Abstract
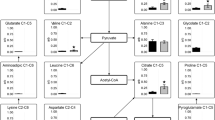
Cuphea seeds contain large amounts of medium chain (C8 to C14) fatty acids, mainly as triacylglycerols. The biosynthesis of these lipids was studied in vivo by incubating developingCuphea lutea seeds with labeled acetate. Incorporation of label into triacylglycerols and into medium chain fatty acids occurred principally during the period of endogenous lipid deposition, but some label was encountered in these products even during seed dehydration. At this later stage palmitate and oleate were the dominant labeled fatty acids. During the period of rapid endogenous lipid deposition acyl lipids other than triacylglycerols were minor labeled components. The labeling patterns were consistent with the Kennedy pathway for triacylglycerol biosynthesis. The fatty acid composition of the acyl-CoA pool was similar to the total lipid fatty acid composition, but the acyl-ACP pool contained relatively more short chain acyl groups. Squalene was labeled from acetate throughout the period of seed development, but labeled sterols were not detected. Using [2-14C]mevalonic acid lactone as substrate, squalene was the principal labeled product. Small amounts of label were found in free sterols. However, in terms of mass, free sterol dominated over squalene. The possibility of two independent sites of isoprenoid biosynthesis in the developing embryo is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hilditch, T.P., and Williams, P.N. (1964)The Chemical Constitution of Natural Fats, 4th ed., pp. 332–343, Wiley & Sons, New York.
Singh, S.S., Nee, T., and Pollard, M.R. (1984) inStructure, Function and Metabolism of Plant Lipids (Siegenthaler, P.-A., and Eichenberger, W., eds.) pp. 161–165, Elsevier Science Publishers BV, Amsterdam.
Slabas, A.R., Harding, J., Hellyer, A., Sidebottom, C., Gwynne, H., Kessell, R., and Tombs, M.P. (1984) inStructure, Function and Metabolism of Plant Lipids (Siegenthaler, P.-A., and Eichenberger, W., eds.) pp. 3–10, Elsevier Science Publishers BV, Amsterdam.
Libertini, L.J., and Smith, S.S. (1978)J. Biol. Chem. 253, 1393–1401.
Knudsen, J., and Grunnet, I. (1982)Biochem. J. 202, 139–143.
Graham, S.A., Hirsinger, F., and Robbelen, G. (1981)Am. J. Bot. 68, 908–917.
Graham, S.A., and Kleiman, R. (1985)J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 62, 81–82.
Hirsinger, F. (1985)J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 62, 76–80.
Hara, A., and Radin, N.S. (1978)Anal. Biochem. 90, 420–426.
Mancha, M., Stokes, G.B., and Stumpf, P.K. (1975)Anal. Biochem. 68, 600–608.
Durst, H.D., Milano, M., Kikta, E.J., Connelly, S.A., and Grushka, E. (1975)Anal. Chem. 47, 1797–1802.
Weete, J.D., Sancholle, M.S., and Montant, C. (1983)Biochim. Biophys. Acta 752, 19–29.
Ichihara, K., and Noda, M. (1980)Phytochem. 19, 49–54.
Slabas, A.R., Roberts, P.A., Ormesher, J., and Hammond, E.W. (1982)Biochim. Biophys. Acta 711, 411–420.
Pollard, M.R., and Stumpf, P.K. (1980)Plant Physiol. 66, 641–648.
Ohlrogge, J.B., Pollard, M.R., and Stumpf, P.K. (1978)Lipids 13, 203–210.
Pollard, M.R., and Stumpf, P.K. (1980)Plant Physiol. 66, 649–655.
Stumpf, P.K., and Pollard, M.R. (1983) inHigh and Low Erucic Acid Rapeseed Oils: Production, Usage, Chemistry and Toxicological Evaluation (Kramer, J.K.G., Sauer, F.D., and Pidgen, W.J., eds.) pp. 131–141, Academic Press, New York.
Sanchez, J., and Mancha, M. (1980)Phytochem. 19, 817–820.
Stumpf, P.K. (1977) inInternational Review of Biochemistry: Biochemistry of Lipids II (Goodwin, T.W., ed.) Vol. 14, Chap. 5, University Park Press, Baltimore, MD.
Ohlrogge, J.B., Shine, W.E., and Stumpf, P.K. (1978)Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 189, 382–391.
Bastic, M., Bastic, L., Jovanovic, J.A., and Spiteller, G. (1978)J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 55, 886–891.
Fioriti, J.A., Kanuk, M.J., and Sims, R.J. (1971)J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 48, 240–244.
Gutfinger, T., Romano, S., and Letan, A. (1972)Food Science 37, 938–940.
Nes, W.R., and McKean, M.L. (1977)Biochemistry of Steroids and Other Isopentenoids, pp. 480–517, University Park Press, Baltimore, MD.
Baisted, D.J. (1971)Biochem. J. 124, 375–383.
McKean, M.L., and Nes, W.R. (1977)Lipids 12, 382–385.
Nes, W.R., Baisted, D.J., Capstack, E., Newschwander, W.W., and Russell, P.T. (1967) inBiochemistry of Chloroplasts (Goodwin, T.W., ed.) Vol. 2, pp. 273–282, Academic Press, New York.
Fang, T-Y., and Baisted, D.J. (1975)Biochem. J. 150, 323–328.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, S.S., Nee, T.Y. & Pollard, M.R. Acetate and mevalonate labeling studies with developingCuphea lutea seeds. Lipids 21, 143–149 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02534436
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02534436