Abstract
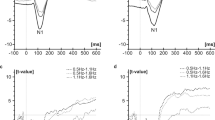
Electrical and mechanical stimulation of the oesophagus has been recently proposed to examine the physiological effects of autonomic stimulation in humans. Cortical evoked potentials (EPs) to oesophageal stimulation provide an assessment of afferent fibres and central processing. However, habituation takes place during averaging of cortical EPs and reduces the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) as the number of stimuli increases. The SNR of cortical EPs to oesophageal stimulation is computed for 15 normal subjects. Habituation is characterised by the Euclidean distance between the EEG response to single stimuli and the averaged EP, to serve as an objective measure of similarity between the averaged EP and the single-stimulus EEG. With electrical stimulation, the SNR is highest (0.41±0.21) for 1–12 stimuli and then significantly decreases to 0.2±0.08 for 13–24 stimuli (p<0.001). With balloon distension (BD), the SNR is highest (0.22±0.16) for 1–12 stimuli and lowest (0.12±0.14) for 13–24 stimuli, but these SNRs are not significantly different from each other. Both electrical and mechanical stimulation of the oesophagus produce rapidly adapting EPs. The SNR of the EPs is higher with electrical stimulation than with BD. The EPs response to BD has a higher variability and is more noisy. Consequently, these results suggest that the overall cortical EP response to electrical stimulation of the oesophagus is more reproducible than that due to balloon distension.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akay, M. (1995): ‘Wavelets in biomedical engineering’.Ann. Biomed. Eng.,23, pp. 531–542
Aziz, Q., Furlong, P. L., Barlow, J., Hobson, A., Alani, S., Bacewicz, J., Ribbands, M., Harding, G. F. A., andThompson, D. G. (1995): ‘Topographic mapping of cortical evoked potentials evoked by distension of the human proximal and distal oesophagus’.Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol.,96, pp. 219–228
Bershad, N. J. andRockmore, A. J. (1974): ‘On estimating the signal to noise ratio using the sample correlation coefficient’.IEEE Trans.,IT-20, pp. 112–114
Castell, D., Wood, J., Freiling, T., Wright, F. andVieth, R. (1990): ‘Cerebral evoked potentials evoked by balloon distension of the human oesophagus’.Gastroenterol.,98, pp. 662–666
Coppola R., Tabor, R. andBuchbasum, M. S. (1978): ‘Signal to noise ratio and response variability measurements in single trial evoked potentials’.Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol.,44, pp. 214–222
Davila, C. E. andMobin, M. S. (1992): ‘Weighted averaging of evoked potentials’.IEEE Trans.,BME-39, pp. 338–345
Frieling, T., Enck, P. andWienbeck, M. (1989): ‘Cerebral responses evoked by electrical stimulation of the oesophagus in normal subjects’.Gastroenterol.,97, pp. 475–478
Froebert, O., Arendt-Nielsen, L., Bak, P., Andersen, O. K., Funch-Jensen, P. andBagger, J. P. (1994): ‘Electric stimulation of the oesophageal mucosa. Perception and brain evoked potentials’.Scand. J. Gastroenterol.,29, pp. 776–781
Froebert, O., Arendt-Nielsen, L., Bak, P., Funch-Jensen, P. andBagger, J. P. (1995): ‘Oesophageal sensation assessed by electrical stimuli and brain evoked potentials—a new model for visceral nociception’.Gut,37, pp. 603–609
Hollerbach, S., Kamath, M. V., Fitzpatrick, D., Shine, G., Fallen, E., Upton, A. R. M. andTougas, G. (1997): ‘The cerebral response to electrical stimuli in the oesophagus is altered by increasing stimulus frequencies’.Neurogastroenterol. Motility 97, pp. 475–478
Laguna, P., Jane, R., Meste, O., Poon, P. W., Caminal, P., Rix, H. andThakor, N. (1992): ‘Adaptive filter for event-related bioelectric signals using an impulse correlated reference input: Comparison with signal averaging techniques’.IEEE Trans.,BME-39, pp. 1032–1043
Malik, M. andCamm, A. J. (Eds.) (1995): ‘Heart rate variability’ (Futura Press, New York)
Malliani, A., Pagani, M., Lombardi, F. andCerutti, S. (1991): ‘Cardiovascular neural regulation explored in the frequency domain’.Circulation,84, pp. 482–492
Raz, J., Turetsky, B. andFein, G. (1988): ‘Confidence intervals for the signal-to-noise ratio when a signal embedded in noise is observed over repeated trials’.IEEE Trans.,BME-35, pp. 298–492
Smout, A. J., DeVore, M. S., Dalton, C. andCastell, D. (1992): ‘Cerebral evoked potentials evoked by oesophageal distnesion in patients with non-cardiac chest pain’.Gut,33, 298–492
Tougas, G., Fitzpatrick, G., Hudoba, P., Talalla, A., Shine, G., Hunt, R. andUpton, A. R. M. (1992): ‘Effects of chronic left vagal stimulation on visceral vagal function in man’.PACE,15 (Part II), pp. 1588–1596
Tougas, G., Hudoba, P., Fitzpatrick, D., Hunt, R. andUpton, A. R. M. (1993): ‘Cerebral evoked potential responses following direct vagal and oesophageal electrical stimulation in humans’.Am. J. Physiol.,264, pp. G486–491
Turetsky, B. I., Raz, J. andFein, G. (1988): ‘Noise and signal power and their effects on evoked potential estimation’.Electroenceph. Clin. Neurophysiol.,71, pp. 310–318.
Upton, A. R. M., Tougas, G., Talalla, A., White, A., Hudoba, A., Fitzpatrick, D., Clarke, B. andHunt, R. (1991): ‘Neurphysiological effects of left vagal stimulation in man’.PACE,14, pp. 70–76
Weusten, B. L. A. M., Franssen, H., Wieneke G. H. andSmout, A. J. P. M. (1994): ‘Multichannel recording of cerebral potentials evoked by oesophageal balloon distension in humans’.Digest. Diseases & Sci.,39, pp. 2074–2083
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kamath, M.V., Tougas, G., Hollerbach, S. et al. Estimation of habituation and signal-to-noise ratio of cortical evoked potentials to oesophageal electrical and mechanical stimulation. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 35, 343–347 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02534088
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02534088