Abstract
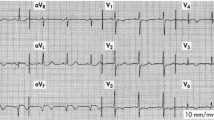
A feed-forward neural network with back-propagation algorithm is used to distinguish anterior wall myocardial infarction (AI) and non-infarction based on analysis of computerised electrocardiograms. Data used in the study are from 132 patients diagnosed as having AI by automated electrocardiograph analysis. Their ECGs show an abnormal Q-wave (or QS complex) or small R progression in leads V1 and V2. However, 66 of them are diagnosed as old AI from the history, physical examination, echocardiogram and other laboratory data, whereas the other 66 are not. The network is trained with the data from half of the AI and non-infarction patients, respectively. The diagnostic accuracy rate is then tested with the remaining 66 patients (33 infarction, 33 non-infarction) who have not been exposed to the network. The neural network correctly identifies 90.2% of the patients with AI and 93.3% of the patients without infarction. The neural network is capable of diagnosing anterior wall myocardial infarction better than a computer electrocardiograph.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baxt, W.G. (1990): ‘Use of an artificial neural network for data analysis in clinical decision-making: the diagnosis of acute cordonary occlusion’,Neural Comput.,2, pp. 480–489
Baxt, W.G. (1991): ‘Use of an artificial neural network for the diagnosis of myocardial infarction,’Ann. Intern. Med.,115, pp. 843–848
Cios, K.J., Chen, K., andLangenderfer, R.A. (1990): ‘Use of neural networks in detecting cardiac disease from echocardiographic images’,IEEE Eng. Med., Biol.,9, pp. 58–60
Davis, G.E., Lowell, W.E., andDavis, G.L. (1993): ‘A neural network that predicts psychiatric length of stay’,M.D. Comput.,10, pp. 87–92
Goldman, M.J.: (1986): ‘Principles of clinical electrocardiography’ (Maruzen Asian Edition)
Guo, Z., Durand, L.G., Lee, H.C., Allard, L., Grenier, M.C., andStein, P.D. (1994): ‘Artificial neural networks in computer-assisted classification of heart sounds in patients with porcine bioprosthetic valves’,Med. Biol. Eng. Comput.,32, pp. 311–316.
Keith, R.D.F., Westgate, J., Ifeachor, E.C., andGreene, K.R. (1994): ‘Sultability of artificial neural networks for feature extraction from cardiotocogram during labor’,Med. Biol. Eng. Comput.,32, pp. S51-S57
Miller, A.S., Blott, B.H., andHames, T.K. (1992): ‘Review of neural network applications in medical imaging and signal processing’,Med. Biol. Eng. Comput.,30, pp. 449–464
Maclin, P.S., andDempsey, J. (1992): ‘Using an artificial neural network to diagnose hepatic masses’,J. Med. Syst.,16, pp. 215–225
Poli, R., Cagnoni, S., Livi, R., Coppini, G., andValli, G. (1991): ‘A neural network expert system for diagnosing and treating hypertension’,Computer,3, pp. 64–71
Suzuki, Y., andOno, K. (1992): ‘Personal computer system for ECG ST-segment recognition based on neural networks’,Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 30, pp. 2–8
Wasserman, P.D. (1989): ‘Neural computing: theory and practice’, (Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York)
Yamauchi, K., Fukatsu, T., Oguri, K., andIwata, A. (1993): ‘A diagnosis support system for chronic liver disease using an artificial neural network’,Modern Med.,48, pp. 619–622 (in Japanese)
Yokoi, M., andIwatsuka, T. (1993): ‘Computer diagnosis of electrocardiograms’Modern Electrocardiol., pp. 1161–1774 (in Japanese)
Wu, Y., Giger, M.I., Doi, K., Vybony, C.J., Schmidy, R.A., andMetz, C.E. (1993): ‘Artificial neural networks in mammography: application to decision marking in the diagnosis of breast cancer’,Radiology,187, pp. 81–87
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ouyang, N., Ikeda, M. & Yamauchi, K. Use of an artificial neural network to analyse an ECG with QS complex in V1–2 leads. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 35, 556–560 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02525541
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02525541