Abstract
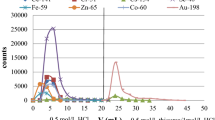
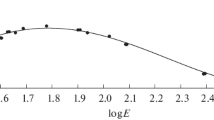
Trace element characterization of bullet lead by instrumental neutron activation analysis (INAA) is hampered by the high spectral background due to antimony, normally present in high concentration in bullet lead. Tin is indicated to be a very useful element for characterization purposes. Beta-active121Sn is a suitable nuclide for quantitation of tin provided it is separated in high radiochemical purity. A radiochemical procedure capable of determining tin down to 10 ppm in bullet lead, a sequential procedure for its determination along with copper, arsenic and antimony and the application of this procedure for the determination of the contents of these elements in various bullet leads are described. This method has been applied to a “Rhinoceros shoot-out” case, referred to our laboratory.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. A. GILLESPIE, S. S. KRISHNAN, Cand. Soc. of Forensic Sci. J., 2 (1969) 95.
H. R. LUKENS, V. P. GUINN, J. Forensic Sci., 16 (1971) 301.
V. P. GUINN, M. A. PURCELL, J. Radioanal. Chem., 39 (1977) 85.
H. R. LUKENS, H. L. SCHLESINGER, V. P. GUINN, R. P. HACKLEMAN, Forensic Neutron Activation Analysis of Bullet Lead Specimens. U. S. A. E. C. Report GA 10141, 1970.
M. A. HANEY, J. F. GALLAGHER, Anal. Chem., 47 (1975) 62.
M. A. HANEY, J. F. GALLAGHER, J. Forensic Sci., 20 (1975) 484.
R. D. GUY, B. D. PATE, J. Radioanal. Chem., 15 (1973) 135.
K. SREENIVAS, V. S. VENKATASUBRAMANIAN, M. SANKAR DAS, J. Ind. Acad. Forensic Sci., 17 (1978) 1.
M. SANKAR DAS., V. S. VENKATASUBRAMANIAN, K. SREENIVAS, J. Ind. Acad. Forensic Sci., 15 (1976) 1.
P. C. OOMS, R. VANWOERKOM, H. A. DAS, J. Radioanal. Chem., 20 (1974) 33.
A. R. BYRNE, J. Radioanal. Chem., 37 (1977) 591.
H. HOLNESS, W. R. SCHOELLER, Analyst, 71 (1946) 70.
M. SANKAR DAS, Ch. VENKATESWARLU, V. T. ATHAVALE, Analyst, 8 (1956) 239.
A. R. BYRNE, J. Radioanal. Chem., 20 (1974) 627.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Desai, H.B., Parthasarathy, R. A radiochemical neutron activation analysis method for the determination of tin, arsenic, copper and antimony for the forensic comparison of bullet lead specimens. J. Radioanal. Chem. 77, 235–240 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02525369
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02525369