Abstract
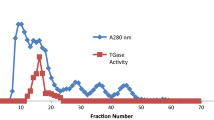
A rat liver cytosolic cholesteryl ester hydrolase (CEH) was purified 12,600-fold by ammonium sulfate precipitation, cation exchange chromatography and gel permeation high-performance liquid chromatography, with an overall yield of 20%. Its properties are compared to those of pancreatic CEH, with which it has sometimes been identified. Liver CEH exhibited a single silver stained band following SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (Mr=66 kDa), was activated by 0.5–10 mM taurocholate but was strongly inhibited by higher levels of taurocholate, which activate pancreatic CEH. Whereas bile salts are known to induce formation of a hexamer of pancreatic CEH, in the current study, 0.5 mM taurocholate dissociated a multimeric form of liver CEH to monomer. Liver CEH did not coelute with pancreatic CEH from cation exchange and chromatofocusing columns, exhibited no immunoreactivity with anti-rat pancreatic CEH IgG in Western blots, was not inhibited by anti-rat pancreatic CEH IgG and had a different amino acid composition from pancreatic CEH. In contrast to liver CEH, which is known to be activated by protein kinases A and C, pancreatic CEH was unaffected by cofactors for protein kinase A and was inhibited by cofactors for protein kinase C.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- cAMP:
-
adenosine 3′,5′-cyclic monophosphate
- CEH:
-
cholesteryl ester hydrolase
- FPLC:
-
fast protein liquid chromatography
- GPHPLC:
-
gel permeation high-performance liquid chromatography
- pI:
-
isoelectric point
- PKA:
-
cAMP-dependent protein kinase
- PKC:
-
protein kinase C
- S104:
-
104,000xg supernatant
- SDS-PAGE:
-
sodium dodecylsulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
References
Treadwell, C.R., and Vahouny, G.V. (1978) inHandbook of Physiology (Code, C.R., ed.) Vol. 3, pp. 1407–1438, Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore.
Nilsson, A. (1976)Biochim. Biophys. Acta 450, 379–389.
Deykin, D., and Goodman, D.S. (1962)J. Biol. Chem. 237, 3649–3656.
Camulli, E.D., Linke, M.J., Brockman, H.L., and Hui, D.Y. (1989)Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1005, 177–182.
Harrison, E.H. (1988)Biochim. Biophys. Acta 963, 28–34.
Gallo, L.L., Cheriathundam, E., Vahouny, G.V., and Treadwell, C.R. (1978)Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 191, 42–48.
Ghosh, S., and Grogan, W.M. (1989)Lipids 24, 733–736.
Laemmli, U.K. (1970)Nature 227, 680–685.
Matsudaria, P. (1987)J. Biol. Chem. 262, 10035–10038.
Ghosh, S., Kounnas, M.Z., and Grogan, W.M. (1990)Lipids 25, 221–225.
Tuhackova, Z., Kriz, O., and Hradec, J. (1980)Biochim. Biophys. Acta 617, 439–445.
Hyun, J., Treadwell, C.R., and Vahouny, G.V. (1972)Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 152, 233–242.
Calame, K.B., Gallo, L.L., Cheriathundam, E., Vahouny, G.V., and Treadwell, C.R. (1975)Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 168, 57–65.
Beckett, J., and Boyd, G.S. (1977)Eur. J. Biochem. 72, 223–233.
Bailey, M.L., and Grogan, W.M. (1986)J. Biol. Chem. 261, 7717–7722.
Ghosh, S., and Grogan, W.M. (1990)Dev. Brain Res. 54, 147–149.
Khoo, J.C., Mahoney, E.M., and Steinberg, D. (1981)J. Biol. Chem. 256, 12659–12661.
Jacobson, P.W., Wiesenfeld, P.W., Gallo, L.L., Tate, R.L., Osborne, J.C. (1990)J. Biol. Chem. 265, 515–521.
Rudd, E.A., Mizuno, N.K., and Brockman, H.L. (1987)Biochim. Biophys. Acta 918, 106–114.
Labow, R.S., Adams, K.A.H., and Lynn, K.R. (1983)Biochim. Biophys. Acta 749, 32–41.
Momsen, W.E., and Brockman, H.L. (1977)Biochim. Biophys. Acta 486, 103–113.
Durham, L.A., and Grogan, W.M. (1984)J. Biol. Chem. 259, 7433–7438.
Eto, Y., and Suzuki, K. (1971)Biochim. Biophys. Acta 239, 293–311.
Kissel, J.A., Fontaine, R.N., Turck, C.W., Brockman, H.L., and Hui, D.Y. (1989)Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1006, 227–236.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Ghosh, S., Grogan, W.M. Rapid three-step purification of a hepatic neutral cholesteryl ester hydrolase which is not the pancreatic enzyme. Lipids 26, 793–798 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02536160
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02536160