthesis in these species. Our data show the unique sterol and fatty acid compositions of slugs and snails, as well as similarities and differences in sterol composition between the two. The results between the two land mollusks are contrasted with those of marine mollusks, such as oysters, clams and scallops.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- TLC:
-
thin-layer chromatography
References
Connor, W.E., and Lin, D.S. (1981)Gastroenterology 81, 276–284.
Connor, W.E., and Lin, D.S. (1982)Metabolism 31, 1046–1051.
Connor, W.E., and Connor, S.L. (1990)Adv. Intern. Med. 35, 139–172.
El-Wakil, H.B., and Radwan, M.A. (1991)J. Environ. Sci. Health B 26, 479–489.
Aloisi, J.D., Fried, B., and Sherma, J. (1991)Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 1100A, 203–204.
Nabih, I., Soliman, A.M., and Abdel-Hamid, A.Z. (1989)Cell. Molec. Biol. 35, 373–377.
Allan, D., Payares, G., and Evans, W.H. (1987)Molec. Biochem. Parasitol. 23, 123–128.
Oudejans, R.C.H.M., and Horst, D.J.V.D. (1974)Lipids 9, 798–803.
Furlong, S.T. and Caufield, J.P. (1988)Experimental Parasitol 65, 222–231.
Fried, B., Beers, K., and Lewis, Jr., P.D. (1991)Int. J. Parasitol. 23, 129–131.
Park, Y.Y., Fried, B., and Sherma, J. (1991)Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 100B, 127–130.
Fried, B., Rao, K.S., Sherma, J., Huffman, J.E. (1993)Parasitol. Res. 79, 471–474.
Thompson, Jr., G.A. (1966)Biochemistry 5, 1290–1296.
Thompson, Jr., G.A., and Hanahan D.J. (1963)J. Biol. Chem. 238, 1628–1631.
Kozloff, E.N. (1976)Plants and Animals of the Pacific Northwest, pp. 80–205, University of Washington Press, Seattle.
Folch, J., Lees, M., and Stanley, G.H.S. (1957)J. Biol. Chem. 266, 497–509.
Lin, D.S., Connor, W.E., and Phillipson, B.E. (1984)Gastroenterology 86, 611–617.
Haust, H.L., Kuksis, A., and Beveridge, J.M.R. (1966)Can. J. Biochem. 44, 119–128.
Connor, W.E., Neuringer, M., and Lin, D.S. (1990)J. Lipid Res. 31, 237–247.
Morrison, W.R., and Smith, L.M. (1964)J. Lipid Res. 5, 600–608.
Levin, E., and Head, C. (1965)Anal. Biochem. 10, 23–31.
Cook, R.P. (1958)Cholesterol, p. 4, Academic Press, New York.
Myant, N.B. (1981)The Biology of Cholesterol and Related Steroids, pp. 152–153, William Heinemann Medical Books Ltd., London.
Neuringer, M., Connor, W.E., Lin, D.S., Barstad, L., and Luck, S. (1986)Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 83, 4021–4025.
Lin, D.S., Connor, W.E., Wolf, D.P. Neuringer, M., and Hachey, D.L. (1993)J. Lipid Res. 34, 491–499.
Gibson, R.A. (1992) inEssential Fatty Acids and Eicosanoids, Invited Papers from the Third International Congress (Sinclair, A., ed.) pp. 210–213, American Oil Chemists' Society, Champaign.
Weinert, J., Blomquist, G.J., and Borgeson, C.E. (1993)Experientia 49, 919–921.
Voss, A., Reinhart, M., Sankarappa S., and Sprecher, H. (1991)J. Biol. Chem. 266, 19995–20000.
Lin, D.S., Anderson, G.J., and Connor, W.E. (1991)J. Nutr. 121, 1924–1931.
Thompson, P.A., Hanison, T.P.J., and Whyte, J.N.C. (1990)J. Physiol. 26, 278–288.
Schener, P.J. (1978)Marine Natural Products, Chemical and Biological Perspectives, pp. 101–105, 122–124, Academic Press, New York.
Douglass, T.S., Connor, W.E., and Lin, D.S. (1981)J. Lipid Res. 22, 961–970.
Albro, P.W., Schroeder, J.L., and Corbett, J.T. (1992)Lipids 27, 136–143.
Idler, D.R., and Wiseman, P. (1970)Comp. Biochem Physiol. 35, 679–687.
Lin, D.S., Ilias, A.M., Connor, W.E., Caldwell, R.S., Cor, H.T., and Daves, G.D. (1982)Lipids 17, 818–824.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, N., Dai, X., Lin, D.S. et al. The lipids of slugs and snails: Evolution, diet and biosynthesis. Lipids 29, 869–875 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02536255
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02536255